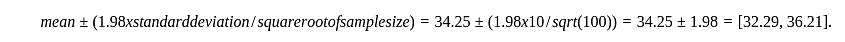UGC NET Paper 2 Economics Mock Test - 10 - UGC NET MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - UGC NET Paper 2 Economics Mock Test - 10
Consider the following statements:
1. The Reserve Bank of India manages and services Government of India Securities but not any State Government Securities.
2. Treasury bills are issued by the Government of India and there are no treasury bills issued by the State Governments.
3. Treasury bills offer are issued at a discount from the par value.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
Which one of the following monetary measures will lead to a decrease in the supply of money in the economy?
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
Which of the following statement correctly describes the relationship between Marginal Cost (MC), Average Total Cost (ATC), and Average Variable Cost (AVC) in the short-run? Choose the correct options from below :
A. The AVC curve intersects the ATC curve at the minimum point of the MC curve.
B. When MC is less than AVC or ATC, it will pull AVC and ATC downward.
C. MC equals ATC and AVC at their maximum points.
D. When MC is above AVC and ATC, it will push AVC and ATC upward.
B. When MC is less than AVC or ATC, it will pull AVC and ATC downward.
C. MC equals ATC and AVC at their maximum points.
D. When MC is above AVC and ATC, it will push AVC and ATC upward.
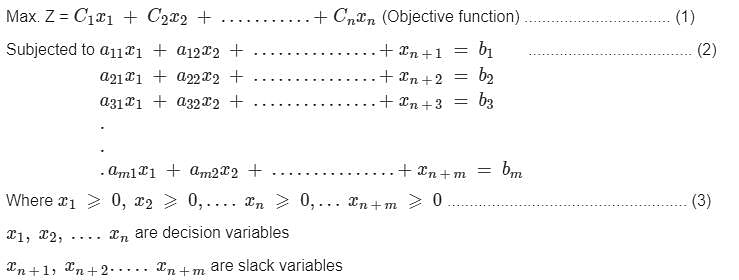
In linear programming problem when does feasibility change?
Compared to the previous fiscal year, how has the 'Manufacturing' sector's growth rate changed in the current fiscal year?
How much has the GDP at constant prices increased from Q2 of 2023-24 to Q2 of 2024-25?
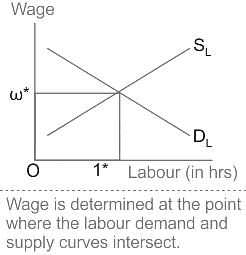
With reference to Wage Determination in Labour Market, consider the following statements:
1. Wage rate is determined at the intersection of the demand and supply curves of labour.
2. Firm will earn more profit by hiring one more unit of labour as long as the value of the marginal product of labour (VMPL ) is greater than the wage rate.
3. At higher wage, less labour is demanded thereby leading to a downward-sloping demand curve.
Which of the above statements is correct?
Match List I with List II

Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
The 95% confidence interval of average age of accidents in any city during last year for a sample of size 100 with mean age 34.25 from population of standard deviation 10 is
Arrange the following in chronological order in which they were introduced:
A. SDGs
B. MPI
C. PQLI
D. HDI
Choose the correct answer from the options given below
The shape of rectangular hyperbola is made by
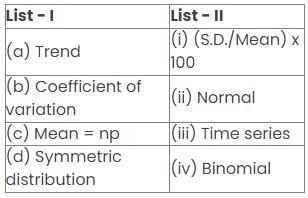
Match the following and choose the correct option.
Simon Hawkins relates to which of the following?
(a) Static Leontief Model
(b) Dynamic Leontief Model
(c) These are necessary and sufficient conditions for the solution of the model.
Choose the correct answer from the given code below.
Which of the following statements are true regarding Cobb-Douglas production function ?
(a) It is long period production function
(b) It is short period production function
(c) It is based on increasing returns to scale
(d) Output elasticities with respect to factors are constant
Select the correct option:
With reference to India, consider the following statements :
1. Retail investors through demat account can invest in ‘Treasury Bills’ and ‘Government of India Debt Bonds’ in primary market.
2. The Negotiated Dealing System Order Matching’ is a government securities trading platform of the Reserve Bank of India.
3. The ‘Central Depository Services Ltd.’ is jointly promoted by the Reserve Bank of India and the Bombay Stock Exchange.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
The weak sustainability approach of sustainable development
Directions In the question given below are two statements labelled as Assertion (A) and Reason (R). In the context of the two statements, which one of the following is correct?
Assertion (A) Screen based trading system cuts down on time, cost and risk of error as well as on the chances of fraud.
Reason (R) Screen based trading system electronically matches the buyer and seller in an order driven system.
The general hedonic wage equation can be expressed as
Directions: Read the given statements carefully and choose the correct option accordingly.
Assertion (A): Monopoly is Pareto inefficient.
Reason (R): It would be possible to change the allocation of resources to make the amount of income he would be prepared to pay in exchange of the reduction in price.
Directions: Read the given statements carefully and choose the correct option accordingly.
Assertion (A): Demand curve is vertical when elasticity of demand is zero.
Reason (R): Marginal utility of a product is increasing.
Consider the following statements.
1. Saving rate was reduced by population growth because of increase in burden of dependency.
2. Rapid growth in population is falling land-human ratio.
Which of the above statement(s) is/are correct?