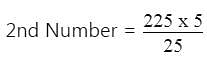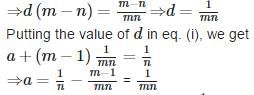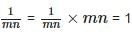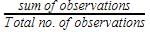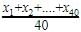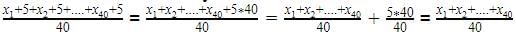BPSC TGT Math & Science Mock Test - 9 - Bihar PGT/TGT/PRT MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - BPSC TGT Math & Science Mock Test - 9
Directions: In each of the following questions, a sentence has been given in Active (or Passive) Voice. Out of the four alternatives suggested, select the one that best expresses the same sentence in Passive/ Active Voice.
Why did she break the garden wall ?
Fill in the blank with the correct option.
Teresa is not a pleasant person. She is ___________ in a bad mood.
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
नीचे दिए गए शब्द का सही बहुवचन वाला विकल्प पहचानिए।
“मैं खाना खा चुका था” इस वाक्य में कौन-सा भूतकालिक भेद है?
Directions: Each of the following consists of a question and two statements numbered I and II given below it. You have to decide whether the data provided in the statements are sufficient to answer the question.
Six persons – F, G, H, I, J and K, each earn a different amount of money. Who earns the maximum?
Statement I: I earns more than only two persons. J earns more than K but not maximum. G earns more than only F.
Statement II: K earns less than only two persons. G earns more than F but less than I. I earns less than K. J earns less than H.
Three out of the four alternatives are same in a certain way and so form a group. Find the odd one that does not belong to the group.
Name the process in which the passage of water goes from a region of higher concentration to a region of lower concentration through a semi permeable membrane?
LCM of two numbers is 225 and their HCF is 5. If one number is 25, the other number will be?
From a circular sheet of paper with a radius 20 cm, four circles of radius 5 cm each are cut out. What is the ratio of the uncut to the cut portion?
In an A.P., if am = 1/n and an = 1/m, then amn =
The points on Y-axis at a distance of 13 units from point (–5, 7) are :
The roots of the equation x2 – 3x – m (m + 3) = 0, where m is a constant, are
The arithmetic mean of a set of 40 values is 65. If each of the 40 values is increased by 5, what will be the mean of the set of new values:
Read the following text and answer the following questions on the basis of the same:
On a weekend Rani was playing cards with her family. The deck has 52 cards.If her brother drew one card.

Find the probability of getting a red face card.
If the diameter of a cylinder is 28 cm and its height is 20 cm, then total surface area (in cm2) is :
A microscope is focused on an ink mark on the top of a table. If we place a glass slab 3cm thick on it, how should the microscope be moved to focus the ink spot again? The refractive index of glass slab is 1.5 cm.
The ionisation isomer of [Cr(H2O)4Cl(NO2)Cl] is
What type of receptors detect taste and smell?
Which of the following statements is not correct about reproduction ?
What is the main purpose of the excretory system in human beings?
Mixed cropping and intercropping involve growing of two or more crops simultaneously on the same field; but the latter differs from the former in that
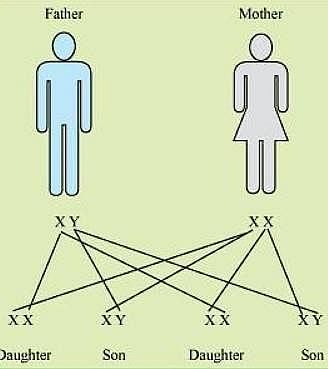
A zygote which has an X-chromosome inherited from the father will develop into a
What happens to auxin concentration when light is coming from one side of the plant?
The earlobe variants found in human population are
(i) Free
(ii) Curved
(iii) Round
(iv) Attached