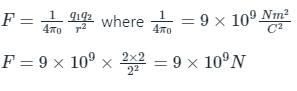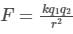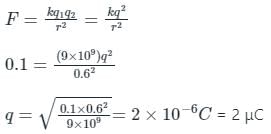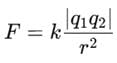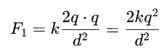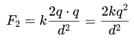Test: Electric Charge - Grade 12 MCQ
20 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Electric Charge
Which of the following methods can be used to charge a metal sphere positively without touching it? Choose the best possible option:
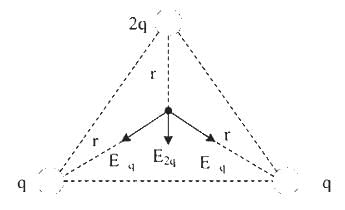
The charges 2q, -q, -q are located at the vertices of an equilateral triangle. At the circumcentre of the triangle
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
Which among the following is safest to take protection from when lightning is expected to happen ?
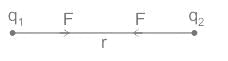
Two charges +2 coulomb each are placed 2 m apart in vacuum, force of repulsion between them will be:
A current of 0.5 A is drawn by a filament of an electric bulb for 20 minutes. The amount of electric charge that flows through the circuit is
If two conducting spheres are separately charged and then brought in contact:
The total negative charge in 1 mol of helium (atomic number 2, atomic mass 4) is:
If number of neutrons become more than the number of electrons in the element then it will become:
Which of the following statements about the properties of electric charge is INCORRECT?
Two identical charges repel each other with a force equal to 10 grams.wt when they are 0.6 m apart in the air (g = 10 ms-2). The value of each charge is
A silk cloth rubbed with a glass rod acquire a charge (-1.6 x 10-19) C. Then the charge on the glass rod is:
Choose the correct statements regarding electric charges.
(i) Electric charge follows principle of superposition of charges.
(ii) Like charges attract each other
(iii) Unlike charges attract each other
Three point charges +q,−2q,+q are placed on a straight line, with equal separations d. Find the net force on the middle charge.
If an object is positively charged, theoretically the mass of the object ______