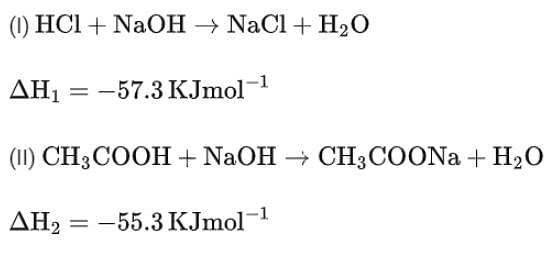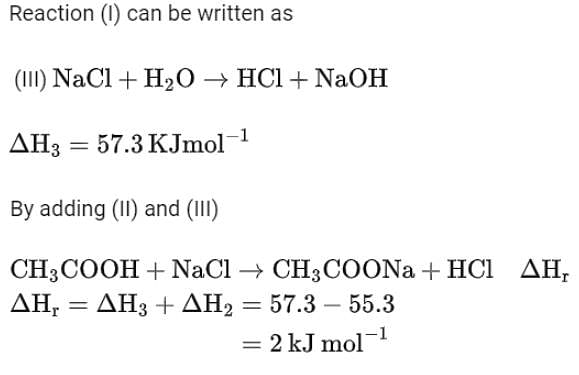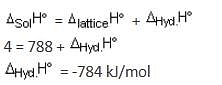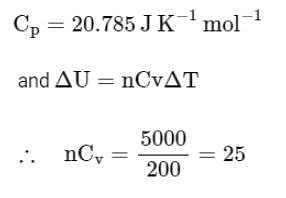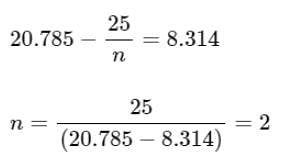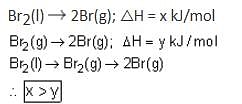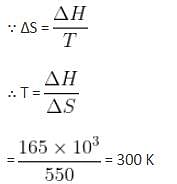Chemistry Unit Test : Thermodynamics (June 15) - JEE MCQ
15 Questions MCQ Test - Chemistry Unit Test : Thermodynamics (June 15)
The standard heat of formation ( ) of ethane (in kJ/mol), if the heat of combustion of ethane, hydrogen and graphite is -1560, -393.5 and -286 kJ/mol, respectively, is ______.(Answer up to 1 decimal place)
) of ethane (in kJ/mol), if the heat of combustion of ethane, hydrogen and graphite is -1560, -393.5 and -286 kJ/mol, respectively, is ______.(Answer up to 1 decimal place)
4.0 L of an ideal gas is allowed to expand isothermally into vacuum until the total volume is 20 L. The amount of heat absorbed in this expansion is _____________ L atm. (In integer)
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
While performing a thermodynamics experiment, a student made the following observations:
HCl + NaOH →NaCl + H2O ΔH = -57.3 kJ mol-1
CH3COOH + NaOH →CH3COONa + H2O ΔH = -55.3 kJ mol-1
The enthalpy of ionization of CH3COOH as calculated by the student is ________ kJ mol-1. (Nearest integer)
HCl + NaOH →NaCl + H2O ΔH = -57.3 kJ mol-1
CH3COOH + NaOH →CH3COONa + H2O ΔH = -55.3 kJ mol-1
The enthalpy of ionization of CH3COOH as calculated by the student is ________ kJ mol-1. (Nearest integer)
A cylinder containing an ideal gas (0.1 mol of 1.0 dm3) is in thermal equilibrium with a large volume of 0.5 molal aqueous solution of ethylene glycol at its freezing point. If the stoppers S1 and S2 (as shown in the figure) are suddenly withdrawn, the volume of the gas in litres after equilibrium is achieved will be ________.(Answer up to 2 decimal places)
(Given, Kf (water) = 2.0 K kg mol-1, R = 0.08 dm3 atm K-1 mol-1)
Among the following, the number of state variables is ______.(In integer)
Internal energy (U)
Volume (V)
Heat (q)
Enthalpy (H)
Lattice enthalpy and enthalpy of solution of NaCl are 788 kJ mol-1 and 4 kJ mol-1, respectively. The hydration enthalpy of NaCl is
According to the following diagram, A reduces BO2 when the temperature is
The molar heat capacity for an ideal gas at constant pressure is 20.785 J K-1mol-1. The change in internal energy is 5,000 J upon heating it from 300 K to 500 K. The number of moles of the gas at constant volume is ______. [Nearest Integer]
(Given: R = 8.314 J K-1 mol-1)
At 300 K, a sample of 3.0 g of gas A occupies the same volume as 0.2 g of hydrogen at 200 K at the same pressure. The molar mass of gas A is ______ g mol-1. (Nearest integer)
Assume that the behaviour of gases as ideal. (Given: The molar mass of hydrogen (H2) gas is 2.0 g mol-1)
If enthalpy of atomisation for Br2(l) is x kJ/mol and bond enthalpy for Br2 is y kJ/mol, the relation between them
At 25°C and 1 atm pressure, the enthalpy of combustion of benzene (I) and acetylene (g) is -3268 kJ mol-1 and -1300 kJ mol-1, respectively. The change in enthalpy for the reaction 3C2H2(g) →+324 kJ mol-1 C6H6(l) is
The standard entropy change for the reaction
4Fe(s) + 3O2(g) → 2Fe2O3(s) is -550 JK-1 at 298 K.
[Given: The standard enthalpy change for the reaction is -165 kJ mol-1]. The temperature in K at which the reaction attains equilibrium is __________. (Nearest Integer)
Which one of the following is correct for the adsorption of a gas at a given temperature on a solid surface?
At 25°C and 1 atm pressure, the enthalpies of combustion are as given below: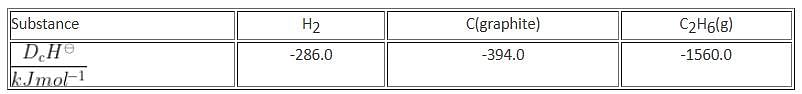
The enthalpy of formation of ethane is
For the reaction:
A(l) →2B(g),
ΔU = 2.1 kcal, ΔS = 20 cal K-1 at 300 K.
Hence, ΔG in kcal is _________.(Answer up to one decimal place)