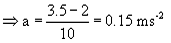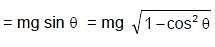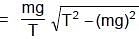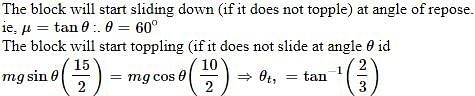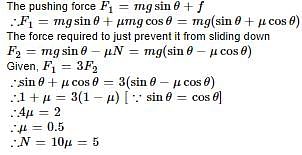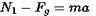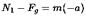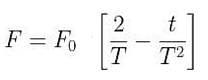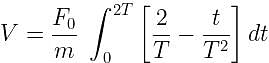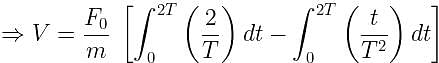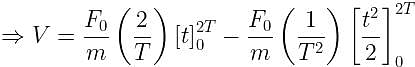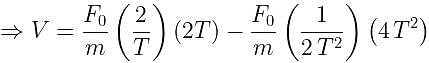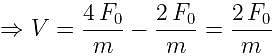Test: Laws of Motion II - JEE MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Laws of Motion II
A car of mass 1000 kg is moving at a velocity of 20 m/s. Suddenly, the driver applies the brakes, and the car comes to a stop in 4 seconds. What is the magnitude of the average force exerted by the brakes on the car? (Assume no external forces are acting on the car)
A constant force acting on a body of mass 3 kg changes its speed from 2 m/s to 3.5 m/s in 10 second. If the direction of motion of the body remains unchanged, what is the magnitude and direction of the force?
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
A simple pendulum is oscillating in a vertical plane. If resultant acceleration of bob of mass m at a point A is in horizontal direction, find the tangential force at this point in terms of tension T and mg.
A painter is applying force himself to raise him and the box with an cceleration of 5 m/s2 by a massless rope and pulley arrangement as shown in figure. Mass of painter is 100 kg and that of box is 50 kg. If g = 10 m/s2, then :
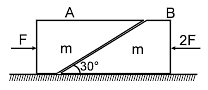
Two blocks ‘A’ and ‘B’ each of mass ‘m’ are placed on a smooth horizontal surface. Two horizontal force F and 2F are applied on the two blocks ‘A’ and ‘B’ respectively as shown in figure. The block A does not slide on block B. Then the normal reaction acting between the two blocks is :
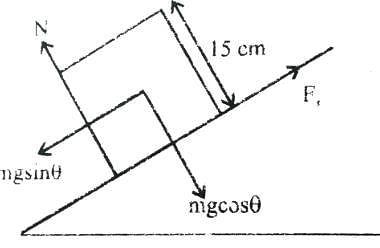
A block of base 10 cm × 10 cm and height 15 cm is kept on an inclined plane. The coefficient of friction between them is . The inclination q of this inclined plane from the horizontal plane is gradually increased from 0º. Then [jee 2009]
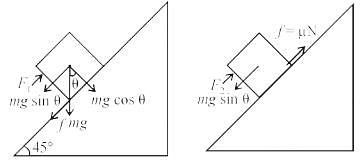
A block is moving on an inclined plane making an angle 45º with horizontal and the coefficient of friciton is μ. the force required to just push it up the inclined plane is 3 times the force requried to just prevent it from sliding down. If we define N = 10μ, then N is
[jee 2011]
The dimensional formula of Plancks’s constant and angular momentum are
Three forces 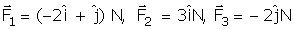 act on an object of mass m = 2 kg. The acceleration of the object in m/s2 is:
act on an object of mass m = 2 kg. The acceleration of the object in m/s2 is:
Upon catching a ball, a cricket fielder swings his hands backwards. The concept behind this is explained by
The mass of a lift is 2000 kg. When the tension in the supporting cable is 28000 N, its acceleration is:
If a lift is moving with constant acceleration 'a' in the upward direction, then the force applied by mass m on the floor of the lift will be:
A man weighs 70 kg. He stands on a weighing scale in a lift which is moving upwards with an acceleration of 5ms2.What would be the reading on the scale? (g=10 ms2)
An average force of 100N acts on a body for 1s. What is the impulse due to the force?
A ball weighing 0.01kg hits a hard surface vertically with a speed of 5m/s and rebounds with the same speed. The ball remains in contact with the surface for 0.01s. The average force exerted by the surface on the ball is
A block is placed on the table. What is the angle between the action of the block on the table and reaction of the table on the block?
A machine gun has a mass of 20 kg fires 35 g bullets at the rate of 400 bullets per second with a speed of 400ms-1 .What force must be applied to the gun to keep in the position?
Which law says that every force is accompanied by an equal and opposite force?
A bomb of mass 16kg at rest, explodes into two pieces of masses 4kg and 12kg. After explosion, the velocity of the 12kg mass is 4m/s. What is the velocity of the 4kg piece?
A block of mass 2 kg is initially at rest on a frictionless horizontal surface. A force of 8 N is applied to the block horizontally for 5 seconds. What is the final velocity of the block?
Two masses are in the ratio 1:5. What is ratio of their inertia?
A 6 kg object is subject to three forces
F1 = 20i + 30j N
F2 = 8i - 50j N
F3 = 2i + 2j N
Find the acceleration of object.
A body of mass 2kg is sliding with a constant velocity of 4m/s on a frictionless horizontal table. The net force required to keep the body moving with the same velocity is
An object of mass 5 kg is initially moving with a velocity of 10 m/s. An unbalanced force of 30 N is applied to the object in the opposite direction of its motion. Calculate the acceleration of the object.
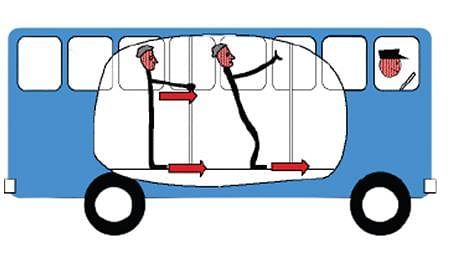
Passengers in a bus lean forward as bus suddenly stops. This is due to
A particle of mass 'm' original at rest, is subjected to a force whose direction is constant but whose magnitude varies with according to the relation
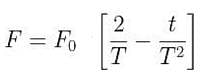
Where F0 and T are constant.
Then speed of the particle after a time 2T is: