MH SET Paper 2 Mock Test - 5 (History) - MAHA TET MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - MH SET Paper 2 Mock Test - 5 (History)
Which of the following is/are the central point in Ashoka’s Dhamma?
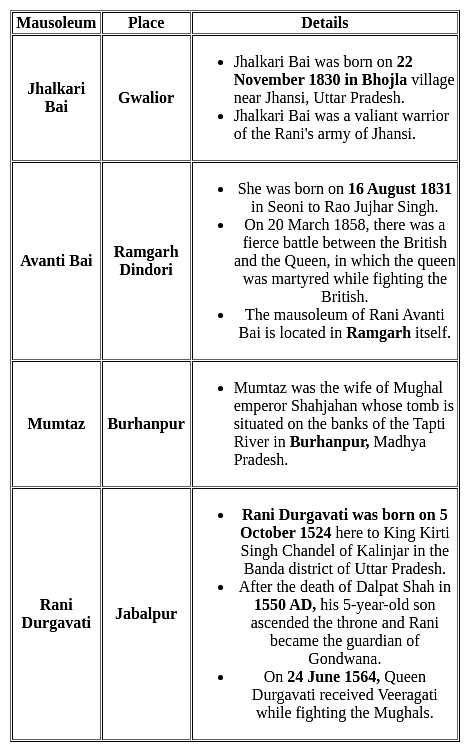
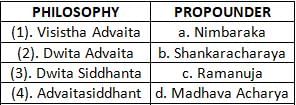
Which of the following is the incorrect match?
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
Consider the following statements regarding the Rig Vedic age:
1. During the Rig Vedic age, the king was elected by a tribal assembly called Samiti.
2. A standing army under the military commander was maintained by the king during the period.
Which of the statements given above are correct?
Consider the following statements regarding Humayun:
1. Shershah Suri defeated Humayun in the Battle of Bilgram
2. He defeated Afghans and set up the Mughal throne.
3. He was a highly learned person.
Which of the above statements is/are correct?On which among the following dates, the Gandhi-Irwin Pact was signed?
Who is the author of the book "The Story of the Integration of the Indian States"?
Who was the author of the Gwalior Prashasti of Mihira Bhoja?
Read the statements (A) and (R) and choose the correct option.
Assertion (A) - During Aurangzeb’s reign, there was a decrease in the number of Mansabdars.
Reason (R) - Their was an increase in the number of jagirs in his reign.
The sculpture of bronze idol of Natraja belonged to which kingdom?
Which of the following is true regarding Government of India Act 1935?
1. The Act never came in force; as princely states did accept the provision of the act.
2. The act abrogated the doctrine of Paramountcy of British over the Princely states in India.
Select the correct answer using the code given below: -
The ‘Dastaks’, the misuse of which was a source of constant friction between the nawab and the East Indian Company, were actually:
Which of the following ancient Tamil Kingdoms came to be known from Sangam Literature?
Consider the following events in the history of India:
1. Rise of Pratiharas under King Bhoja.
2. Establishment of Pallava power under Narshimhavarman I.
3. Establishment of Rashtrakutas power by Dantidurga.
4. Rise of Pala dynasty under Dharmapala.
What is the correct chronological order of the above events, starting from the earliest time?
Who was the first Muslim to invade India in 712 AD?
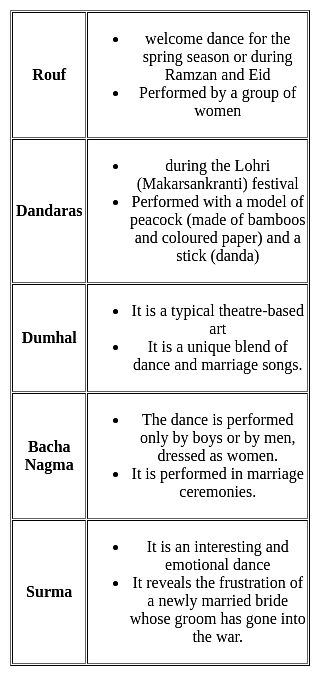
Which of the following dances have influence of Persian Literature and Sufi Philosophy?
Consider the following statements.
1. The term Saracenic has been derived from Roman people that lived in Arabia.
2. It was a synthesis of Victorian Gothic architecture with Mughal architecture.
3. The Pietra dura technique developed in French Gothic architecture.
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
According to Historical Materialism, the primary driver of social change is
Below given are two statements, one is labelled as Assertion (A) and the other as Reason (R)
Assertion(A): Big buildings were the distinguishing feature of both Harappa and Mohen-jo-daro.
Reason(R): Their monuments symbolized the ability of the ruling class to mobilize labour and collect tax.
Select the correct answer using the codes given below :