APSET Paper 2 Mock Test - 9 (Geography) - AP TET MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - APSET Paper 2 Mock Test - 9 (Geography)
For interpolation of satellite data used for monitoring dynamic changes that occur on the earth surface, the most suitable orbit for the satellite is:
‘The structure of movement and household travel behavior’ was given by
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
Consider the following States:
1. Karnataka
2. Andhra Pradesh
3. Goa
4. Rajasthan
Which of the above are the major maize-producing states?
Given below are two statements. One is labelled as Assertion (A) and the other is labelled as Reason (R).
Assertion (A): Software industry has developed rapidly in India since 1990s.
Reason (R): India has a lot of technically skilled manpower.
Select the correct answer from options given below:
Given below are two statements. One is labelled as Assertion (A) and the other is labelled as Reason (R).
Assertion (A): Foreign Direct Investment is not beneficial for economic growth.
Reason (R) : Foreign Direct Investment increases trade in the economy.
Select the correct answer from options given below:
Study the following pairs (P, Q, R, S) with respect to GPS receivers used in GPS surveys and select the correct answer based on the matching.
P : GPS receivers : L-band radio processor
Q : Self-contained GPS receivers : Also known as 'GPS mice'
R : Dual-frequency receivers : Survey grade GPS, position accuracy according to differential correction within sub-centimetre
S : Carrier phase receivers : GPS receivers with 10 to 30 cm position accuracy with differential correction
The temperature-depth profile of the ocean is an interesting topic of study. Which of the following statements is/are incorrect regarding this?
1. About 90 per cent of the total volume of water is found below the thermocline in the deep ocean.
2. The thermocline layer is characterised by a rapid decrease in temperature with increasing depth.
3. The highest temperature of the ocean waters is recorded at the equator.
Identify the correct answer from the codes given below.Choose the correct option for the statements gien below:
(A) Endogenic forces sometimes produce sudden movements
(B) Sudden moments like earthquakes and volcanoes cause mass destruction on the surface of the earth
(a) Ratzel applied organic theory to biogeography.
(b) Humboldt was of the opinion that life of people living in islands, plains and mountains was similar.
(c) Kant described the impact of environment in late 18th century.
(d) Darwin’s theory of origin of species is dependent on the idea that the nature changes with time.
Code:
(a) Altimetric frequency histograms and curves are two basic techniques to study high lands of geomorphological significance.
(b) Baulig suggested use of grid method to remove deficiencies in altimetric analysis.
(c) The accuracy of altimetric analysis depends upon the benchmarks.
(d) The grid method is used in altimetric analysis when there is deficiency in density of spot heights.
Code:
Read the following statements and state which of them are true?
Spykman's Rimland Theory was a variant of Mackinder's Heartland Model. Both the models emphasised on
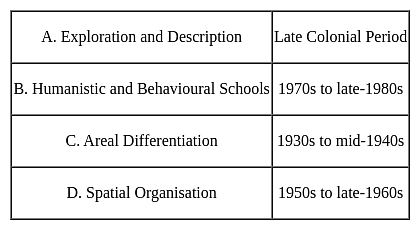
Which of the following is not correctly matched:
Approaches - Periods
Assertion (A) : In the concentric zone model the rich high-class citizens live in the fourth zone.
Reason (R) : Detached homes are found in the fourth zone which is at quite a bit of distance from the Central Business District.
Code :
Which scale is used to measure three dimensions on a scale?
When was National environment planning and coordination (NEPC) established?
_______ are lines drawn on a map to locate, in the plan view, points of equal ground elevation.
Critics of the Malthusian Theory argue that advancements in which field have mitigated the challenges predicted by Malthus?
According to Malthus, what are preventive checks in the context of population control?
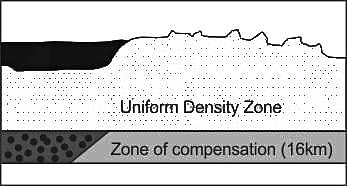
Who put forward the idea of "uniform depth with varying density" while expressing isostasy?
Which one of the following statements is correct about remote sensing?
(A) Active sensors emit their own electromagnetic energy
(B) Altimeters and scatterometers comes under the non-imaging microwave sensors category
(C) Passive sensors that measure the emitted energy
(D) LIDAR is an example of a passive remote sensor
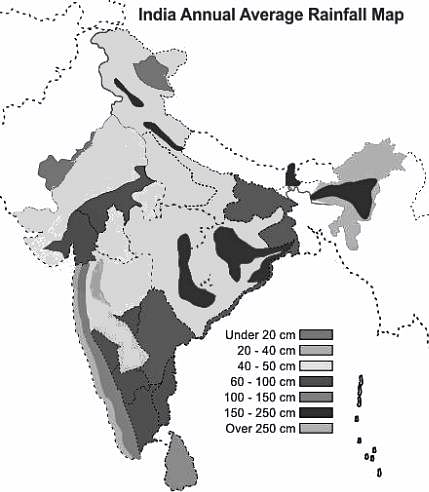
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:Which of the following part of India receives the first monsoon in summer?
i. Demangeon was the pupil of Vidal de la Blache
ii. “La Picardie et les regions veisines” is his monograph
ii. He wrote L’Lomme el la Terre
iv. He was of the view that man destroyed natural flora and fauna.
Choose the correct option from below.