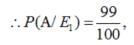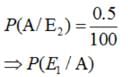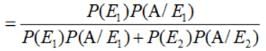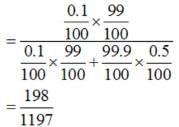HSSC TGT Math Mock Test - 2 - HSSC PGT/TGT MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - HSSC TGT Math Mock Test - 2
The Indian Parliament passed a Central Legislation named Air Pollution Control Act in the year:
Which act of Government of India includes noise as environmental pollution ?
A doctor is to visit a patient. From the past experience, it is known that the probabilities that he will come by train, bus, and scooter or by other means of transport are respectively 0.3, 0.2, 0.1 and 0.4. The probabilities that he will be late are 1/4 , 1/3 and 1/12, if he comes by train, bus and scooter respectively, but if he comes by other means of transport, then he will not be late. When he arrives, he is late. The probability that he comes by bus is:
A laboratory blood test is 99% effective in detecting a certain disease when it is in fact, present. However, the test also yields a false positive result for 0.5% of the healthy person tested (i.e. if a healthy person is tested, then, with probability 0.005, the test will imply he has the disease). If 0.1 percent of the population actually has the disease, what is the probability that a person has the disease given that his test result is positive?
If f(x) = x2 and g(x) = x are two functions from R to R then f(g(2)) is:
The area bounded by y = |sinx| , the x – axis and the line |x| = π is
For a moderately skewed distribution, quartile deviation and the standard deviation are related by
The mean and variance of a binomial distribution are 4 and 3 respectively, then the probability of getting exactly six successes in this distribution is:



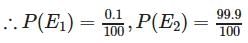 Let A = event that the test result is positive
Let A = event that the test result is positive