Test: Mechanical Properties of Solids - Hooke’s law & Stress-strain curve (29 July) - JEE MCQ
Test Description
10 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Mechanical Properties of Solids - Hooke’s law & Stress-strain curve (29 July)
Test: Mechanical Properties of Solids - Hooke’s law & Stress-strain curve (29 July) for JEE 2024 is part of JEE preparation. The Test: Mechanical Properties of Solids - Hooke’s law & Stress-strain curve (29 July) questions and answers have been prepared
according to the JEE exam syllabus.The Test: Mechanical Properties of Solids - Hooke’s law & Stress-strain curve (29 July) MCQs are made for JEE 2024 Exam.
Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests for Test: Mechanical Properties of Solids - Hooke’s law & Stress-strain curve (29 July) below.
Solutions of Test: Mechanical Properties of Solids - Hooke’s law & Stress-strain curve (29 July) questions in English are available as part of our course for JEE & Test: Mechanical Properties of Solids - Hooke’s law & Stress-strain curve (29 July) solutions in
Hindi for JEE course.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for JEE Exam by signing up for free. Attempt Test: Mechanical Properties of Solids - Hooke’s law & Stress-strain curve (29 July) | 10 questions in 20 minutes | Mock test for JEE preparation | Free important questions MCQ to study for JEE Exam | Download free PDF with solutions
Test: Mechanical Properties of Solids - Hooke’s law & Stress-strain curve (29 July) - Question 1
Which of the following options is correct?
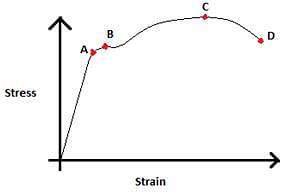

Detailed Solution for Test: Mechanical Properties of Solids - Hooke’s law & Stress-strain curve (29 July) - Question 1
Test: Mechanical Properties of Solids - Hooke’s law & Stress-strain curve (29 July) - Question 2
The stress corresponding to fracture point is called ______
Detailed Solution for Test: Mechanical Properties of Solids - Hooke’s law & Stress-strain curve (29 July) - Question 2
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
Test: Mechanical Properties of Solids - Hooke’s law & Stress-strain curve (29 July) - Question 3
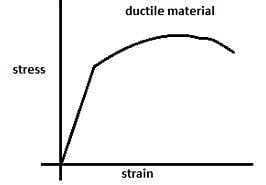
Which of the following statements is correct for ductile materials.
Detailed Solution for Test: Mechanical Properties of Solids - Hooke’s law & Stress-strain curve (29 July) - Question 3
Test: Mechanical Properties of Solids - Hooke’s law & Stress-strain curve (29 July) - Question 4
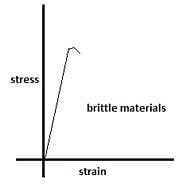
Which of the following statements is correct for brittle materials.
Detailed Solution for Test: Mechanical Properties of Solids - Hooke’s law & Stress-strain curve (29 July) - Question 4
Test: Mechanical Properties of Solids - Hooke’s law & Stress-strain curve (29 July) - Question 5
What does the area under the stress-strain curve represent?
Detailed Solution for Test: Mechanical Properties of Solids - Hooke’s law & Stress-strain curve (29 July) - Question 5
Test: Mechanical Properties of Solids - Hooke’s law & Stress-strain curve (29 July) - Question 6
Which law states about strain being proportional to stress producing it within the elastic limit of a material?
Detailed Solution for Test: Mechanical Properties of Solids - Hooke’s law & Stress-strain curve (29 July) - Question 6
Test: Mechanical Properties of Solids - Hooke’s law & Stress-strain curve (29 July) - Question 7
According to Hooke's law, if stress is increased the ratio of stress to strain will _________
Detailed Solution for Test: Mechanical Properties of Solids - Hooke’s law & Stress-strain curve (29 July) - Question 7
Test: Mechanical Properties of Solids - Hooke’s law & Stress-strain curve (29 July) - Question 8
Two rods A and B are made of the same material. The diameter of both the rods is equal, but the length of rod A is more than rod B. If the tensile force applied on both the rods are equal, then which of the following statement is correct?
Detailed Solution for Test: Mechanical Properties of Solids - Hooke’s law & Stress-strain curve (29 July) - Question 8
Test: Mechanical Properties of Solids - Hooke’s law & Stress-strain curve (29 July) - Question 9
A wire of diameter 7 mm and length 1 m is stretched within the elastic limit by the 77 kN pull. If the elongation of the wire for this force is noted as 2 mm, then find Young's modulus of elasticity for the material of the wire.
Detailed Solution for Test: Mechanical Properties of Solids - Hooke’s law & Stress-strain curve (29 July) - Question 9
Test: Mechanical Properties of Solids - Hooke’s law & Stress-strain curve (29 July) - Question 10
If material is loaded within the elastic limit then the slope of the stress-strain curve:
Detailed Solution for Test: Mechanical Properties of Solids - Hooke’s law & Stress-strain curve (29 July) - Question 10
Information about Test: Mechanical Properties of Solids - Hooke’s law & Stress-strain curve (29 July) Page
In this test you can find the Exam questions for Test: Mechanical Properties of Solids - Hooke’s law & Stress-strain curve (29 July) solved & explained in the simplest way possible.
Besides giving Questions and answers for Test: Mechanical Properties of Solids - Hooke’s law & Stress-strain curve (29 July), EduRev gives you an ample number of Online tests for practice
Download as PDF