Test: Bond Parameters (May 23) - JEE MCQ
10 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Bond Parameters (May 23)
Amongst the following elements whose electronic configurations are given below, the one having the highest ionisation enthalpy is
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
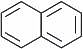
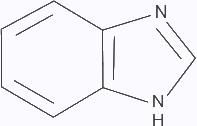
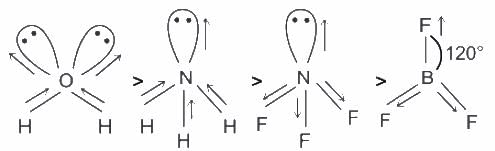
Structure isoelectronic with naphthalene is ___________.
Among the following, the one which has maximum ionic character is
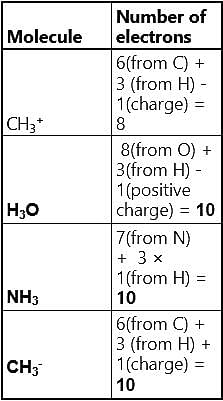
Pick out the isoelectronic structure from the Following:
I.CH3+,
II.H3O+,
III. NH3,
IV. CH3-
Which of the following statement(s) is/are correct as per the Fajan’s rule?
A. For a compound to have ionic bond, low positive charge is required.
B. For a compound to have covalent bond, small cation is required.
C. Smaller cation with high charge has less polarizing power.
Which of the following is the correct order of dipole moment ?
Which of the following statement(s) is / are true ?
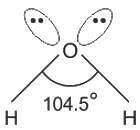
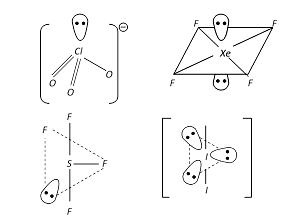
Among the following compounds the maximum number of lone pair is present on the central atom of: