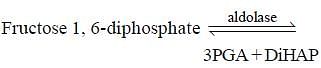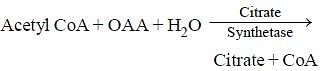Test: Respiration in Plants - Assertion and Reasoning - NEET MCQ
20 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Respiration in Plants - Assertion and Reasoning
Assertion : Stomata are absent in submergedhydrophytes.
Reason : Respiration occurs by means of air chambers in submerged plants.
Reason : Respiration occurs by means of air chambers in submerged plants.
Assertion : Glycolysis is the first step of respiration in which glucose completely breaks into CO2 and H2O.
Reason : In this process, there is net gain of twenty four molecules of ATP
Reason : In this process, there is net gain of twenty four molecules of ATP
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
Assertion : Glycolysis occurs in cytoplasm.
Reason : Enzymes for glycolysis are found in cytoplasm. It is common in aerobic/anaerobic respiration.
Reason : Enzymes for glycolysis are found in cytoplasm. It is common in aerobic/anaerobic respiration.
Assertion : Substrate level phosphorylation is present in glycolysis.
Reason : Substrate level phosphorylation causes synthesis of ATP.
Assertion: Fructose-1, 6 diphosphate is converted into glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate and dihydroxy-acetone-3-phosphate.
Reason: In the presence of enzyme aldolase, conversion of fructose-1,6 diphosphate into 3-phosphoglyceraldehyde and dihydroxyacetone-3-phosphate is facilitated.
Assertion: Plants do not have specialised respiratory organs.
Reason: There is very little transport of gases from one plant part to another.
Assertion: The process of glycolysis is also known as EMP pathway.
Reason: It is the only process of respiration in aerobic organisms.
Assertion: This conversion of 1,3-biphosphoglycerate (BPGA) to 3- phosphoglyceric acid (PGA) is an energy yielding step.
Reason: By the formation of ATP, this energy is trapped.
Assertion: The incomplete oxidation of glucose into lactic acid or ethanol is fermentation.
Reason: In only prokaryotes, it takes place under anaerobic condition.
Assertion : Banking industry makes use of yeasts such as Saccharomyces cerevisiae.
Reason : Carbon dioxide produced during fermentation causes bread dough to rise by thermal expansion.
Assertion: During strenuous exercise, anaerobic respiration sometimes occurs in our skeletal muscles.
Reason: Pyruvic acid is reduced to lactic acid in the presence of lactate dehydrogenase and in the absence of oxygen
Assertion : In alcoholic fermentation, the hexose molecule is converted into glucose and fructose.
Reason : Alcoholic fermentation is anaerobic respiration brought about by enzyme zymase.
Assertion : Under aerobic conditions, pyruvate gives rise to lactate.
Reason : Under anaerobic condition, pyruvate gives rise to acetyl CoA.
Assertion: Both in aerobic and anaerobic conditions terminal oxidation occurs.
Reason: Terminal oxidation stops at terminal step of respiration.
Assertion: The breaking of the C- C bonds of complex compound through oxidation within the cells and release of large amount of energy is respiration.
Reason: During respiration, the compounds that are oxidised are called respiratory substrates.
Assertion: In TCA cycle, the first step is the condensation of pyruvate with oxaloacetic acid and water.
Reason: This reaction is catalysed by enzyme pyruvate synthase.
Assertion : The product of the first reaction of the Kreb's cycle is citric acid, a six carbon compound.
Reason : The first reaction of the Kreb's cycle is the condensation of acetyl CoA with oxaloacetate.
Assertion : The inner membrane of mitochondria contains systems involving electron transport.
Reason : The mitochondrial matrix contains enzymes of Kreb's cycle.
Assertion : F1 particles are present in the inner mitochondrial membrane.
Reason : An electron gradient formed on the inner mitochondrial membrane, forms ATP.
Assertion : In electron transport chain, there is a loss of energy at each step.
Reason : At each step of ETC, there are electron carriers.