MPPGCL JE Electronics Mock Test - 6 - Electronics and Communication Engineering (ECE) MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - MPPGCL JE Electronics Mock Test - 6
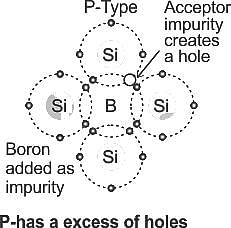
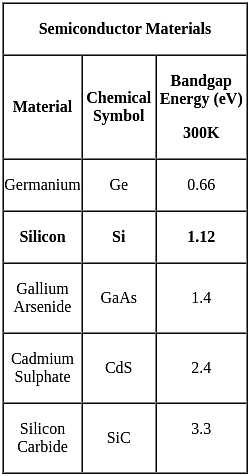
N-type materials are the type of materials formed by adding group _____ elements to the semiconductor crystals.
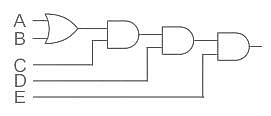
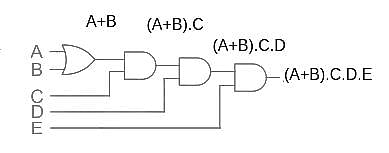
Which of the following boolean expression for the logic circuit (shown in this picture) is correct?


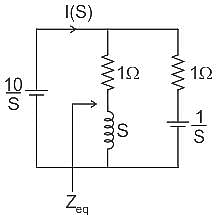
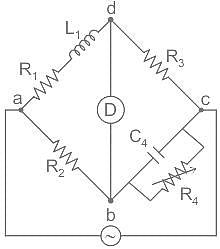
The value of the current i(t) in amperes in the above circuit is
For the Zener diode network shown in figure, determine the value of VL?

Which of the following is not a transmission type of IPv6?
A 4-bit XS-3 parallel adder needs_____ 4-bit parallel adder IC 74LS83s.
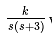 . The value of 'k' that yields a damping ratio of 0.5 for the closed loop system is -
. The value of 'k' that yields a damping ratio of 0.5 for the closed loop system is -
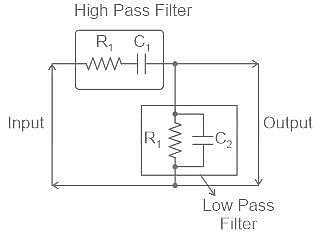
Which of the following bridges is also used in an oscillator?
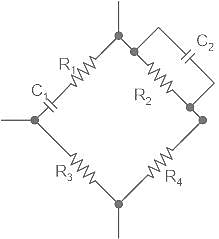
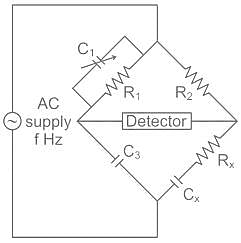
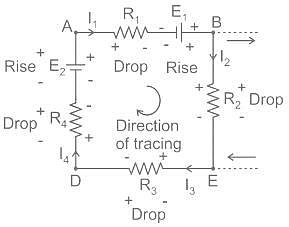
Which of the following statement is wrong with respect to the given network ?

Find the channel capacity of the noiseless discrete channel, with n symbols; x1, x2, x3,…, xn.
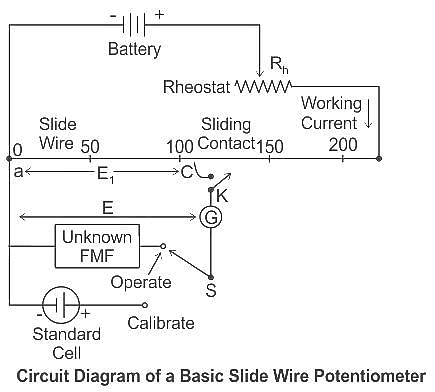
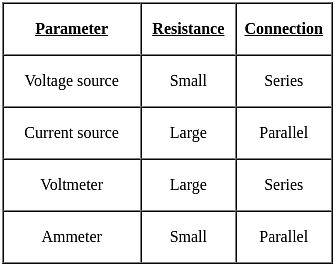
A galvanometer can be converted into a voltmeter by:
In this questions, a number series is given with one term missing. Choose the correct alternative that will continue the same pattern and fill in the black spaces.
Q. 34, 18, 10, 6, 4, (___)
Directions: A sentence is given here with a blank and you need to fill the blank choosing the word/words given below. If all the words given can fill the blank appropriately, choose ‘All are correct’ as your answer.
The troubled crypto firm Block-Fi has filed for bankruptcy in the US, as the dramatic collapse of FTX continues to _______________ across the industry.
I. Reverberate
II. Echo
III. Resonate
Directions to Solve
In each of the following questions find out the alternative which will replace the question mark.
Question -
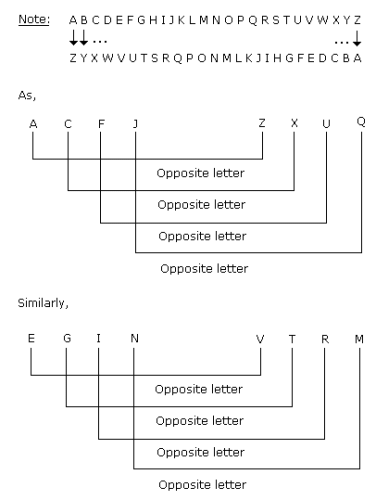
ACFJ : ZXUQ :: EGIN : ?
Directions: In the question below, three statements are given with a phrase or an idiom highlighted as underline. They might be contextually or grammatically incorrect. Select the answer choice that states the combination of statements in which the idiom or the phrase has been correctly used.
I. She felt like the belle of the ball as she danced the night away with her beau.
II. The linebacker made a beeline for the quarterback when he saw an opening.
III. Many children broke one’s neck how technology works.
Which one of the following provisions fails to ensure fair and equal chance to compete to candidates and political parties?
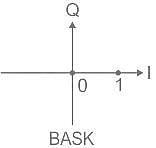
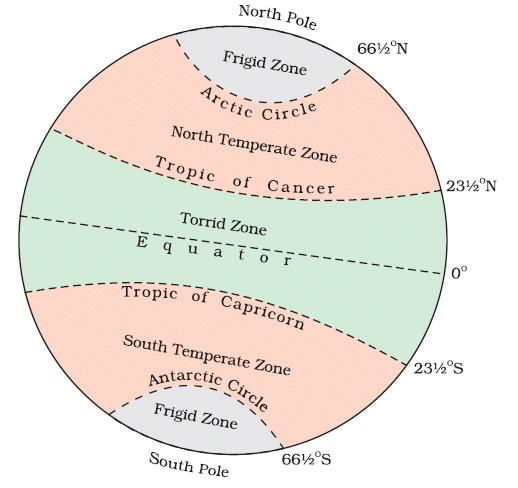
Study the given Picture carefully and answer the question that follows:
This picture is related to which of the following.

Why does the Torrid Zone receive maximum amount of heat?
Directions: Read the given information carefully and answer the questions given beside:
A certain number of people are sitting in a row watching F1 racing. All of them are facing towards the south direction. The distance between any two adjacent persons is the same.
The number of people sitting between A and C is the same as the number of people sitting between X and C. At most 25 people are sitting in a row. X is an immediate neighbour of D, who sits on one of the ends. Two people are sitting between A and Z. The number of people sitting between D and C is the same as the number of people sitting between C and Y. C sits fourth to the right of Z. The number of people sitting to the right of A is the same as the number of people sitting to the left of Z.
Q. Who among the following sits near A?
Directions: In each of the following questions, a sentence has been given in Active (or Passive) Voice. Out of the four alternatives suggested, select the one that best expresses the same sentence in Passive/ Active Voice.
You should not offer meat to vegetarians.


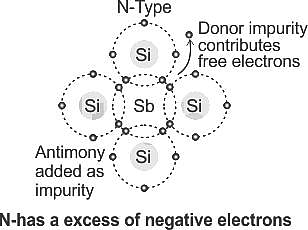
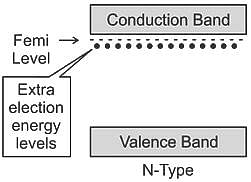



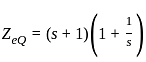


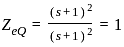
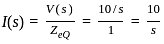
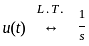


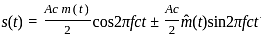

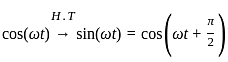
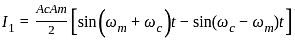
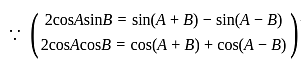

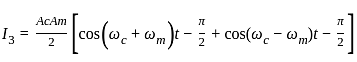
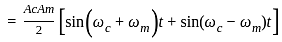
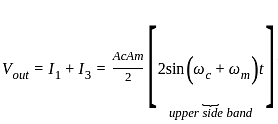

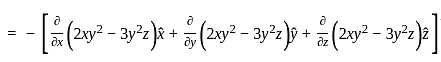
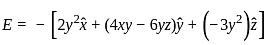



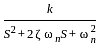 , where
, where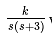
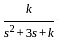
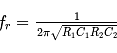
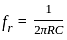

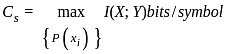

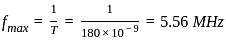


 Hence, Case 1 is the final arrangement.
Hence, Case 1 is the final arrangement.














