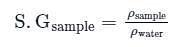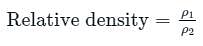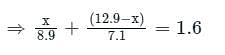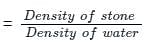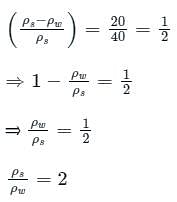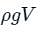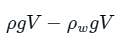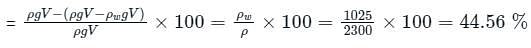Test: Archimedes Principle - 2 - EmSAT Achieve MCQ
10 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Archimedes Principle - 2
An object is put one by one in three liquids P, Q, and R having different densities. Consider the following statements and arrange the liquids in ascending order of densities.
(A) In liquid P, the object is completely submerged
(B) In liquid Q, objects float with (1/4)th part of their volume inside the liquid
(C) In liquid R, objects float with (1/2)th of their volume inside the liquid
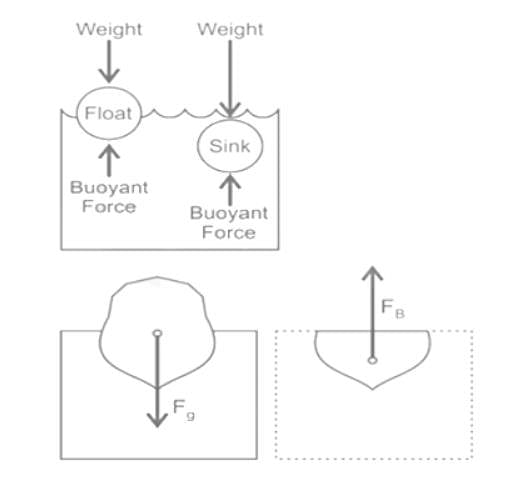
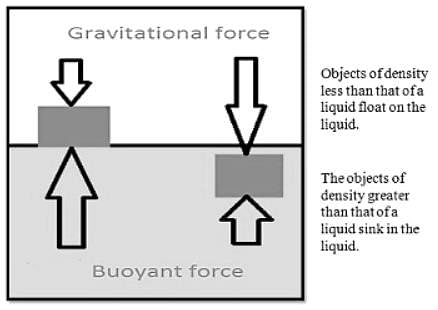
When the weight of the fluid displaced is less than the weight of the solid body then:
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
A piece of brass (alloy of copper and zinc) weighs 12.9 g in air. When completely immersed in water weighs 11.3 g. what is the mass of copper contained in the alloy? Specific gravities of copper and zinc are 8.9 and 7.1 respectively.
What is the specific gravity of a marble stone, which weighs 400 N in air, and 200 N in the water? (g = 10m/s2)
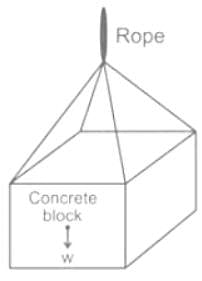
A crane is used to lower weights into the sea (seawater density = 1025 kg/m3) for an underwater construction project. What is the percentage reduction in the tension in the rope of the crane due to a rectangular 0.4 m × 0.4 m × 3 m concrete block (density = 2300 kg/m3) when it is completely immersed in water compared to the tension in the rope when it was suspended in air
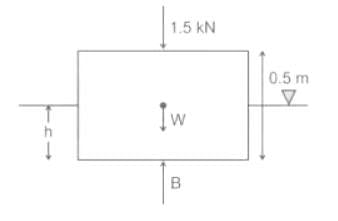
A wooden plank (sp.gr 0.5) 1 m × 1 m × 0.5 m floats is water with 1.5 kN load on it with 1 m × 1 m surface horizontal. The depth of plank lying below water surface shall be:
An object X sinks in liquids P and Q but floats in liquid R. Which of the following conclusions can be made from these observations?
A) Density of X is more than the density of P
B) Density of X is less than the density of R
C) Density of P is equal to the density of R
D) Density of P is less than the density of R
Submarines works on which of the following principle?
Consider the following statement
Assertion: A human floats easily by using a rubber tube.
Reason: An inflated rubber tube has low weight and large volume and increases the upthrust.
On which of the following factors the magnitude of the buoyant force acting on a body in a given fluid depends?