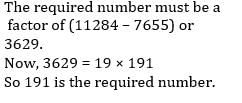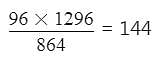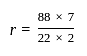MPPGCL JE Electronics Mock Test - 1 - Electronics and Communication Engineering (ECE) MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - MPPGCL JE Electronics Mock Test - 1
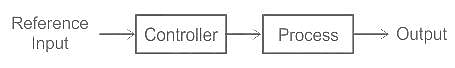
Which is the classification of drive according to dynamics and transients?
What will be the decimal number equivalent to the binary number (11001)2?
The energy per bit Eb of ASK, PSK and FSK follow:
If x[n] ↔ X(z), the z-transform of x[-n] will be:
What will be the time response expression for a standard first order system having unit step function  as the input
as the input
What is the maximum data rate that can be transmitted using a QPSK modulation with a roll-off factor of 0.2 for a 36 MHz transponder?
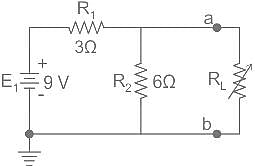
What is Thevenin's equivalent resistance for circuit shown in the given figure?
Schottky diodes drop about 0.3 V when conducting. This diode is connected in series with a resistor of 1 kΩ and forward biased with a battery of 1 V. Calculate the diode current.
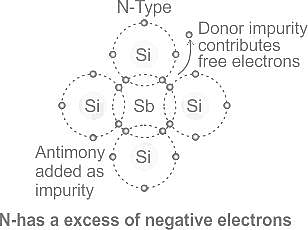
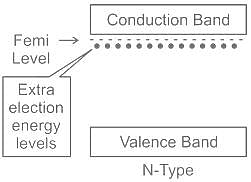
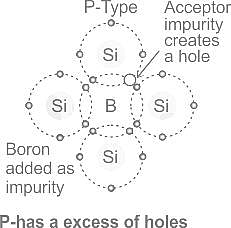
N-type materials are the type of materials formed by adding group _____ elements to the semiconductor crystals.
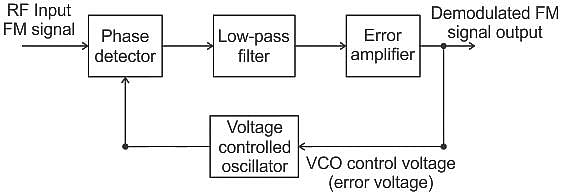
A phase locked loop can be used to demodulate
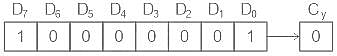
If contents of the accumulator in 8085 are 81 H and carry flag is '0', find accumulator contents after executing the instruction RRC?
Assuming zero initial conditions, the response y(t) of the system given below to a unit step input 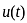 is ____
is ____
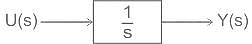
The question consists of two statements, one labeled as ‘Statement (I)’ and the other labeled as ‘Statement (II)’. You are to examine these two statements carefully and select the answers to these items using the codes given below:
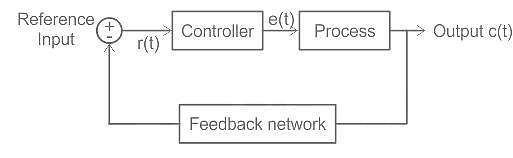
Statement (I): The control system which operates on a time basis is an open-loop system
Statement (II): A field control d.c. motor is an example of an open-loop system.
Systems in which the output has no effect on the control action are called:
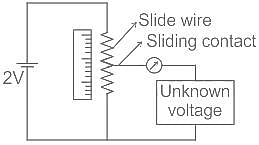
Which type of measurement cannot be done by potentiometer?
Which of the following provide deflecting force for voltmeters only?
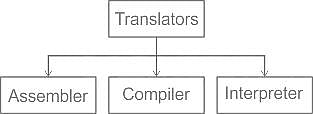
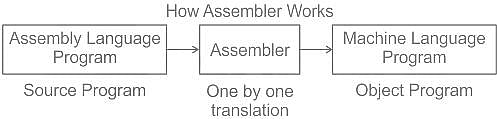
________ converts assembly language into machine language
Which of the following layers in the ISO/OSI network model provides Error and Flow control at respective transmission levels?
'Calf' is related to 'Cow' in the same way as 'Kitten' is related to:
The numbers 11284 and 7655, when divided by a certain number of three digits, leave the same remainder. Find that number of three digits.
The H.C.F. of two numbers is 96 and their L.C.M. is 1296. If one of the number is 864, the other is
Directions to Solve
In each of the following questions find out the alternative which will replace the question mark.
Question -
Peacock : India :: Bear : ?


 for holes and
for holes and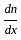 for electrons.
for electrons.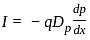 -----(1)
-----(1)
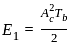 and energy of bit 0,
and energy of bit 0, 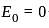
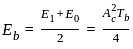
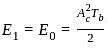
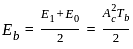
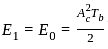

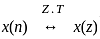 , then the time-reversal property states that:
, then the time-reversal property states that: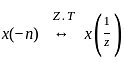



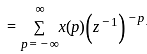
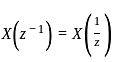

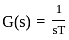
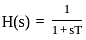 (assume unity negative feedback)
(assume unity negative feedback)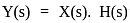
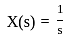
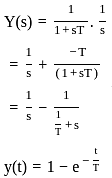
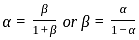

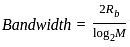
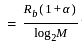


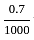


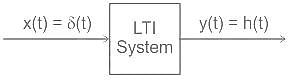
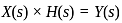
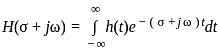

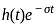
 . i.e,
. i.e,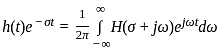
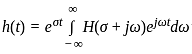
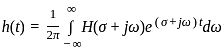

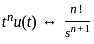 ⋯ (i)
⋯ (i)