TS SET Paper 2 Mock Test - 2 (Geography) - TS TET MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - TS SET Paper 2 Mock Test - 2 (Geography)
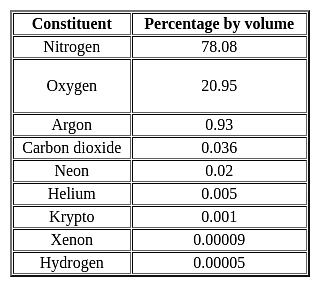
Major constituent gasses of the atmosphere are _____________.
The thickness of the Troposphere is maximum at the Equator during which of the following seasons?
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
Consider the following statements regarding Census-2011:
1. The percentage decadal growth of population during 2001-2011 has registered the sharpest decline since independence.
2. It created the National Population Register (NPR) which will build up a comprehensive identity database of usual residents of the country.
3. Census 2011 was conducted in two phases - the house listing phase and the population enumeration phase.
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
What among the following is essential for the sustained quality of life and global peace?
What is remote sensing image interpretation? Choose the correct option.
Directions: The question consists of two statements, an assertion and a reason. The student must first determine whether each statement is true. Each question below consists of an assertion and a reason.
Assertion (A): Tigers are an endangered species.
Reason(R): Tigers are being poached by humans.
A tourist in Mumbai observes high tide near Gateway of India at 7.00 AM. At what time, he should expect another high tide on the same day?
Heritage power project Sonapani mini-hydel power project is located in which state?
Identify the rightly matched pairs:
1. Selvas - Amazon tropical rainforest
2. Prairies - Grasslands of Argentina and Uruguay
3. Pampas - Grasslands of North America
Select the correct answer from the options given below.Use the map below to answer the question that follows.
{{358.PNG}}
Which of the following is the main religion of the three numbered areas on the map?
In India which age group is considered as economically productive?
Given below are two statements. One is labelled as Assertion (A) and the other is labelled as Reason (R).
Assertion (A): Growth Centers may have a population ranging from 50000 to 500000.
Reason (R): Growth Poles would generally be the capital cities of the states.
Select the correct answer from options given below:
After which one of the following tribes of India has a supercontinent of ancient geological history of the world been named?
Solifluction is a geomorphic process involving a special type of soil flow that is noticed in
A geographer is analyzing global trade routes in the era of sailing ships. Which of the following two essential elements of geography would likely form the conceptual bases of the geographer's study?
Consider the following statements regarding the distribution of pressure belts in the globe:
1. The sub-polar low belts are thermally induced and the temperature contrast between the subtropical and the polar regions gives rise to cyclonic storms here.
2. Only vertical currents are experienced in the equatorial low belt.
3. Calm conditions with feeble and variable winds are found in the subtropical high belt.
Which of the above statements is/are correct?(a) The industrial region of Mumbai-Pune flourished due to the development of cotton textile industry.
(b) The Kollam-Thiruvanathapuram industrial region has agricultural processing and market-oriented light industries.
(c) Chotanagpur industrial region is called Ruhr of India.
(d) The Gurgaon-Delhi-Meerut industrial region is famous from heavy industries.
Which of the following statements about inversion of temperature is/are correct?
1. Temperature increases with increasing altitude.
2. A long winter night with clear skies is an ideal situation.
3. It is a short term phenomenon and is common all over the globe except at the poles.
Select the correct answer using the code given below :
i. Air mass thunderstorm occur as a result of vertical displacement of air mass within an air mass.
ii. Local heat thunderstorm is a type of air mass thunderstorm
Choose the correct answer:
a) Sea level Changes are only affected by Eustatic changes.
b) Marine sediments depict about global sea level change.
c) Evidences of sedimentary deposits of various sorts depict sea level changes during the pre-quaternary stages.
d) Sea level has risen by about 10 to 16 cm in the past 100 years.
Which of the following statements is correct?