MH SET Paper 2 Mock Test - 10 (Commerce) - MAHA TET MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - MH SET Paper 2 Mock Test - 10 (Commerce)
The market demand curve for a perfectly competitive market is QD = 12 - 2P. The market supply curve is QS = 3 + P. The market will be in equalibrium if :
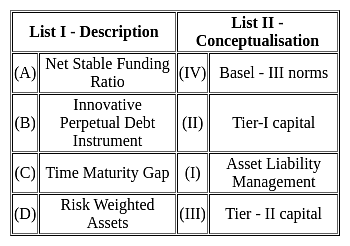
Match List I with List II:
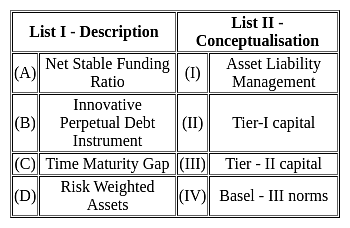
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
Which of the following tests are not recommended for the top-level positions?
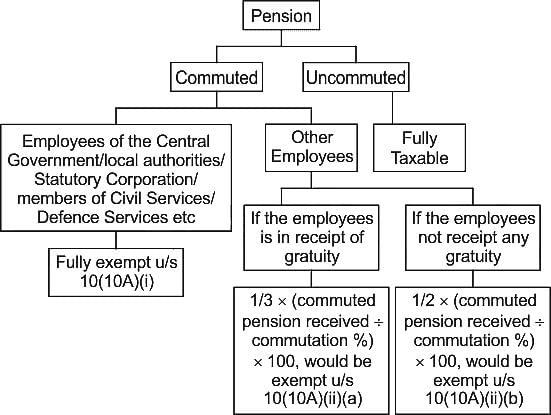
The uncommitted pension received by a Government servant is _______.
Which of the following are true about conditions according to the Sale of Goods Act?
a) Title
b) Description
c) Quite possession
d) Encumbrances
Choose the correct answer from the following options
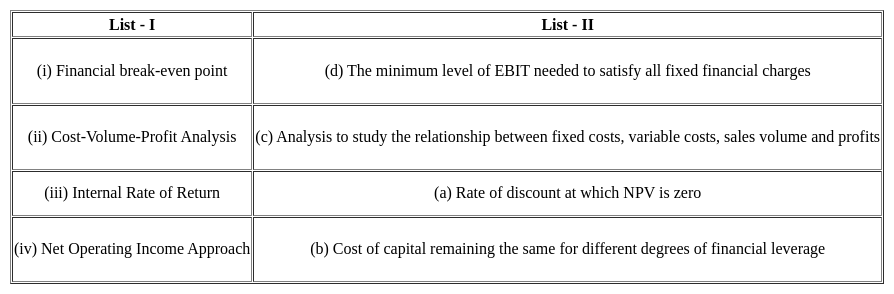
Match the given lists and select the correct code for the answer:
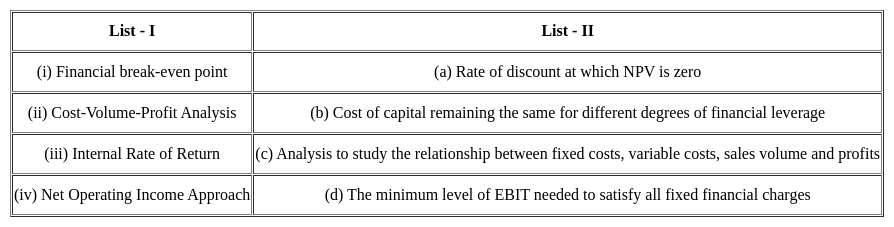
Match the following statements with their authors.

Given the production function Q = 10 L0.8 K0.2, the marginal product of labour (MPL) and capital (MPk) respectively are given by
A. MPL = 8(K/L)0.2
B. MPL = 8(L/K)0.2
C. MPK = 2(L/K)0.8
D. MPK = 2(K/L)0.2
Choose the correct answer
Which of the following is not an example of probability sampling?
Which of the following is correct with respect to GST in India?
I. GST The Act was passed by the Parliament in 2016.
II. GST The law came into force from July 2016.
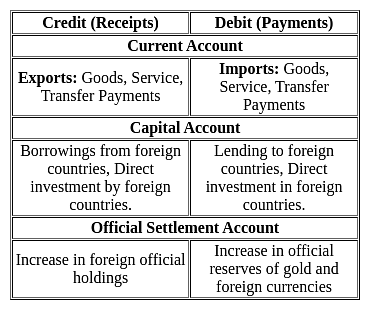
In the balance of payment account, the transfer payments are included in which one of the following?
Assertion: 'Targeting' solely focuses on selecting the largest market segment.
Reason: A target market is chosen based on its attractiveness, size, growth potential, profitability, competitive positioning, and resonance with the organization's objectives.
The primary responsibility of the 'Segmentation' stage of STP is
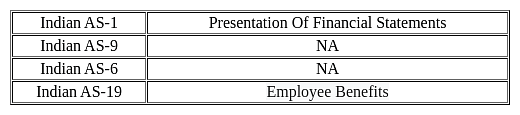
Employee benefits provided by the employer during an accounting period are recognized as per ____ .
Arrange the following initiatives taken by the Government of India to tackle the Non-performing assets in their ascending order of chronology :
(A) Corporate Debt Restructuring
(B) Compromise Settlement
(C) The Debt Recovery Tribunals (DRTs)
(D) Credit Information Bureau
(E) SARFAFSI Act
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
Direction: The following are the two statements regarding elasticity of demand and its measurement.
Statement I: On every point on the straight line demand curve, the point elasticities are all equal
Statement II: On every point on the rectangular hyperbola shaped demand curve, the point elasticities are not equal
Select the correct option for those below:
Which of the following economies accrue all the firm in an industry?
A purchases budget is used instead of a production budget by: