UGC NET Paper 2 History Mock Test - 2 - UGC NET MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - UGC NET Paper 2 History Mock Test - 2
consider the following statement about Junagarh Inscription :
1. The earliest specimen of the Kavya style was found in the Junagarh Inscription.
2. This inscription was made under the rule of Rudradaman 1.
3. This inscription was written in the Prakrit language.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
Who is the author of the book 'Understanding Harappa'?
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
Who has been credited to have said that the historian's task is "simply to show how it really was"?
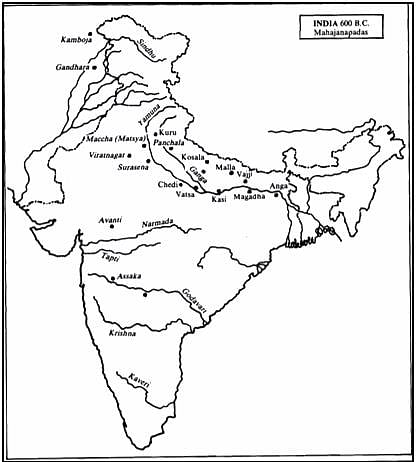
In the context of pre-Mauryan history, consider the following statements:
1. The Mahajanapada period is referred to as the first urbanisation.
2. During this period, the political centre shifted from Indo-Gangetic plains to lower Ganga valley.
3. The 16 mahajanapadas find reference only in Buddhist scriptures.
4. Among the mahajanapadas, rajyas were monarchies and ganas were republics.
Which of the above statements is/are not correct?
Consider the following options.
1. The fifth report submitted to the British Parliament in 1813 AD.
2. Jotedars were quite powerful.
3. Santhals were a great danger to Paharis.
4. No Zamindari was auctioned in Bengal.
With reference to Cholas, consider the following statements:
1. Karikala Chola established the city of Puhar at the mouth of river Cauvery.
2. Parantaka I captured the capital city of Pandyas- Madurai and assumed the title of ‘Maduraikonda’.
3. Under the Rajendra I kingship, colas annexed northern Sri Lanka.
4. Rajaraja I defeated Mahinda V and annexed the whole of Sri Lanka in 1018 A.D.
How many of the statements given above are correct?
Consider the following statements regarding Natesa, the 9th century’s rare sandstone idol.
1. It is a rare sandstone idol from the Dravidian Style of architecture.
2. It was stolen from a temple in Tamil Nadu and smuggled to the UK.
Which among the above statements is/are correct?
The principal sources from which the Government of India act 1935 drew its material were:
1). Simon commission report
2). Nehru report
3). Discussions of all three round table conferences
4). Lothian report
5). Joint select committee report
Consider the statements regarding to Dyarchy
1). In case of reserved subject Governor, though advised by ministers, could act in his own
2). Was abandoned all together in 1937
Which of the above statement(s) is/are correct?
Consider the following statements:
1) The discussions in the Third Round Table Conference eventually led to the passing of the Government of India Act of 1935
2) The Government of India Act of 1935 provided for the establishment of All India Federation to be based on a Union of the provinces of British India and the Princely States
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
With reference to the Pali texts, consider the following statements.
1) The Pali texts speak of two types of villages.
2) The first category included the typical village inhabited by various castes and communities.
3) The second category included the suburban villages which were in the nature of craft villages.
Choose the correct statement
Postmodern critiques of historical representation often rely on the concept of:
The Panchsheel, or Five Principles of Peaceful Coexistence, played a significant role in shaping Sino-Indian relations. Among the following statements regarding Panchsheel, which are CORRECT?
(a) The principles were first articulated during negotiations to resolve the border dispute between India and China's Tibet region.
(b) The Panchsheel aimed to promote a non-interventionist approach to international relations, particularly among newly independent states.
(c) The principles were strictly adhered to by both India and China throughout their entire relationship.
(d) The concept of Panchsheel originated entirely from Chinese foreign policy ideology.
Navdatoli, Eran and Nagada are the three best known settlements of
The Rashtrakuta king who defeated the Pratihara ruler Nagabhatta II was
The English edition of ‘Gitanjali’ was published in the year-
Acharanga Sutra is associated with which of the following religions?
Giak & Kiari are located in which of the following ?
Every Veda consists of which of the following parts?
- Samhita
- Brahmana
- Aranyaka
- Upanishad
Select the correct option from the codes given below:
Vallabhbhai Patel got the title of Sardar due to leadership and success in which one of the following movements?
At which of the following places the Dutch established their earliest factory in India?
Which of the following is correct about Balban?
Consider the following pairs:
- Ajanta cave: Buddhist in theme
- Ellora cave: Hinduism in theme
Which of the pairs given above is/are correct?
Consider the following statements.
- Indian National Army was formed by Subhash Chandra Bose.
- The INA founded the first provincial government of free India at Singapore.
Choose the correct statement.
Which of the following states was first to be annexed by Lord Dalhousie under the Doctrine of Lapse?
Who among the following was the first Bhakti Saint to use Hindi for the propagation of his message?
Consider the following statements:
- A.O.Hume came to be known as the Founder Father of Congress.
- He was the one to suggest the name “Indian National Congress”.
- He was the author of “Old Man’s Dream”.
- The “Safety Value Theory” was the reason given by him in the formation of the “Indian National Congress”.
Choose the correct statements.
Which of the following were included in the fourteen points of Jinnah?
- Separate set of Fundamental Rights for Muslims
- Reservation of one Third of Seats for Muslims
- Separation of Sindh from Bombay
- One Third Muslim Ministers
Select the correct option from the codes given below: