DSSSB PRT Mock Test - 1 - DSSSB TGT/PGT/PRT MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - DSSSB PRT Mock Test - 1
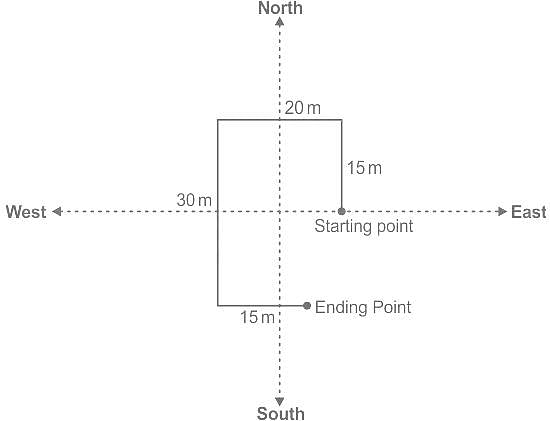
Ramu walks 15m towards the north then turns left and covers 20m then covers also 30m by turning south then again turns left and covers 15m. What is the total distance covered by him?
Among the four answer figures, which one/ones of them can be formed from the cut out pieces given below.
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
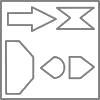
Direction: If a Paper (Transparent Sheet) is folded in a manner and a design or pattern is drawn. When unfolded this paper appears as given below in the answer figure. Choose the correct answer figure given below.
A piece of paper is folded and cut as shown below in the question figures. From the given answer figures, indicate how it will appear when opened.
Question Figure
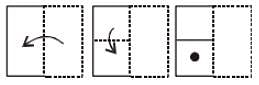
Answer figure
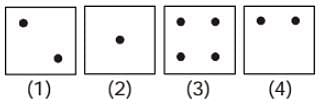
Question Figure

Answer figure

Direction: In the following question, a sentence has been given in Active/Passive Voice. Out of the four alternative suggested, select the one which best expresses the same sentence in Passive/Active Voice.
My father has promised me a bicycle.
Which of the following statements is true about psycho-social approaches in psychology?
I. They are unrelated to the psychoanalytical approach.
II.They focus on social and cultural factors that influence an individual's development and behavior.
Which of the following statement is correct regarding instrumental aggression?
I. Instrumental aggression produces some positive reward or advantage (impact) on the aggressor unrelated to the victim’s discomfort.
II. The act of aggression is meant to obtain a certain goal or object.
The form of communication before children learn to speak is _____________.
Choose the correct statement.
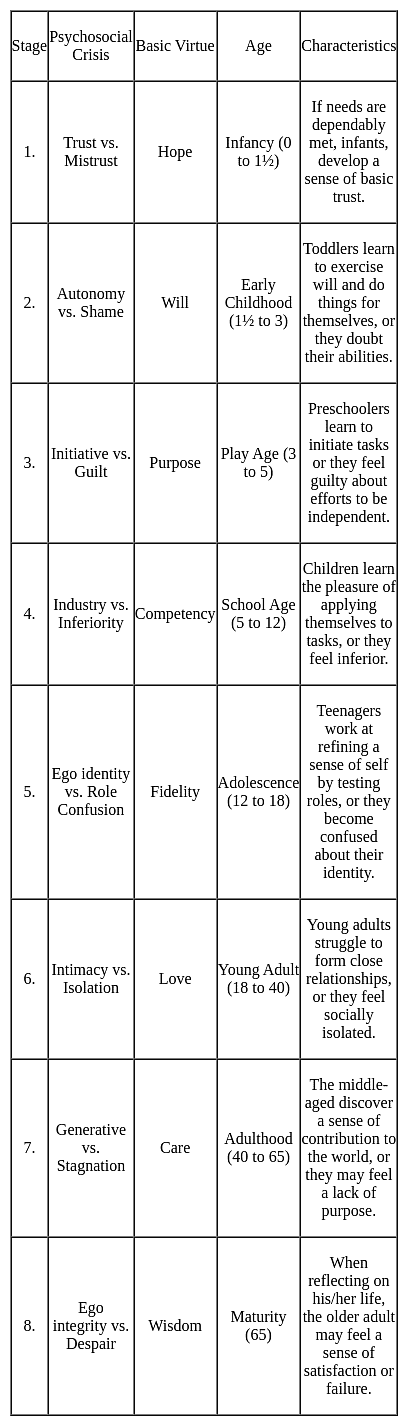
Statement I: Erik Erikson's theory has 6 stages.
Statement II: Piaget has a psychosocial theory of development.
Given below are two statements
Statement I: As per Piaget's stages of cognitive development, the child learns a language and begins to use symbols to represent objects during the pre-operational stage.
Statement II: As per Piaget's stages of cognitive development, the child learns through reflexes, senses and movement-actions on the environment during the formal operational stage.
In light of the above statements, choose the correct answer from the .Both Statement I and Statement II are false options given below
Which of the following are essential elements of Cooperative Learning?
A. students work in groups.
B. students share in groups.
C. students compete positively with others in groups.
D. students support each other in groups.
NCF 2005 draws attention on which of the following other curriculum areas:
A. The Art and Heritage craft
B. Yoga and Physical Education
C. Peace Education
D. Health Education
What is your role as a teacher to facilitate meaning-making learning?
I. You need to create a congenial environment in the classroom and school.
II. You should record each student’s perception of the issue on the blackboard so that all the statements are visible to all students.
According the Gardner's Theory of Multiple Intelligences, the dimension that would most contribute to success in cooperative learning activities would be:
Koodiyattam is a traditional performing art form in the state of ________.
Which among the following is not among the four fundamental principles of Rabindranath Tagore's educational philosophy?