TS SET Paper 2 Mock Test - 4 (Geography) - TS TET MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - TS SET Paper 2 Mock Test - 4 (Geography)
Biosphere reserves are:
i) area comprising terrestrial, marine and coastal ecosystems.
ii) monitored by national governments.
iii) areas where threatened animals and plants are kept in their habitat.
iv) wildlife sanctuaries.
Choose the correct statements from the options given below:
In which of the following countries, Ruhr industrial region is located?
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
Given below are two statements. One is labelled as Assertion (A) and the other is labelled as Reason (R). Assertion (A): The Puranas name the region of Madagascar and Eastern Africa as Shalmali.
Reason (R) : The region of East-Africa is rich in silk-cotton trees.
Select the correct answer from options given below:
Consider the following pairs :
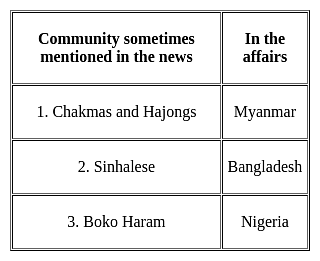
Which of the pairs given above is/are correctly matched?
Critics of the Malthusian Theory argue that advancements in which field have mitigated the challenges predicted by Malthus?
What is the primary assertion of the Malthusian Theory of Population?
Which of the following are true about the paradigm shift in Geography?
(A) It is a usual and accepted way of thinking about something that changes completely
(B) New paradigms brought adverse degradation of human efforts and morals
(C) Paradigm shift majorly focuses on the historical perspective
(D) Khun introduced the stages of development of a new paradigm
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:The earliest arrivals in India are believed to be Negritos. At which one of the following places are they mainly found now?
Biosphere reserves are:
i) area comprising terrestrial, marine and coastal ecosystems.
ii) monitored by national governments.
iii) areas where threatened animals and plants are kept in their habitat.
iv) wildlife sanctuaries.
Choose the correct statements from the options given below:
a) The land in the rural urban fringe is cheaper than the land in the central city.
b) Urbanization at a rapid rate takes place in the rural urban fringe as compared to the city.
c) The traffic in the rural urban fringe is high and dense in comparison to the central city.
d) There is ample space for development in the rural urban fringe.
Code:
Which of the following is/are the ideal conditions for temperature inversion to occur?
A. Cloudy skies
B. Calm and stable air
C. Long summer days
Select the correct answer using the codes given below:
a) Troposphere is also known as the convective region.
b) The Stratosphere is referred to as the point from where the decrease of temperature stops.
c) The most destructive gases that lower the effectiveness of the ozone are known as CFCs.
d) The three layers that fall under the Heterosphere are mesosphere, ionosphere, and exosphere.
Which of the following statements are correct?
Which of the following pairs of "Ocean- Maximum Deepest Point" is correct?
1. Pacific Ocean - Mariana Trench
2. Indian Ocean - Sunda Trench
Process of chemical weathering is represented by-
Which of the following statements is correct regarding the unevenness of population distribution?
I. The distribution of population can be analysed on the basis of continents and countries.
II. South Asia is one of the major concentrations which accounts for about half of the world's population.
Area between two breaker zones is called

Choose the correct option:

















