Test: Mechanical Properties of Solids - Introduction to stress and strain (28 July) - JEE MCQ
Test Description
10 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Mechanical Properties of Solids - Introduction to stress and strain (28 July)
Test: Mechanical Properties of Solids - Introduction to stress and strain (28 July) for JEE 2024 is part of JEE preparation. The Test: Mechanical Properties of Solids - Introduction to stress and strain (28 July) questions and answers have been prepared
according to the JEE exam syllabus.The Test: Mechanical Properties of Solids - Introduction to stress and strain (28 July) MCQs are made for JEE 2024 Exam.
Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests for Test: Mechanical Properties of Solids - Introduction to stress and strain (28 July) below.
Solutions of Test: Mechanical Properties of Solids - Introduction to stress and strain (28 July) questions in English are available as part of our course for JEE & Test: Mechanical Properties of Solids - Introduction to stress and strain (28 July) solutions in
Hindi for JEE course.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for JEE Exam by signing up for free. Attempt Test: Mechanical Properties of Solids - Introduction to stress and strain (28 July) | 10 questions in 20 minutes | Mock test for JEE preparation | Free important questions MCQ to study for JEE Exam | Download free PDF with solutions
Test: Mechanical Properties of Solids - Introduction to stress and strain (28 July) - Question 1
The slope of the stress-strain curve in the elastic deformation region is ____________
Detailed Solution for Test: Mechanical Properties of Solids - Introduction to stress and strain (28 July) - Question 1
Test: Mechanical Properties of Solids - Introduction to stress and strain (28 July) - Question 2
Which point on the stress strain curve occurs after the proportionality limit?
Detailed Solution for Test: Mechanical Properties of Solids - Introduction to stress and strain (28 July) - Question 2
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
Test: Mechanical Properties of Solids - Introduction to stress and strain (28 July) - Question 3
Which point on the stress strain curve occurs after yield plateau?
Detailed Solution for Test: Mechanical Properties of Solids - Introduction to stress and strain (28 July) - Question 3
Test: Mechanical Properties of Solids - Introduction to stress and strain (28 July) - Question 4
The impact strength of a material is an index of its
Detailed Solution for Test: Mechanical Properties of Solids - Introduction to stress and strain (28 July) - Question 4
Test: Mechanical Properties of Solids - Introduction to stress and strain (28 July) - Question 5
Hooke's law holds good up to the limit of __________ .
Detailed Solution for Test: Mechanical Properties of Solids - Introduction to stress and strain (28 July) - Question 5
Test: Mechanical Properties of Solids - Introduction to stress and strain (28 July) - Question 6
The plastic response (deformation) of a material to compressive force is known as:
Detailed Solution for Test: Mechanical Properties of Solids - Introduction to stress and strain (28 July) - Question 6
Test: Mechanical Properties of Solids - Introduction to stress and strain (28 July) - Question 7
Modulus of rigidity is defined as:
Detailed Solution for Test: Mechanical Properties of Solids - Introduction to stress and strain (28 July) - Question 7
Test: Mechanical Properties of Solids - Introduction to stress and strain (28 July) - Question 8
In the given stress-strain curve of mild steel, DE represents:
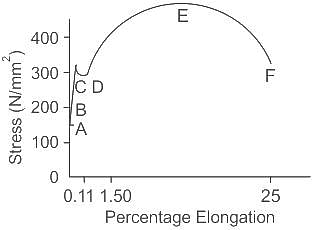
Detailed Solution for Test: Mechanical Properties of Solids - Introduction to stress and strain (28 July) - Question 8
Test: Mechanical Properties of Solids - Introduction to stress and strain (28 July) - Question 9
Where is the necking region?
Detailed Solution for Test: Mechanical Properties of Solids - Introduction to stress and strain (28 July) - Question 9
Test: Mechanical Properties of Solids - Introduction to stress and strain (28 July) - Question 10
If a piece of material neither expands nor contracts in volume when subjected to stresses, then the Poisson’s ratio must be
Detailed Solution for Test: Mechanical Properties of Solids - Introduction to stress and strain (28 July) - Question 10
Information about Test: Mechanical Properties of Solids - Introduction to stress and strain (28 July) Page
In this test you can find the Exam questions for Test: Mechanical Properties of Solids - Introduction to stress and strain (28 July) solved & explained in the simplest way possible.
Besides giving Questions and answers for Test: Mechanical Properties of Solids - Introduction to stress and strain (28 July), EduRev gives you an ample number of Online tests for practice
Download as PDF

















