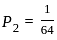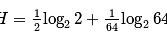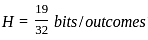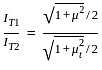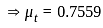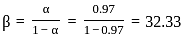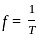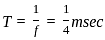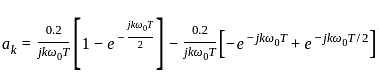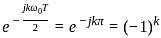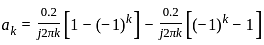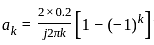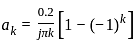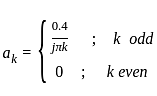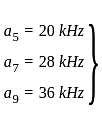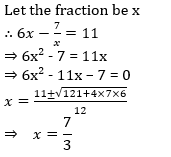MPPGCL JE Electronics Mock Test - 2 - Electronics and Communication Engineering (ECE) MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - MPPGCL JE Electronics Mock Test - 2
Which among the given statement is/are CORRECT?
(a) Avalanche breakdown voltage increases with temperature
(b) Zener breakdown voltage decreases with temperature
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
A bandpass signal occupies the bandwidth 390 kHz to 410 kHz. What minimum sampling frequency would you use from the options given below, so as to avoid aliasing?
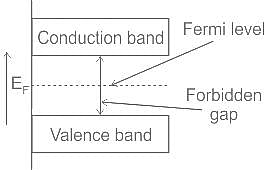
The valence band and conduction band for a semiconductor are:
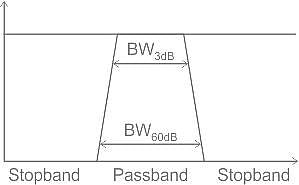
If a filter has 60 dB bandwidth of 10 kHz and 3 dB bandwidth of 4 kHz, the shape factor will be _______.
A second order control system is NOT required to satisfy the following specification:
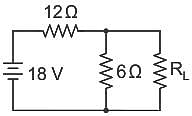
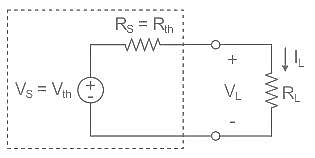
In the circuit shown above, the maximum power absorbed by the load resistance RL is
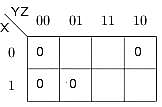
A boolean function is given as F(x, y, z) = ∑(1, 3, 6, 7). What is its equivalent canonical form?
When a diode is given an external voltage that increases its potential barrier and restricts the flow of current, then it is called?
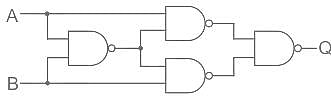
Which of the following will be the value of Q
An event has two possible outcomes with probability P1 = 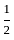 and P1 =
and P1 = 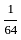 . The rate of information with 16 outcomes per second is -
. The rate of information with 16 outcomes per second is -
In the following, pick out the linear systems
(i) d2y(t)/dt2 + 9a1dy(t)/dt + a2y(t) = u(t)
(ii) y(t)dy(t)/dt + a1y(t) = a2 u(t)
(iii) 2d2y(t)/dt2 + tdy(t)/dt + t2y(t) = 5
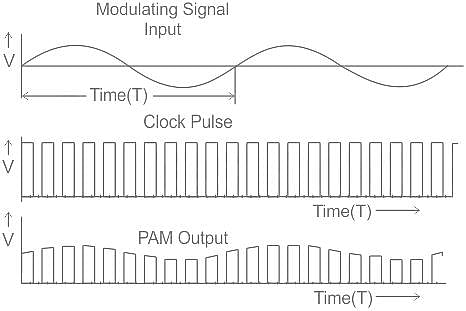
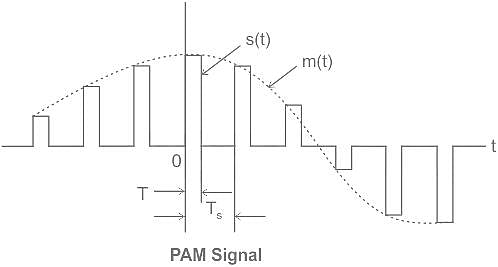
Determine whether the following statements are true or false with respect to Pulse Amplitude Modulation.
a) Instantaneous sampling of the message signal m(t) every Ts second, where the sampling rate fs = 1/Ts is chosen in accordance of the sampling theorem.
b) Lengthening the duration of each sample obtained to some constant value T.
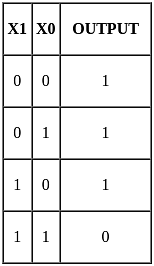
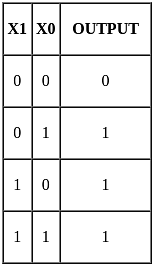
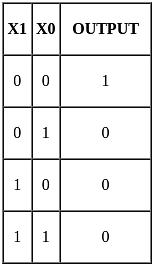
Which of the following gates has output LOW if and only if all the inputs are HIGH?
The antenna current of an AM broadcast transmitter, modulated to a depth of 40% by an audio sine wave is 11A. It increases to 12A as a result of simultaneous modulation by another audio sine wave. What is the modulation index due to the second wave?
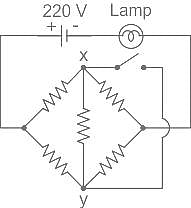
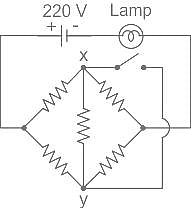
For the circuit shown, if the resistance of each resistor is 100 ohm, the potential at X is ________.
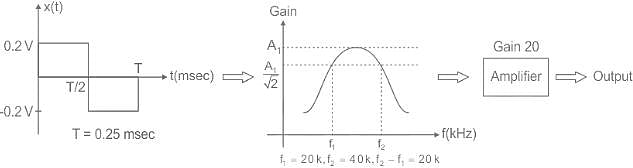
A 4 kHz square wave of duty cycle 50% and p-p (0.2V to +0.2V) is applied as input to 20 kHz narrow bandpass filter which is followed by an amplifier of voltage gain 20. Find out the frequency components present in the output. Given that cut off frequencies of a narrow bandpass filter is 20 kHz and 40 kHz.
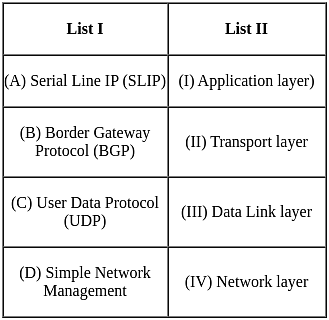
Match List I with List II
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
The name of the famous mathematician who is credited with discovering the total value of the very first 100 natural numbers is
6 times of a fraction is greater than 7 times of its reciprocal by 11. What is the fraction?


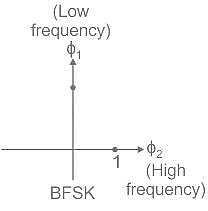


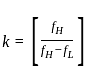 (Where [ .] denotes the floor value)
(Where [ .] denotes the floor value)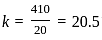
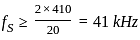
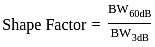 ---(1)
---(1)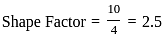
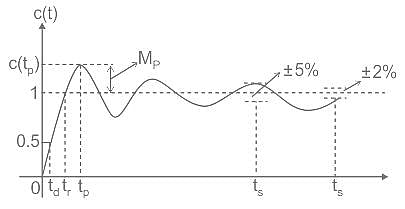
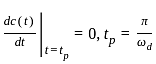

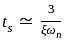 for a 5% tolerance band.
for a 5% tolerance band.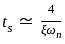 for 2% tolerance band
for 2% tolerance band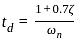
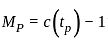

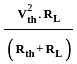

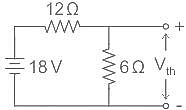
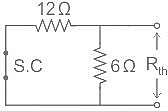

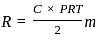
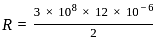
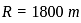

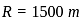

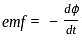 ----(1)
----(1)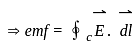
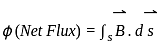
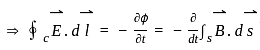
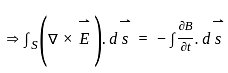
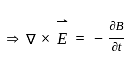
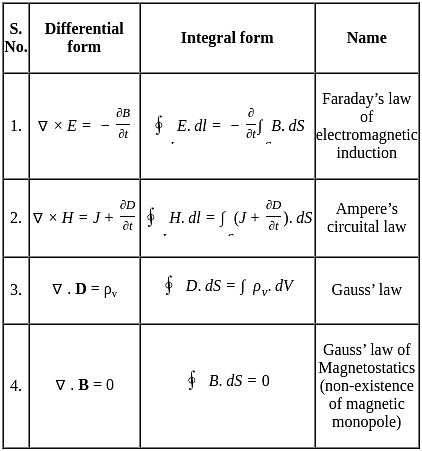
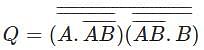
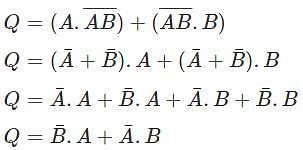
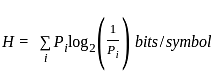
 , and
, and