UGC NET Paper 2 History Mock Test - 6 - UGC NET MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - UGC NET Paper 2 History Mock Test - 6
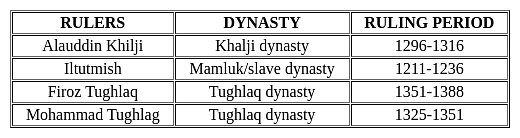
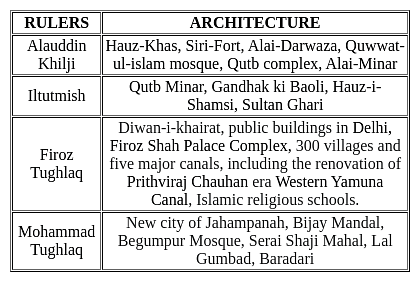
As per the Dual government the Company got the Diwani rights. For exercising the functions company appointed two deputies Diwans, one for Bengal and one for Bihar. Who was appointed as deputy diwan for Bihar?
What was the cause of the death of Hyder Ali?
Consider the following statements regarding the Indus Valley civilization:
1. People were following phallic worship.
2. Mixed types of burial systems were observed.
Which of the following is/are statements are correct?
In 1889, __________ established the Mukti Mission, a refuge for young widows who had been deserted and abused by their families.
Which of the following statements about the agrarian structure of the Gupta period are true?
(i) In the first half of the Gupta period, the king or the state claimed theoretical ownership of the land, though in practice the peasants had ownership rights.
(ii) The Poona Copper Plate of Prabhavatigupta provides us sufficient evidence for land survey during the Gupta period.
(iii) An officer called Pustapala was in charge of land revenue collection at the district level.
(iv) The Gupta inscriptions from Bengal and Bihar authorise the grantees to make a further gift of their lands to others.
(v) The Gupta land grants in central India and western India give not only fiscal rights but also rights of judicial administration to the recipients.
Select the answer from the codes given below:
Consider the following statements regarding the Harshavardhana:
1. He was a Shaivite during his early years of life.
2. He defeated Chalukyas and made Kannauj his Capital.
Which of the above statements is/ are not correct?With reference to the significance of the Revolt of 1857, consider the following statements:
1. It exposed the shortcomings in the Company's administration.
2. It brought India under politico-administrative unification.
3. It brought out in the open the grievances of people.
Which of the statements given above are correct?
Consider the following statements regarding the Gupta age:
1. Law-abiding people.
2. Equality was well established in society.
3. Non-veg food was allowed.
Which of the above descriptions were not mentioned in Fa-Hien’s account?Assertion: Lord Rippon followed spirited forward policy towards Afghanistan
Reason: Lord Rippon dumped erstwhile policy of "Masterly Inactivity"
Consider the following statements:
Assertion(A):- Indian villages were largely self-sufficient, however, Extensive trade within the country and between India and other countries of Asia and Europe was carried on under the Mughals.
Reason(R):- The trade continued because of the good means of communication provided by the Mughals.
Consider the following statements.
1) Satyendranath Tagore became the first Indian ICS officer in 1868.
2) Lord William Bentick was the first to form local courts called Munsif Courts, presided over by the Indians.
3) T.B. Macaulay became the first Law Member.
4) Charles Wilkins was the first to translate Ramayan into English.
Choose the correct statements.
Consider the following statements:
Assertion(A):- We do not find many bronze objects in prehistoric times.
Reason(R):- Tin was scarce even in ancient times.
The emergence of the "positive" school of historical writing in the 19th century was a reaction to which of the following trends in historical scholarship?
Consider the statements (A) and (B) about 'Provincial Autonomy' and choose the correct option.
(A) The government announced elections to the Provincial legislatures in 1937.
(B) After Incoming results, the congress formed governments in 7 out of 11 Provinces.
- Introduction of cash crops at the expense of subsistence crops
- Heavy taxation and land revenue systems
- Natural environmental fluctuations
- Immediate post-independence economic policies
With reference to freedom struggle of India, consider the following statements of Swadeshi Movement:
1. In Rawalpindi (Punjab), the arsenal and railway workers went on strike led by Lala Lajpat Rai and Ajit Singh.
2. Subramania Siva and Chidambaram Pillai led strikes in Tuticorin and Tirunelveli in a foreign-owned cotton mill.
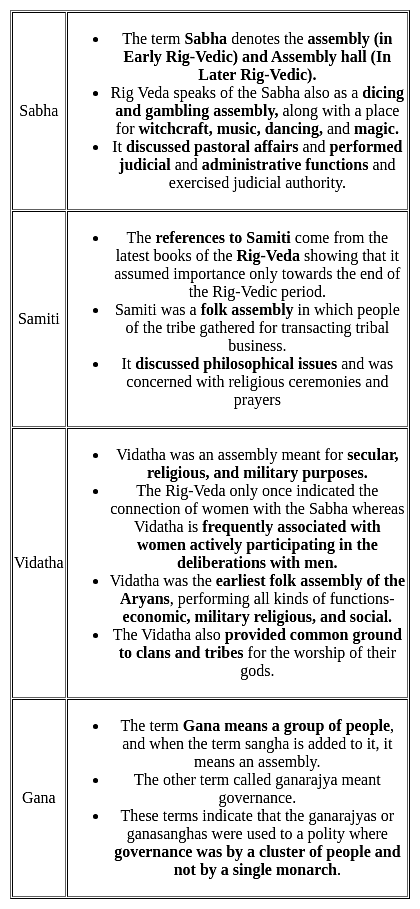
Which of the above statements is/are not correct?Consider the following Pairs:
1. Sabha: Broad-based folk assembly, presided over by the Rajan.
2. Samiti: Smaller body meant for elites.
3. Vidatha: Tribal assembly with diverse functions.
4. Gana: Assembly or troop.
Which of the pairs given above are correctly matched?
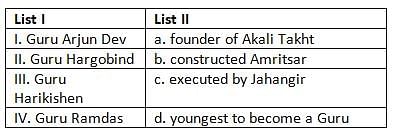
Match the items in List-I with the items in List-II
List-I (Wars)
A. Second Anglo-Sikh war
B. Second Anglo-Maratha war
C. Third Anglo-Mysore war
D. Anglo-Nepal war
List-II (Period)
1. 1814-16
2. 1890-92
3. 1803-05
4. 1848-49
Select the correct answer from the codes given below:
Match List I with List II, and select the correct answer by using the codes given below the lists:
FESTIVAL
1. Navreh
2. Cheti Chand
3. Ugadi
4. Rongali Bihu
PLACE
a. Assam
b. Sindh
c. Kashmir
d. Andhra Pradesh
Codes:
Who developed Jij Muhammad-shahi in 18th century India?
Consider the following organisations with their founders:
- British India Society – William Adam
- Indian National Union – A.O. Hume
- National Indian Association – Mary Carpenter
Which of the above is/are correct?