MH SET Paper 2 Mock Test - 4 (History) - MAHA TET MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - MH SET Paper 2 Mock Test - 4 (History)
Who was the Kotwal of Delhi before the Revolt of 1857?
Which of the following Gupta kings had issued a gold coin which depicts a rhinoceros?
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
Who is the first Armament Chief of Marathas?
The role of the British Government in the genesis of our Constitution was openly opposed by ______.
Analyze the significance of the Harappan city plans in light of contemporary archaeological theories.
Compare and contrast the prevailing theories regarding the Harappan decline, analyzing the strengths and weaknesses of each.
Who is the author of the book 'Understanding Harappa'?
The principal sources from which the Government of India act 1935 drew its material were:
1). Simon commission report
2). Nehru report
3). Discussions of all three round table conferences
4). Lothian report
5). Joint select committee report
From which among the following district Coins of Kushana ruler, Vima Kadphises have been found?
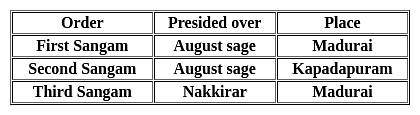
Where of the following the second Sangam was organized?
Consider the following statements.
1) Indian agriculture during the 18th century was technically progressing.
2) However, the peasants suffered from shortage of lands some of the times.
Choose the correct statements.
The role of arches in an arcuate architecture was to
A. beautify the superstructure
B. give shape to the superstructure
C. carry the weight of the superstructure
Choose the correct option.
Among the four sites mentioned below the earliest cultural phase comes from:
Jugantar Patrika was a Bengali weekly newspaper. It served as a propagating organ for which of the following organizations?
Which of the following statements relating to Government of India act 1935 are correct?
1). It introduced provincial autonomy
2). It proposed bicameral Legislatures at federal level
3). It proposed establishment of federal court
Which is the correct chronology of following events occurring during the reign of Akbar?
a. Declaration of Mazhar (Infallibility decree)
b. Abolition of zazia
c. Declaration of Tohid-i-Ilahi
d. Construction of Ibadatkhana
Choose the correct combination given below:
The term, 'Amaram', in the Vijayanagar Empire stood for-
The Journal Bahishkrit Bharat was started by
Who among the following Governor Generals created the Covenanted Civil Service of India which later came to be known as the Indian Civil Service ?
Choose the correct pair, with reference to the Jaina Council.
- First Council:- resulted in the compilation of 14 Purvas.
- Second Council:- resulted in final compilation of 12 Angas and 12 Upangas.