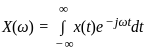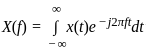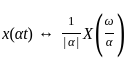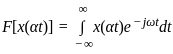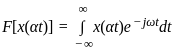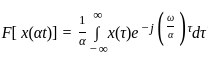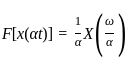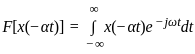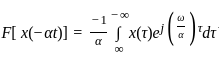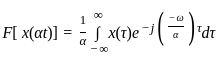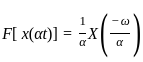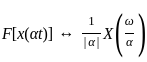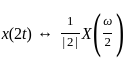MPPGCL JE Electronics Mock Test - 9 - Electronics and Communication Engineering (ECE) MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - MPPGCL JE Electronics Mock Test - 9
Which of the following statements is correct about pure resistive AC circuit?
In data communication, jitter refers to ___________
If f(E) is Fermi dirac distribution function, then 1 – f(E) is the probability:
(Where Ef is Fermi level)
A phase modulated signal can be obtained from frequency modulator by passing the modulating signal through a
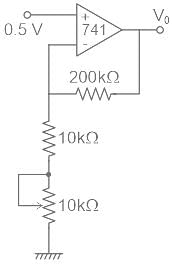
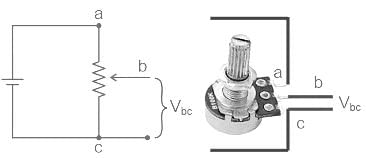
What range of output voltage is developed in the circuit shown in figure?
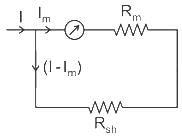
A galvanometer has an internal resistance of 100 ohm and a shunt resistance of 20 ohm. Find the multiplying factor.
Considering initial value of storage elements as 1, how does the phase of carrier vary for message m(n) = { 1, 0, 1, 1, 0, 1 …} in case of DPSK ?
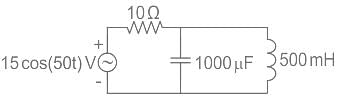
The above circuit can be represented in the frequency domain as:
The minterm function f(A, B, C, D) = ∑(1, 3, 4, 6, 9, 11, 12, 14) is ________.
The unit step response of a closed loop control system is given by c (t) = te-t. The transfer function of the system is
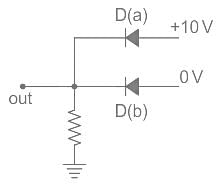
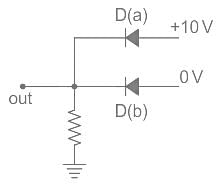
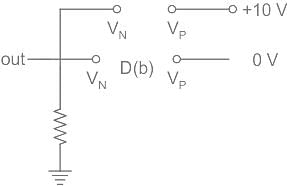
What will be the biasing of D(a) and D(b) in the given circuit?
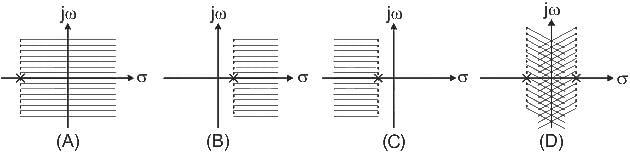
For which of the following ROCs, Fourier transforms is not defined?
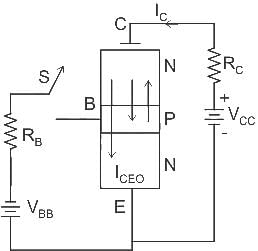
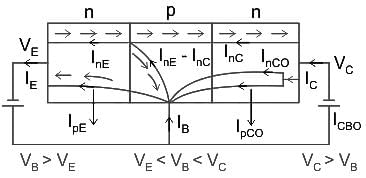
The leakage current in an NPN transistor is due to the flow of:
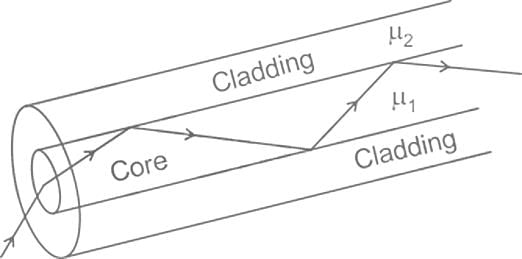
Optical fibre works on the phenomenon of _______
Output data ratio of a 8-bit PCM-TDM system sampling 24 voice channels, comparing these using μ-law at the rate of 8 kHz with a 1 frame alignment word, is:
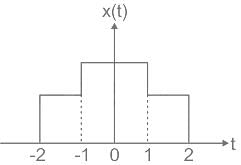
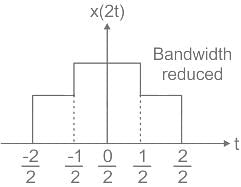
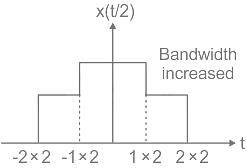
Consider a signal v(t) with Fourier transform V(f). If V '(f) represents the Fourier transform of v(2t), what is the relation between V '(f) to V(f)
It is easier
P :to venture into space
Q :for men
R :beneath their feet
S :than to explore
The Proper sequence should be:
In the following question, assuming the given statements to be true, find which of the conclusion among given conclusions is/are definitely true and then give your answer accordingly.
Statement: P < Q < R < S = T
Conclusion:
I. Q < T
II. P > S
III. R = T
Directions: In each of the following questions, a sentence has been given in Active (or Passive) Voice. Out of the four alternatives suggested, select the one that best expresses the same sentence in Passive/ Active Voice.
Shut the door.
Direction: In the following question, the sentences have been given in Active/ Passive Voice. From the given alternatives, choose the one that best expresses the given sentence in Passive/ Active Voice.
She took the dog for a walk.
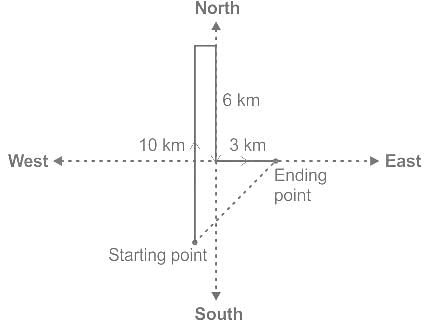
Mr. X walks 10 km towards the North. From there it is 6 km towards south then moves 3 km to the east. In which direction is he now standing from his starting point?
Directions to Solve
Each of the following questions has a group. Find out which one of the given alternatives will be another member of the group or of that class.
Question -
Pathology, Cardiology, Radiology, Ophthalmology
Which of the following freedoms is not available to an Indian citizen?



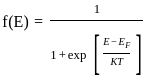
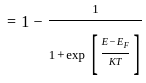
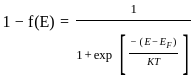
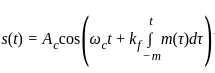
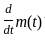 as the input to the frequency modulator, i.e.
as the input to the frequency modulator, i.e.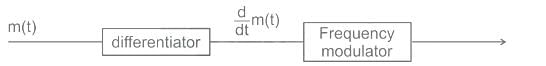
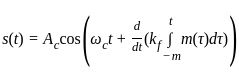
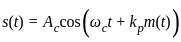
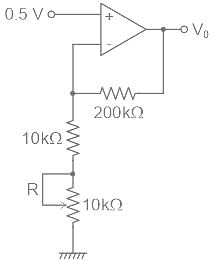
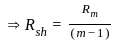
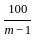
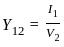
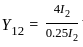
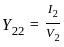
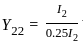
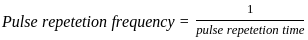
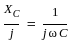
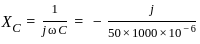
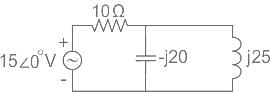
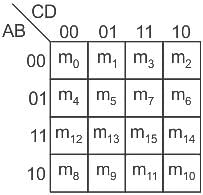
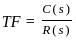
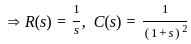
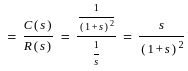
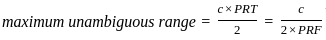
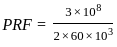
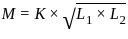 ... (1)
... (1)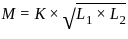 H
H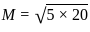 H
H