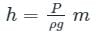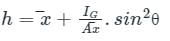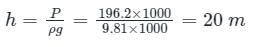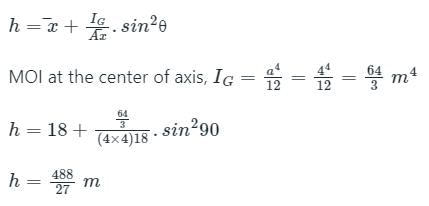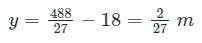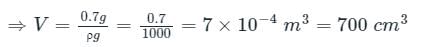Test: Archimedes Principle - 1 - EmSAT Achieve MCQ
10 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Archimedes Principle - 1
A rectangular block 2 m long, 1 m wide and 1 m deep floats in water. The depth of immersion is 0.5 m. If water weighs 10 kN/m3. Then the weight of the block is
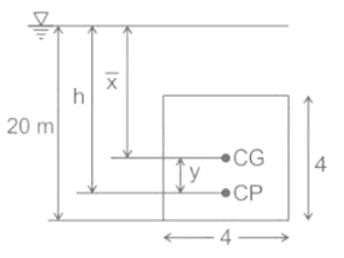
A vertical gate closes a horizontal tunnel 4 m high and 4 m wide running full with water. The pressure at the bottom of the gate is 196.2 kN/m2. What will be the location of center of pressure? [ρ = 1000 kg/m3 , g = 9.81 m/s2]
A piece of ice is dropped in a vessel containing kerosene oil. When ice melts, the level of kerosene oil will
When a floating ice cube melts, the volume of water
What percent of the total volume of an iceberg floats above the water surface? Assume the density of ice to be 920 kg/m3 and the density of water to be 1000 kg/m3 .
A 700 gm solid cube having an edge of length 10 cm floats in water. How much volume of the cube is outside the water? The density of the water 1000 kgm-3
The upward force exerted by the liquid displaced by the body when it is placed inside the liquid is called
The balls of iron and aluminium of same diameter are dipped in water. Which is the correct statement?
A solid of density 900 kg/m3 floats in oil. The oil floats on water of density 1000 kg/m3 . The density of oil in kg/m3 could be.