MH SET Paper 2 Mock Test - 3 (Geography) - MAHA TET MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - MH SET Paper 2 Mock Test - 3 (Geography)
Which factor of globalization has largest share in spreading out production of services recent days?
Which of the following theories mention that the political and economic relationships between countries and regions of the world control and limit the economic development possibilities of the poor areas?
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
Which of the following statement best characterizes New International Division of Labour?
What are true in relation to jet stream?
(i) Jet stream blow across Asian Continent at latitudes North of Himalayas parallel to Tibetan highlands.
(ii) Tibetan highland divides jet stream into North and South branches.
(iii) The northern branch of jet stream plays important role in winter weather in India.
Which among the following state of India is best known for Saffron Cultivation?
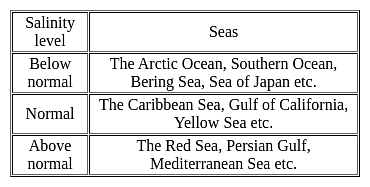
Which among the following factors influence the salinity of ocean water?
1. Precipitation
2. Evaporation
3. Ocean Currents
4. Temperature
Select the correct code from the options given below:At what plate boundary setting is the ocean floor deepest?
What is the depth range of shallow seawater over the continental shelf?
Given below are two statements. One is labelled as Assertion (A) and the other is labelled as Reason (R).
Assertion (A): La Nina is the phenomenon that leads to droughts in India.
Reason (R): The Humboldt Current decreases temperature of water by 5-60 C
Select the correct answer from options given below:
Use the information below to answer the question that follows.
• fluctuating water table
• large herbivores, carnivores, and scavengers
• tall, coarse grass
• low-growing, drought-resistant tree species
The information presented best describes major features of which of the following grassland biomes?
Consider the following statements about Equator and choose the correct option:
(A) The equator is a real line running on the globe, which divides it into two equal parts.
(B) The equator is the longest latitude.
(C) The equator represents the 180° latitude.
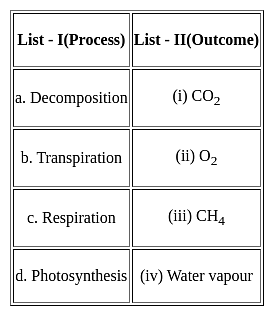
Match the List - I with List - II and select the correct answer from the code given below:
With reference to Dispersed Settlements, consider the following:
1. These settlements are fragmented into several units physically separated from each other.
2. This segmentation of a large village is often motivated by social and ethnic factors.
3. Uttranchal, Himachal Pradesh and Kerala have this type of settlement.
Which of the above statement is/are not correct?
Choose the correct option regarding 'Immigration'.
(A) People may move within a country or between countries
(B) People who leave a country
(C) When a person enters a new country.
a) Conduction is a slow process of heat transfer in terms of warming of the atmosphere.
b) The latent heat of evaporation and condensation are not quite responsible for the heating and cooling of the atmosphere.
c) Temperature over snow covered regions or grounds remain low even during daylight hours.
d) Loo is a typical example of the advection process.
Which of the following statements are correct?
Given below are two statements, one is labeled as Assertion (A) and the other as Reason (R).
Assertion (A): Chile is the leading producer of copper in the world.
Reason (R): Andes Region of North Chile is enriched with the largest deposits of Porphyry copper.
Select the correct answer from the code given below :
Consider the following statements regarding temperature inversion:
1. Long winter nights with clear skies and still air is an ideal condition.
2. It is common throughout the year in the polar areas.
3. In hills and mountains, inversion is the result of air drainage.
Which of the above statements is/are correct?Assertion(A)- Fogs, urban smog’s, frost generally affect the economy.
Reason(R)- Inversion of temperature is known as the negative lapse rate.
Choose the correct options.
Given below are two statements- one is labelled as Assertion (A) and the other is labelled as Reason (R):
Assertion(A)- The other name for doldrums is subtropical high-pressure belt.
Reason(R)- Frequent calm conditions exist in the equatorial low-pressure belt.
Choose the correct option: