Software Development Exam > Software Development Tests > Test: Environmental Awareness (Water Pollution) - Software Development MCQ
Test: Environmental Awareness (Water Pollution) - Software Development MCQ
Test Description
20 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Environmental Awareness (Water Pollution)
Test: Environmental Awareness (Water Pollution) for Software Development 2025 is part of Software Development preparation. The Test: Environmental Awareness (Water Pollution) questions and answers have been prepared
according to the Software Development exam syllabus.The Test: Environmental Awareness (Water Pollution) MCQs are made for Software Development 2025 Exam.
Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests for Test: Environmental Awareness (Water Pollution) below.
Solutions of Test: Environmental Awareness (Water Pollution) questions in English are available as part of our course for Software Development & Test: Environmental Awareness (Water Pollution) solutions in
Hindi for Software Development course.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Software Development Exam by signing up for free. Attempt Test: Environmental Awareness (Water Pollution) | 20 questions in 20 minutes | Mock test for Software Development preparation | Free important questions MCQ to study for Software Development Exam | Download free PDF with solutions
Detailed Solution for Test: Environmental Awareness (Water Pollution) - Question 1
Test: Environmental Awareness (Water Pollution) - Question 2
Which of the following is a nonpoint source of water pollution?
Detailed Solution for Test: Environmental Awareness (Water Pollution) - Question 2
Test: Environmental Awareness (Water Pollution) - Question 3
Rekha's mother adds alum to water collected from the pond every day in order to
Detailed Solution for Test: Environmental Awareness (Water Pollution) - Question 3
Test: Environmental Awareness (Water Pollution) - Question 4
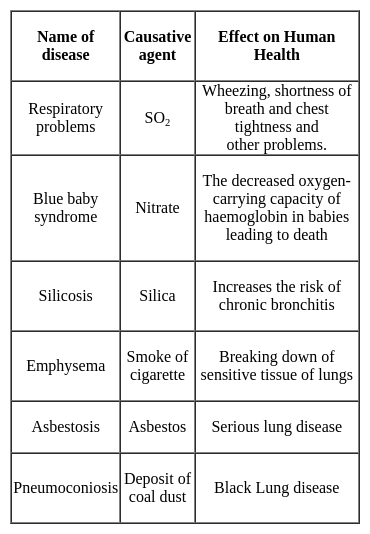
Minamata and Itai-Itai diseases caused by metallic water pollution are caused by the following metals respectively:
Detailed Solution for Test: Environmental Awareness (Water Pollution) - Question 4
Test: Environmental Awareness (Water Pollution) - Question 5
The fish die due to sewage being dumped in the water bodies, because:
Detailed Solution for Test: Environmental Awareness (Water Pollution) - Question 5
Test: Environmental Awareness (Water Pollution) - Question 6
High value of BOD in a water stream indicates which of the following?
Detailed Solution for Test: Environmental Awareness (Water Pollution) - Question 6
Detailed Solution for Test: Environmental Awareness (Water Pollution) - Question 7
Test: Environmental Awareness (Water Pollution) - Question 8
_______ is used for emergency disinfection of water.
Detailed Solution for Test: Environmental Awareness (Water Pollution) - Question 8
Test: Environmental Awareness (Water Pollution) - Question 9
Which method is used to purify water?
Detailed Solution for Test: Environmental Awareness (Water Pollution) - Question 9
Test: Environmental Awareness (Water Pollution) - Question 10
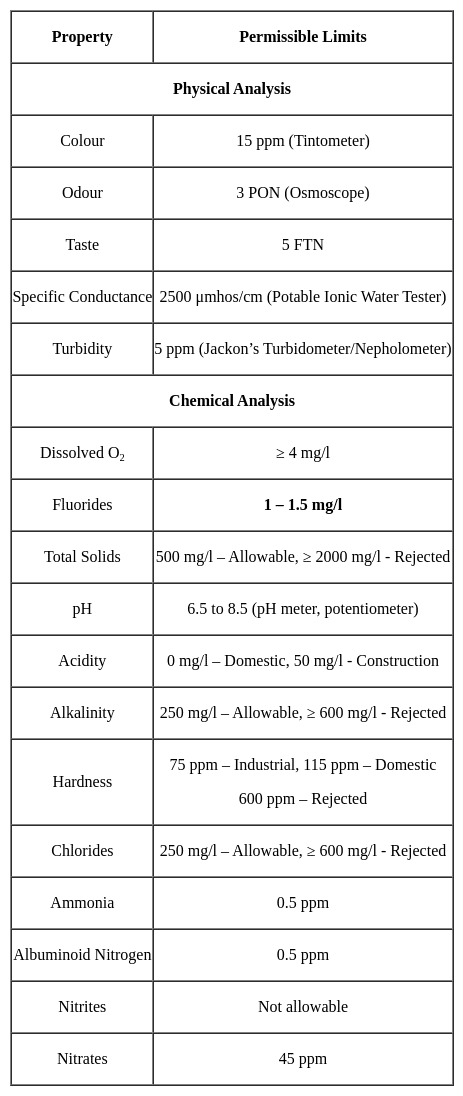
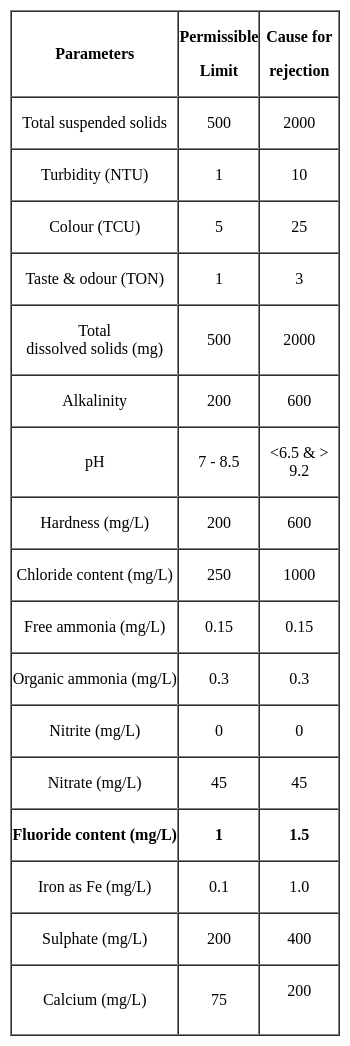
The maximum permissible limit for fluoride in drinking water is:
Detailed Solution for Test: Environmental Awareness (Water Pollution) - Question 10
Test: Environmental Awareness (Water Pollution) - Question 11
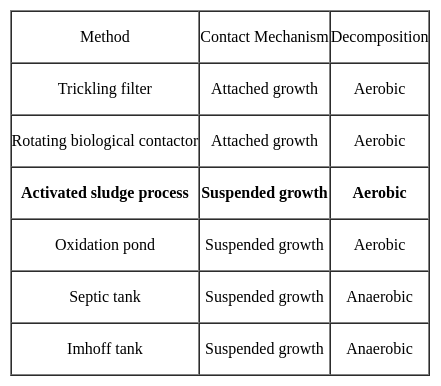
Activated sludge process is an example of ______ growth process.
Detailed Solution for Test: Environmental Awareness (Water Pollution) - Question 11
Test: Environmental Awareness (Water Pollution) - Question 12
What does Chemical Oxygen Demand (COD) indicate?
Detailed Solution for Test: Environmental Awareness (Water Pollution) - Question 12
Test: Environmental Awareness (Water Pollution) - Question 13
The primary source of organic pollution in fresh water bodies is
Detailed Solution for Test: Environmental Awareness (Water Pollution) - Question 13
Test: Environmental Awareness (Water Pollution) - Question 14
The typical steps in a conventional wastewater treatment follows the sequence:
Detailed Solution for Test: Environmental Awareness (Water Pollution) - Question 14
Test: Environmental Awareness (Water Pollution) - Question 15
Permanent hardness in water is due to:
Detailed Solution for Test: Environmental Awareness (Water Pollution) - Question 15
Test: Environmental Awareness (Water Pollution) - Question 16
Which element is not involved in physical pollution of water?
Detailed Solution for Test: Environmental Awareness (Water Pollution) - Question 16
Test: Environmental Awareness (Water Pollution) - Question 17
BOD of safe drinking water should be
Detailed Solution for Test: Environmental Awareness (Water Pollution) - Question 17
Test: Environmental Awareness (Water Pollution) - Question 18
After which sewage treatment can the water be sent to the natural source?
Detailed Solution for Test: Environmental Awareness (Water Pollution) - Question 18
Test: Environmental Awareness (Water Pollution) - Question 19
Safe and clean water is defined as:
Detailed Solution for Test: Environmental Awareness (Water Pollution) - Question 19
Test: Environmental Awareness (Water Pollution) - Question 20
What is the major source of water pollution?
Detailed Solution for Test: Environmental Awareness (Water Pollution) - Question 20
Information about Test: Environmental Awareness (Water Pollution) Page
In this test you can find the Exam questions for Test: Environmental Awareness (Water Pollution) solved & explained in the simplest way possible.
Besides giving Questions and answers for Test: Environmental Awareness (Water Pollution), EduRev gives you an ample number of Online tests for practice
Download as PDF