Software Development Exam > Software Development Tests > Test: Environmental Awareness (Energy) - Software Development MCQ
Test: Environmental Awareness (Energy) - Software Development MCQ
Test Description
20 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Environmental Awareness (Energy)
Test: Environmental Awareness (Energy) for Software Development 2025 is part of Software Development preparation. The Test: Environmental Awareness (Energy) questions and answers have been prepared
according to the Software Development exam syllabus.The Test: Environmental Awareness (Energy) MCQs are made for Software Development 2025 Exam.
Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests for Test: Environmental Awareness (Energy) below.
Solutions of Test: Environmental Awareness (Energy) questions in English are available as part of our course for Software Development & Test: Environmental Awareness (Energy) solutions in
Hindi for Software Development course.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Software Development Exam by signing up for free. Attempt Test: Environmental Awareness (Energy) | 20 questions in 20 minutes | Mock test for Software Development preparation | Free important questions MCQ to study for Software Development Exam | Download free PDF with solutions
Test: Environmental Awareness (Energy) - Question 1
Which of the following is NOT a fossil fuel?
Detailed Solution for Test: Environmental Awareness (Energy) - Question 1
Detailed Solution for Test: Environmental Awareness (Energy) - Question 2
Detailed Solution for Test: Environmental Awareness (Energy) - Question 3
Detailed Solution for Test: Environmental Awareness (Energy) - Question 4
Test: Environmental Awareness (Energy) - Question 5
The nuclear energy in nuclear reactor is produced by
Detailed Solution for Test: Environmental Awareness (Energy) - Question 5
Test: Environmental Awareness (Energy) - Question 6
A green building
i) uses minimum amount of energy
ii) generates waste
iii) consumes a lot of water
iv) conserves natural resources
v) creates space for healthy living
Choose the correct statements from the options given below:
Detailed Solution for Test: Environmental Awareness (Energy) - Question 6
Test: Environmental Awareness (Energy) - Question 7
Which of the statements is correct about solar energy?
Detailed Solution for Test: Environmental Awareness (Energy) - Question 7
Test: Environmental Awareness (Energy) - Question 8
Which one of the following statements is not true for hydropower generated from river dams?
Detailed Solution for Test: Environmental Awareness (Energy) - Question 8
Test: Environmental Awareness (Energy) - Question 9
Which one of the following food habit will help to reduce 'carbon footprint' :
Detailed Solution for Test: Environmental Awareness (Energy) - Question 9
Test: Environmental Awareness (Energy) - Question 10
Which one of the following pairs is mismatched
Detailed Solution for Test: Environmental Awareness (Energy) - Question 10
Test: Environmental Awareness (Energy) - Question 11
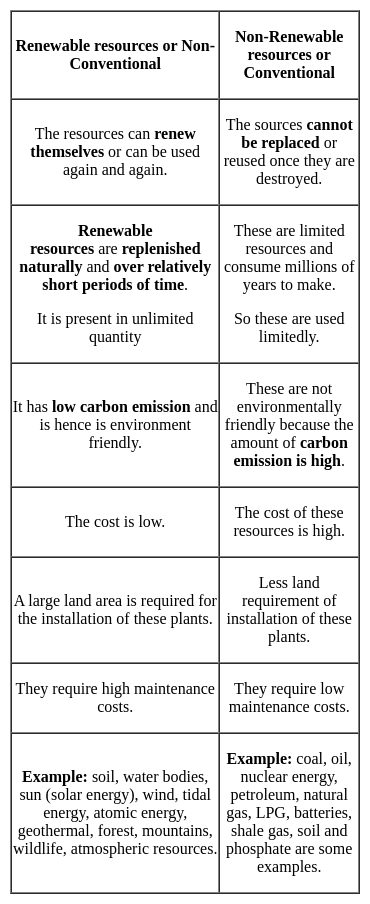
Identify the true statement with reference to the characteristics of the renewable resources.
Detailed Solution for Test: Environmental Awareness (Energy) - Question 11
Test: Environmental Awareness (Energy) - Question 12
The concept of carbon credit originated from which one of the following.
Detailed Solution for Test: Environmental Awareness (Energy) - Question 12
Test: Environmental Awareness (Energy) - Question 13
Which of the following is the major environment issue?
Detailed Solution for Test: Environmental Awareness (Energy) - Question 13
Detailed Solution for Test: Environmental Awareness (Energy) - Question 14
Detailed Solution for Test: Environmental Awareness (Energy) - Question 15
Detailed Solution for Test: Environmental Awareness (Energy) - Question 16
Test: Environmental Awareness (Energy) - Question 17
Which of the following methods of energy production can lead to greenhouse effect?
Detailed Solution for Test: Environmental Awareness (Energy) - Question 17
Test: Environmental Awareness (Energy) - Question 18
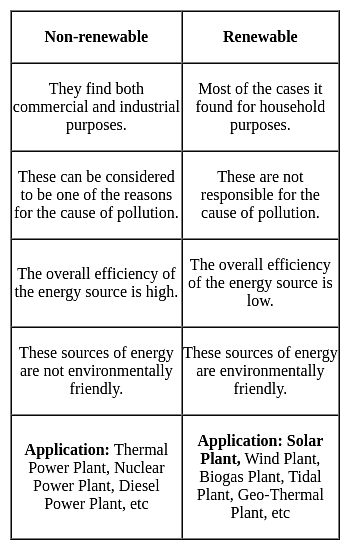
Which among the following is conventional source of energy?
Detailed Solution for Test: Environmental Awareness (Energy) - Question 18
Test: Environmental Awareness (Energy) - Question 19
What is the aim of all energy conservation techniques?
Detailed Solution for Test: Environmental Awareness (Energy) - Question 19
Detailed Solution for Test: Environmental Awareness (Energy) - Question 20
Information about Test: Environmental Awareness (Energy) Page
In this test you can find the Exam questions for Test: Environmental Awareness (Energy) solved & explained in the simplest way possible.
Besides giving Questions and answers for Test: Environmental Awareness (Energy), EduRev gives you an ample number of Online tests for practice
Download as PDF