APSET Paper 2 Mock Test - 1 (Geography) - AP TET MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - APSET Paper 2 Mock Test - 1 (Geography)
Which of the following are evidences of Continent Drift Theory?
At what plate boundary setting is the ocean floor deepest?
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
What is a significant reason for the formation of submarine canyons on the continental shelf?
What is the shallow submerged extension of a continent called?
Which among the following is the largest Bay of the world?
As per the Census 2011, which state has the lowest population in India?
As the temperature of the black body increases,the dominant wavelength of the emitted radiation according to Wein's displacement law is:
Which of the following is true about Tropical Rain forest?
(A) These forest are called evergreen forests.
(B) The trees in these forests shed their leaves at different times of the year.
(C) Sal, Teak and Shisham are important trees of these forests.
(D) These forests are called monsoon forests.
Choose the correct option
Which among the following is / are correct statements with respect to Shifting Cultivation as practiced in India?
- India’s largest area under shifting cultivation is in the state of Arunachal Pradesh
- In recent years, the cycle of shifting cultivation on a particular land has reduced drastically
Select the correct option from the codes given below:
In an ecotone, the species which become abundant are called:
(a) With shift in technology, there has been a shift in the structure of industries.
(b) The globalization has caused a new international division of labour.
(c) The high tech industrial regions have very little to no place for blue collar jobs.
(d) R&D is the most important feature of traditional large scale industrial regions.
Choose the correct option from below:
Which of the following statement is not correct about andesitic or acidic lava?
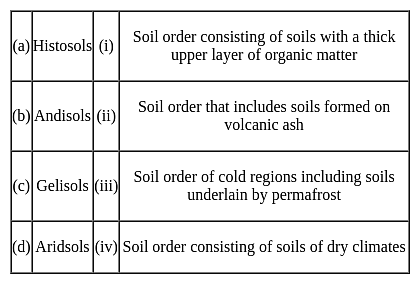
Match the following soil orders with their descriptions:
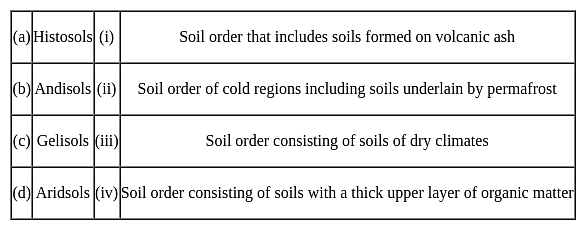
Choose the correct option from those given below:
Read the following statements for physical features of India and choose the correct options:
A. Many popular hill stations are situated in middle Himalaya.
B. Northern plains are highly populated areas because river plains have fertile land for cultivation.
C. Western ghats are rich in minerals and are highly populated.
The term cadastral is derived from the ______ word cadestre meaning register of territorial property.
Considering the insolation received in 100, which of the following statements is/are correct regarding the heat budget of the Earth?
1. Around 35 units are reflected back before reaching the surface of the Earth.
2. 65 units are absorbed by the atmosphere and the Earth’s surface.
3. The earth radiates back 51 units as terrestrial radiation.
Select the correct answer from the options given below.Given below are two statements. One is labelled as Assertion (A) and the other is labelled as Reason (R).
Assertion (A): There is high density of population in Chotanagpur plateau.
Reason (R) : Various minerals are found in the Chotanagpur plateau.
Select the correct answer from options given below:


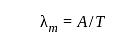
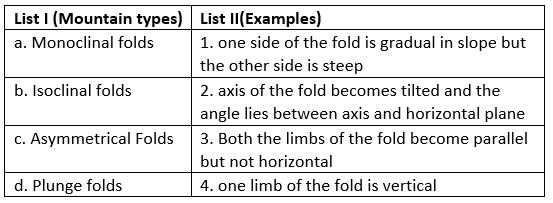
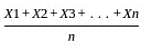 .
.