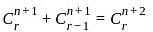Indian Army Agniveer Technical Mock Test - 2 - Indian Army Agniveer MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - Indian Army Agniveer Technical Mock Test - 2
Mahatma Gandhi returned to India in the year 1915, from which country among the following?
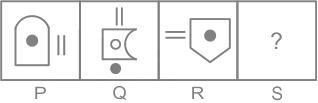
In each of the following Questions, figures P and Q are related to each other in a certain way. Select a figure from the Answer figures A, B, C and D which has the same relationship with figure R.
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
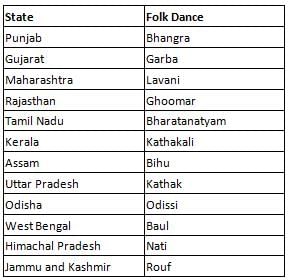
The folk dance Hojagiri originated and is associated with which part of India?
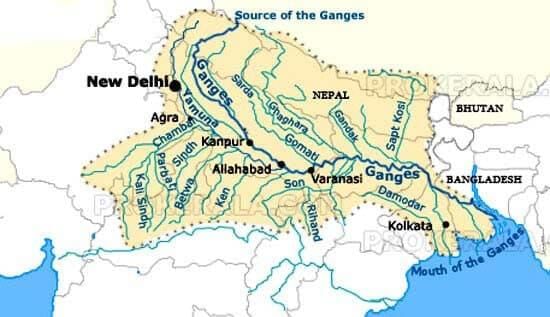
Which among the following is the source of Ganga river?
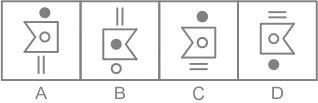
Select the figure from the options that can replace the question mark (?) and complete the pattern.
Arrange the following words in the logical and meaningful order.
1. Publishing
2. Information
3. Printing
4. Verifying
5. Editing
If cosec θ = 1(7/22), find the value of cot2 θ.
An unbiased dice is thrown. What is the probability of getting a multiple of 3?
Let f ∶ R → R be the function defined by f(x) = 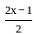 and g ∶ Q → R be another function defined by g(x) = x + 2. Then (g o f)
and g ∶ Q → R be another function defined by g(x) = x + 2. Then (g o f) 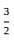 is
is
If 2 dice are thrown what is the probability of getting the same digits on both dice?
C(n, r) +2C(n, r - 1) + C(n, r - 2) = ?
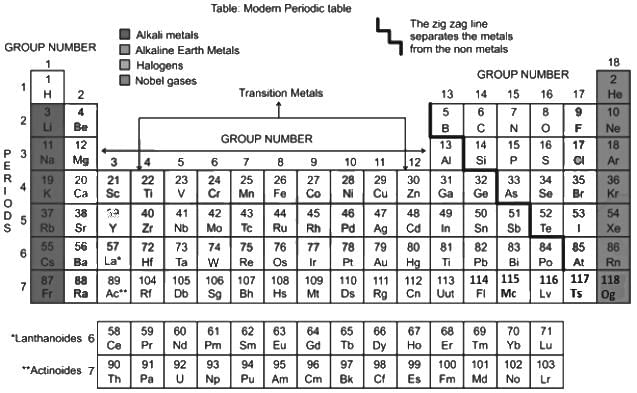
Which of the following elements does NOT belong to group 1 of the modern periodic table?


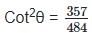
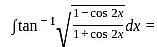
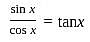
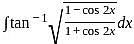
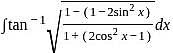
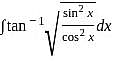
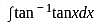
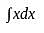
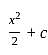
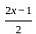 and g(x) = x + 2.
and g(x) = x + 2.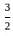 )=
)=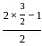 =
= 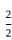 = 1
= 1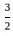
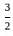 ))
))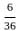
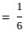
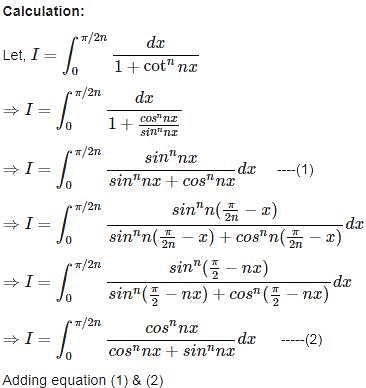
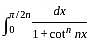 is equal to
is equal to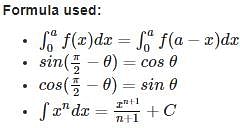
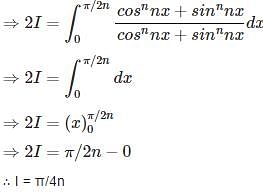
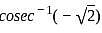 ?
?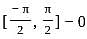
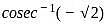
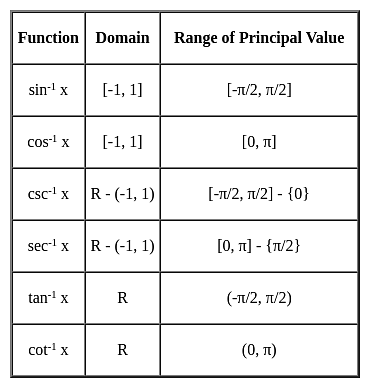
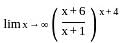 ?
?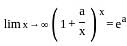
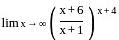
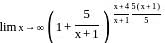

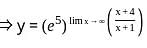
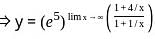
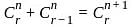 ........(equation 1)
........(equation 1)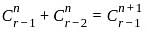 .......(equation 2)
.......(equation 2)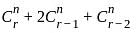
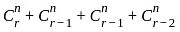 (Using equation 1 and 2)
(Using equation 1 and 2)