APSET Paper 2 Mock Test - 4 (History) - AP TET MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - APSET Paper 2 Mock Test - 4 (History)
Indian National Congress as a Political Party should be disbanded post-independence, who advised it?
Consider the following statements:
1) Adi Brahmo Sabha was founded by Raja Ram Mohan Roy in Kolkata.
2) All India Brahmo Samaj was founded by Debendranath Tagore.
3) Sadharan Brahmo Samaj was founded by Anand Mohan Bose and Kesab Chandra Sen.
Choose the incorrect statements.
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
The term, 'Amaram', in the Vijayanagar Empire stood for-
Consider the following statements:
1. A strong resolution was adopted declaring Congress support for the INA cause at the first Post-war Congress session.
2. An INA Relief and Enquiry Committee was formed to give money, food, and employment support to the affected.
Which of the above statement(s) is/are correct?
Choose the correct statements.
1) In 1858 Lord Canning sent forth the royal proclamation in a grand Darbar at Delhi.
2) It was then proclaimed that all treaties and engagements of East India Company with princely states would be maintained and honoured.
3) The document was called “Magnacarta of the People of India”.
Which of the following statements regarding the land revenue system under Mughal Administration is not correct?
Who among the following Governor Generals created the Covenanted Civil Service of India which later came to be known as the Indian Civil Service ?
Which of the following Vedas contains the famous Gayatri - Mantra ?
Consider statements A, B and C and choose the correct option.
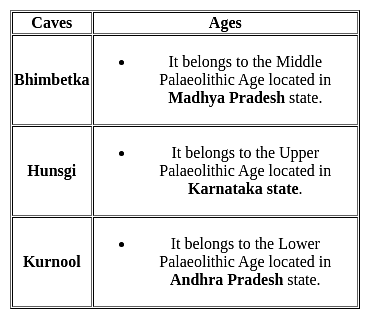
(A) The palaeolithic period extends from 2 million years ago to about 12,000 years ago.
(B) This long stretch of time is divided into the lower, middle and upper palaeolithic.
(C) This long span of time covers 99% of human history.
Among the four sites mentioned below the earliest cultural phase comes from:
Jugantar Patrika was a Bengali weekly newspaper. It served as a propagating organ for which of the following organizations?
What made Jahangir issue a farman in 1613 permitting the English to establish a factory permanently in Surat?
Arrange the following events of Jahangir's reign in the chronological order.
(i) Revolt of Mahabat Khan
(ii) Khurram was Viceroy of the Deccan
(iii) Captain Hawkins visit to his court
(iv) Sir Thomas Roe's arrival at Jahangir's court
Choose the correct answer from the following codes :
Consider the following statements related to the Revolt of 1857:
- The administrative policy of the east India Company underwent frequent changes during the long period between 1757- 1857, however, it never lost sight of its main objects which were to increase the Company’s profit.
- However, they did not focus much on the law and order in the country which ultimately caused the revolt of 1857.
Which of he statements given above is/are correct?
Which one of the following observations is not true about the Quit India Movement of 1942?