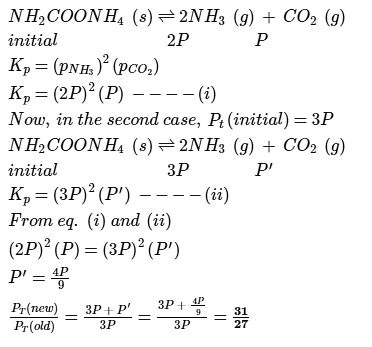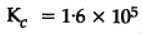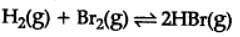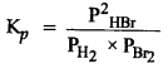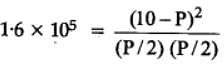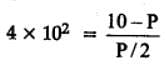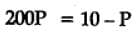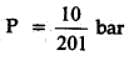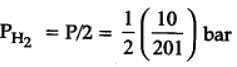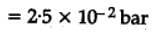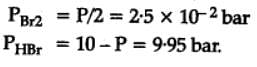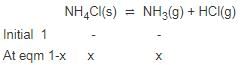Test: Homogeneous Equilibria & Heterogeneous Equilibria (4 July) - JEE MCQ
10 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Homogeneous Equilibria & Heterogeneous Equilibria (4 July)
One of the reactions that takes place in producing steel from iron ore is the reduction of iron (II) oxide by carbon monoxide to give iron metal and carbon dioxide.
FeO (s) + CO (g)  Fe (s) + CO2(g); Kp = 0.265 atm at 1050 K
Fe (s) + CO2(g); Kp = 0.265 atm at 1050 K
Initial partial pressure
CO(g) = 1.40 atm
CO2(g) = 0.80 atm
Q. When equilibrium is attained,
FeO (s) + CO (g)
 Fe (s) + CO2(g); Kp = 0.265 atm at 1050 K
Fe (s) + CO2(g); Kp = 0.265 atm at 1050 KInitial partial pressure
CO(g) = 1.40 atm
CO2(g) = 0.80 atm
A sample of N2O4(g)with a pressure of 1.00 atm is placed in a flask. When equilibrium is reached, 20% of N2O4(g)has been converted to NO2(g)
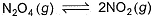
If the original pressure is made 10% of the earlier pressure, then per cent dissociation will be
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
Direction (Q. Nos. 1-13) This section contains 13 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONLY ONE option is correct.
Q. Given the reactions, 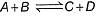 If one mole each of A and B are take in 5 L flask at 300 K, 0.7 mole of C are formed. Molar concentration of each species at equilibrium, when one mole of each are taken initially is
If one mole each of A and B are take in 5 L flask at 300 K, 0.7 mole of C are formed. Molar concentration of each species at equilibrium, when one mole of each are taken initially is

Ammonium carbamate dissociates as,
In a closed vessel containing ammonium carbamate in equilibrium with its vapour, ammonia is added such that partial pressure of NH3 now equals the original total pressure. Thus, ratio of the total pressure to the original pressure is
A gaseous phase reaction taking place in 1L flask at 400 K is given,
Starting with 1 mole N2 and 3 moles H2, equilibrium mixture required 250 mL of 1M H2SO4 . Thus, Kc is
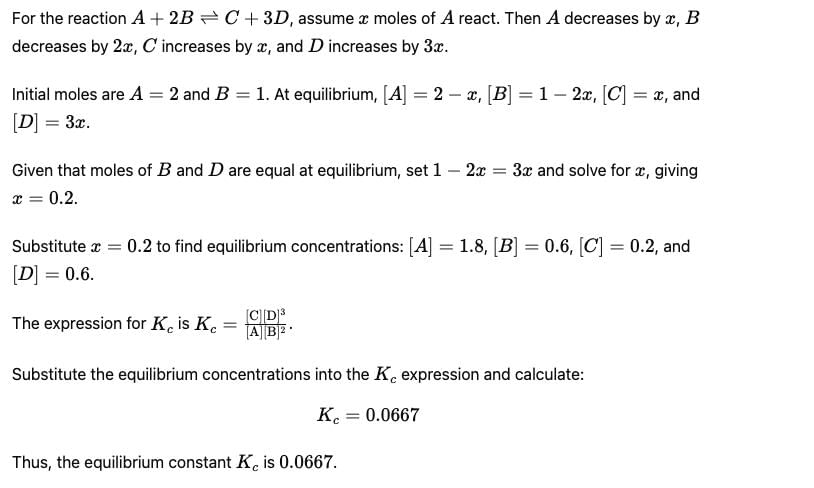
Following equilibrium is set up at 298 K in a 1 L flask.
If one starts with 2 moles of A and 1 mole of B, it is found that moles of B and D are equal. Thus Kc is
The equilibrium constant for the following reaction, is 1.6 x 105 at 1024 K.
H2(g) + Br2(g) ⇌ 2HBr(g)
HBr (g)at 10.0 bar is introduced into a sealed container at 1024 K. Thus, partial pressure of H2(g) and Br2(g), together is
For the following equilibrium,
Ca(HCO3)2 is strongly heated and after equilibrium is attained, temperature changed to 25° C.
Ca(HCO3)2(s)⇌CaO(s) + 2CO2 (g) + H2O(g)
Kp = 36 (pressure taken in atm)
Thus, pressure set up due to CO2 is
Solid ammonium chloride is in equilibrium with ammonia and hydrogen chloride gases
0.980 g of solid NH4CI is taken in a closed vessel of 1 L capacity and heated to 275° C.
Q. Percentage decomposition of the original sample is