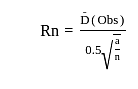UGC NET Paper 2 Geography Mock Test - 5 - UGC NET MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - UGC NET Paper 2 Geography Mock Test - 5
Who propounded the concept of 'Geographical Pivot of History'?
For interpolation of satellite data used for monitoring dynamic changes that occur on the earth surface, the most suitable orbit for the satellite is:
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
As per the theory of demographic transition, the post-transitional stage of demographic transition is characterised by ______.
Assertion (A)- All living things have intrinsic value.
Reason (R) - Diversity of life forms contribute to the realization of these values .
Assertion (A): The River Ganga has a deep but narrow channel at Rishikesh.
Reason (R) : Lateral cutting occurs at the youthful stage in rivers.
Select the correct answer from options given below:
Assertion (A): The hilly topography of Jammu and Kashmir is most favorable for development of ground water resources.
Reason (R) : Groundwater level is falling rapidly all over the country.
Select the correct answer from options given below:
Consider the following States:
1. Karnataka
2. Andhra Pradesh
3. Goa
4. Rajasthan
Which of the above are the major maize-producing states?
Which of the following is/are included in National Population Policy (NPP) 2000?
1. Promoting delayed marriage for girl
2. Free and compulsory school education up to 14 years of age
3. Protection from unwanted pregnancies
4. Providing nutritional services
Select the correct answer from the codes given below.
Given below are two statements, one is labelled as Assertion (A) and the other is labelled as Reason (R). Read the statements and choose the correct answer using the code given below.
Assertion (A) :Nearest Neighbor Analysis measures the spread or distribution of something over geographical space
Reason (R) : The Rn value determines the randomness of the given settlements.
Identify the option that arranges the following states' literacy rates in descending order, according to Census 2011.
A. Kerala
B. Himachal Pradesh
C. Haryana
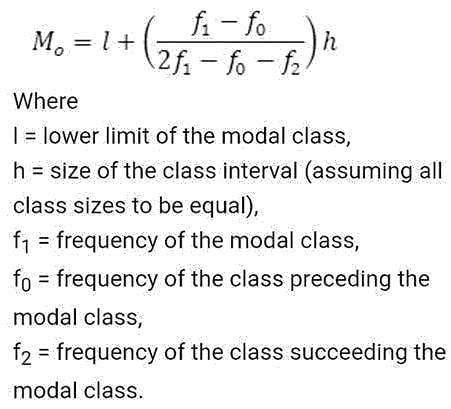
The histogram is the most useful to find the value of:
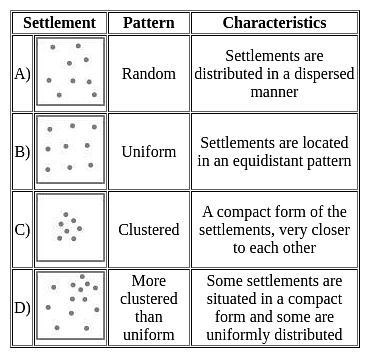
Match List-I with List-II :
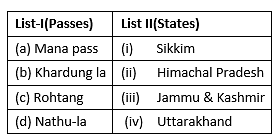
Select the correct answer from the options given below:
Which state is the largest producer of wheat in India ?
When was the first modern paper mill of the country set up?