Kerala SET Paper 2 Mock Test - 3 (Commerce) - KTET MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - Kerala SET Paper 2 Mock Test - 3 (Commerce)
A _________ letter of credit is a type of financial guarantee, known as a letter of credit.
Modern marketing concepts emphasize on:
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
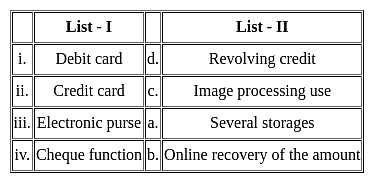
Match the given lists and select the correct code for the answer.

Direction: Read the statements carefully and choose the correct answer.
Statements: (I): The greater is the likely level of EBIT than the financial indifference point, the stronger is the case for issuing levered financial plans to maximise the EPS.
Statements(II): The financial break-even point is found at that level of EBIT where the EPS is zero for a particular financial plan.
Financial management is concerned with the:
Which is the Act which provides legal framework for e-Governance in India:
In the first stage of most grievances redressal procedure, the grievance is verbally conveyed by the employee to the _______.
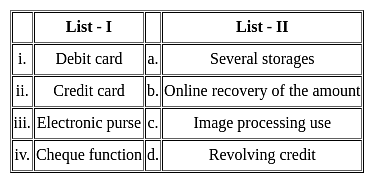
Match the given lists and select the correct code for the answer.
Breach of contract can be of ____________ breach.
Deductions under Chapter VI-A of the Income Tax Act, 1961 are allowed after excluding which of the following incomes from the gross total income?
(i) Income from house property
(ii) Long-term capital gains
(iii) Short-term capital gains under Section 111A
(iv) Income from lotteries
Which of the following is 'true' regarding the Prudence Principle of Accounting?
Reserve Bank of India controls the activities of which of the following banks in India:
(i) Commercial Banks
(ii) Cooperative Banks
(iii) Foreign Banks
(iv) Rural Banks
Codes:
Who among the following provide financial assistance to start-ups in the early stage of a company?
I. Corporate investors
II. Venture capitalists
III. Stage governments
Which two of the following statements are true?
(a) The sum of the deviations from mean (ignoring algebraic signs) is greater than the sum of the deviations from median (ignoring algebraic signs).
(b) Standard deviation is independent of change of origin and change of scale.
(c) In a symmetrical distribution, mean deviation equals 4/5 of standard deviation.
(d) In a symmetrical and bell shaped distribution quartile deviation is 1/3 of standard deviation.
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
Who monitors the compliance of SEBI regulations by the mutual fund?
Gratuity received by an employee covered by the Payment of Gratuity Act, 1972 is exempt to the maximum of ______ for the Assessment year 2021-22.
Which of the given combinations of the following factors influence the working capital requirement?
I. Market conditions
II. Production policy
III. Firm's goodwill
IV. Supply conditions
When goods in the domestic market are sold at a high price and in the foreign market at a low price, it is a situation of:
For-profit maximization of a firm,
(i) MC = MR
(ii) Marginal cost curve must cut the average cost curve from below.
Choose the correct option.