Test: Photosynthesis in Higher Plants - Assertion and Reasoning - NEET MCQ
20 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Photosynthesis in Higher Plants - Assertion and Reasoning
Assertion: Chloroplasts mostly occur in mesophyll cells along their walls inside the leaves.
Reason : The membrane system of chloroplast is responsible for trapping the light energy and also for the synthesis of ATP and NADPH.
Reason : The membrane system of chloroplast is responsible for trapping the light energy and also for the synthesis of ATP and NADPH.
Assertion : Rhoeo leaves contain anthocyan inpigments in epidermal cells.
Reason : Anthocyanins are accessory photosynthetic pigments.
Reason : Anthocyanins are accessory photosynthetic pigments.
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
Assertion: Leaf colouration is due to the presence of four pigments - Chlorophyll a, chlorophyll b, xanthophylls and carotenoids.
Reason : Chlorophyll b is the chief pigment associated with photosynthesis.
Reason : Chlorophyll b is the chief pigment associated with photosynthesis.
Assertion: Bacterial photosynthesis occurs by utilizing wavelength longer than 700 nm.
Reason: Here reaction centre is B-890.
Assertion : There is a decrease in photosynthesis, if the photosynthetic cells are illuminated by light of P680 nm or more wavelength.
Reason : In red drop phenomenon the rate of photosynthesis decreases.
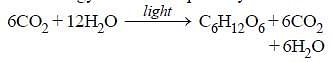
Assertion : 6 molecules of CO2 and 12 molecules of NADPH+ + H+ and 18 ATP are used to form one hexose molecule.
Reason : Light reaction results in formation of ATP and NADPH2.
Assertion : Cyclic pathway of photosynthesis first appeared in some eubacterial species.
Reason : Oxygen started accumulating in the atmosphere after the non-cyclic pathway of photosynthesis evolved.
Assertion : Cyclic photophosphorylation synthesizes ATP.
Reason : ATP synthesise in cyclic photophosphorylation is not associated with NADPH formation.
Assertion : Each molecule of ribulose-1, 5-bisphosphate fixes one molecule of CO2.
Reason : Three molecules of NADPH and two ATP are required for fixation of one molecule of CO2.
Assertion :The stromal thylakoids are rich in both PS I and PS II.
Reason : The granal membranes are rich in ATP synthetase
Assertion :Cyclic photophosphorylation synthesizes ATP.
Reason : ATP synthesise in cyclic hotophosphorylation is not associated with NADPH formation.
Assertion : Oxidative phosphorylation requires oxygen.
Reason : Oxidative photophosphorylation occurs in mitochondria.
Assertion : Plants utilize 5-10 of the absorbed water in photosynthesis.
Reason : Reduced leaf hydration decrease the photosynthesis.
Assertion: Six molecules of CO2 are fixed to form a hexose.
Reason: One molecule of CO2 is fixed to produce 686 kcal in photosynthesis
Assertion: 686,000 calories energy are produced in the formation of one molecule of glucose.
Reason: The energy is provided by a total of 12 NADPH and 18 ATP.
Assertion: The stroma lamellae have both PS I and PS II.
Reason : The grana lamellae lack PS II as well as NADP reductase enzyme.
Assertion: The proton gradient is broken down due to the movement of protons across the membrane to stroma through the transmembrane channel of the F0 of the ATP ase.
Reason: It is the breakdown of proton gradient that leads to release of energy.
Assertion: The splitting of water is associated with PS II.
Reason : Water is split into H+, O2 and electrons
Assertion : Water splitting complex is associated with PS-II.
Reason : Water splitting complex and PS-II both are physically located on the outer side of the membrane of thylakoid.
Assertion : Cyclic pathway of photosynthesis first appeared in some eubacterial species.
Reason : Oxygen started accumulating in the atmosphere after the non-cyclic pathway of photosynthesis evolved.