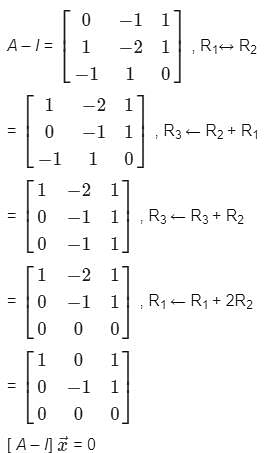UGC NET Paper 2 Economics Mock Test - 9 - UGC NET MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - UGC NET Paper 2 Economics Mock Test - 9
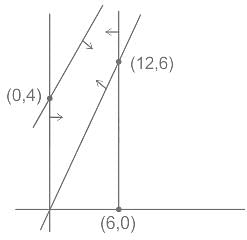
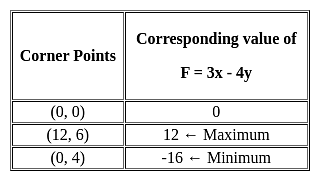
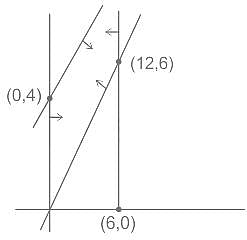
The feasible region for an LPP is shown in the given figure. Let F = 3x - 4y be the objective function. The maximum value of F is?

According to FRBM Act, India's fiscal deficit should not exceed:
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
All the non-banking financial institutions in India come under the category of ________.
I. Organised sector
II. Unorganised sector
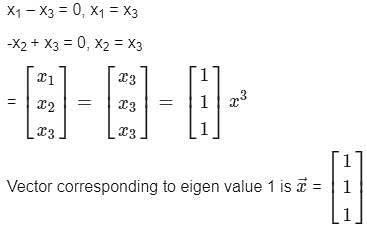
Find the eigen vector corresponding to Largest eigen value of matrix A = 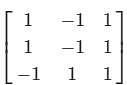
According to the Specific Factors Model, which of the following occurs when there is an increase in the price of a good?
A) The wage rate and rental rate of all sectors rise.
B) The specific factor in the industry producing the good experiences an increase in its reward.
C) The increased price does not affect the income distribution within the economy.
D) All sectors experience the same rise in production due to the increase in the price of that good.
The Balance of Payments deficit can be reduced by
1. Sale of sovereign bonds in international markets
2. Demand Slowdown
3. Restrictions on non-essential imports
Select the correct answer using the codes given below:
Which of the following is true regarding the term “Hot Money”?
1. It is the capital which is frequently transferred between financial institutions in an attempt to maximize interest or capital gain.
2. It is the particular currency, which is has high fluctuations in its value, due to frequent exchanges.
Select the correct answer using the code given below:-
Did the Capital to Risk Weighted Assets Ratio (CRAR) increase or decrease from March 2022 to September 2022?
Identify the non-probability sampling procedures from the following:
(A) Simple random sampling
(B) Quota sampling
(C) Cluster sampling
(D) Snowball sampling
(E) Dimensional sampling
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
Match List I with List II
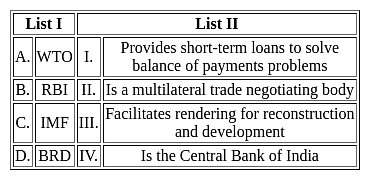
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
The economies across the world have undertaken massive use of “Above-the-line” fiscal policy measures, the full cost of which reflects in the fiscal deficit and government debt. Which of the following are the “Above-the-line” fiscal measures?
1. Spending on unemployment benefits
2. Tax relief measures
3. Special Credit Facility to Street Vendors
Select the correct answer using the code given below.
According to Malthus, population increases by progression of which kind?
What is the growth forecast for the 2015-16 year as announced by Union Home Minister while presenting the Economic Survey for 2015-16 on 27th Feb 15?
Total utility of a commodity is measured by which price of that commodity?
Let A be an n × n matrix from the set of numbers and A3 - 3A2 + 4A - 6I = 0 where I is an n × n unit matrix. If A-1 exists, then
The economic survey 2020-2021 talks about “the bare necessities”, in this context consider the following statement,
1. Bare necessities mean the minimum level of nutrition required for a healthy life.
2. Access to bare necessities is the highest in the States such as Kerala, Punjab, Haryana and Gujarat while it is the lowest in Bihar, Uttarpardesh and Rajasthan.
3. As compared to 2012“the bare necessities” has improved across all States in the country in 2018.
Which of the following statement is/are correct?
Assertion (A) IBRD was created to provide long-term finance.
Reason (R) IMF was created to solve short-term balance of payment problem of the member countries.
Which of the following is not specifically mentioned as a determinant of the demand for money?
Arrange the following in the order in which they appeared. Use the codes given below.
(i) Imperialism
(ii) Mercantalism
(iii) Capitalism
(iv) Feudalism
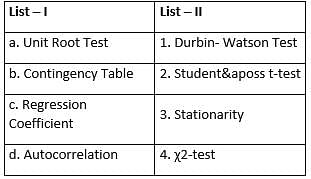
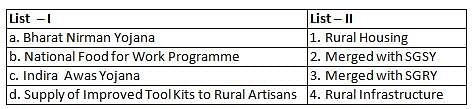
Match items of List – I with items of List – II:
In imperfect factor and product markets, labor exploitation is represented by:
(A) When ARP is > Average wage
(B) When ARP is > Marginal wage
(C) When ARP is < MRP
(D) When ARP is < Marginal wage