UGC NET Paper 2 History Mock Test - 1 - UGC NET MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - UGC NET Paper 2 History Mock Test - 1
Who is the author of 'The Idea of Progress'?
Which one of the following statements regarding Satvahanas is NOT correct?
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
Which of the following statement is correct?
Consider the following statements.
1) Coins made of metal appear first in the age of Guptas.
2) The earliest are made largely of silver though a few copper also appears.
3) In Vedic times the exchange was carried on through means of barter.
Choose the correct statement.
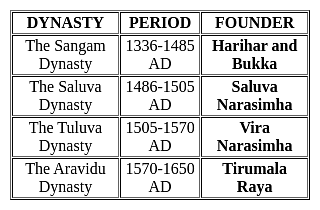
Which of the following statement/s is/are not correct about Vijayanagara empire?
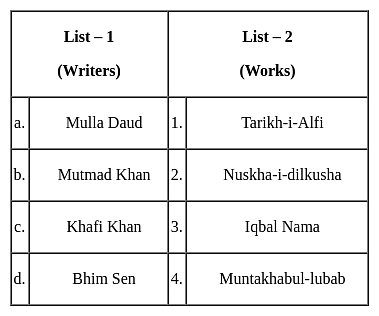
Match the following (writers and works during the Mughal period)
Select the correct answer :
B.R. Ambedkar played a pivotal role in shaping the Indian Constitution. Among the following statements regarding his contributions and the features of the Constitution, which are CORRECT?
(a) Ambedkar championed a socialist economic system and advocated incorporating it directly into the Constitution.
(b) The Constitution incorporates a federal system with a strong central government to ensure national unity.
(c) Ambedkar, though the Chairman of the Drafting Committee, faced significant opposition to his ideas during the Constituent Assembly debates.
(d) The Constitution enshrines Fundamental Rights as justiciable rights, enforceable by the courts.
Which of the following statements is/are incorrect about Prabhavati Gupta?
1. She was the daughter of Chandragupta I.
2. She married Vakataka king Rudrasena II.
3. She took over as queen after the sudden death of her husband.
Consider the following statements regarding Muhammad Tughluq:
1. He shifted the capital to Daulatabad in the south.
2. He paid his soldiers in land grants.
3. His administrative measures were a failure.
4. He levied additional taxes to meet the need of the large soldiers.
Which of the following statements is/are true?
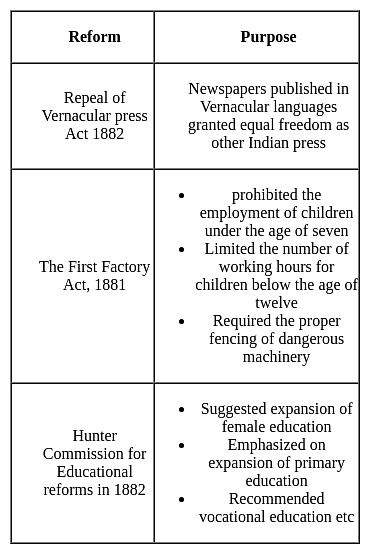
With reference to the Indian Factory Act,1891, consider the following statements:
1. Working hours of children were reduced to 7 hours per day.
2. Moderates supported the Act.
Which of the following is/ are not correct?
Assertion (A): Lord Ripon introduced the Ilbert Bill.
Reason (R): This put back the Vernacular press on a footing of equality with the English press.
In light of the above two statements, choose the correct answer from the options given below:
State whether true or false:
(a) Harishena composed a Prashasti in praise of Gautamiputra Shri Satakarni.
(b) The rulers of Aryavarta brought tribute for Samudragupta.
(c) There were twelve rulers in Dakshinapatha
(d) Taxila and Madurai were important centers under the control of the Gupta rulers.
(e) Aihole was the capital of the Pallavas.
(f) Local assemblies functioned for several centuries in south India
Consider the following statement about Hellenistic art :
1. The Sakas introduced features of Hellenistic art in the North-West frontiers of India.
2. The Hellenistic influence appears in the Pillars of Ashoka.
3. Gandhara art is the best example of Hellenistic influence.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?Below given are two statements, one is labelled as Assertion (A) and the other as Reason (R):
Assertion (A) : The Congress Boycotted the Simon Commission.
Reason (R) : The Commission did not have a single Indian member.
Codes:
Who was the founder of 'Harijan Sewak Sangh'?
In which Buddhist Council, Buddhism was divided into Mahayana and Hinayana sects?
Consider the following statements about Jainism:
- It rejected god as the creator of the Universe
- It denies the authority of Vedas
- It accepted the doctrines of karma and rebirth
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
Who headed the Sadar Nizamat Adalat at Calcutta established under Warren Hastings Plan of 1772?
The term, 'Amaram', in the Vijayanagar Empire stood for-
Stupas have a great significance in Buddhist architecture. In this reference, consider the following statements about the Bharhut stupa:
- It was initially built by Ashoka and was later improvised by the Sungas.
- Its railing contains numerous birth stories of the Buddha’s previous lives or Jataka stories.
- It represents the aniconic phase of Buddhist art.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
Which of the following pairs is/are correctly matched?
- Gandhara school: Grey sandstone/bluish-grey sandstone
- Mathura school: Spotted red sandstone
- Amravati school: White Marbles
Select the correct answer from the codes given below:
Consider the given statements.
I. Harshavardhana was converted into Hinayana Buddhism by the Chinese Buddhist traveler Huan tsang.
II. He also conducted the Buddhist conferences called Sangeethis at Prayag.
III. Harshavardhana was defeated by Pulakesin I in the battle of Narmada.
Choose the correct statement/statements.
Consider the following statements about the Quit India Movement:
- It was a natural corollary of the failure of the Cripps Mission
- It was launched at the Bombay session of the All-India Congress Committee
- Congress party was banned after the launch of the movement
- The Quit India Movement was not supported by the Muslim League
Which of the above statements are correct?