UGC NET Paper 2 Sociology Mock Test - 5 - UGC NET MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - UGC NET Paper 2 Sociology Mock Test - 5
Which of the following characterize the Jajmani System?
1. Functional interdependence of castes
2. Mahalwari system
3. Village social structure
Select the correct answer from the codes given below:
Which index has recently replaced the gender development index of human development report?
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
Which of the following Committee recommended in 1986 for the Constitutional status of the Panchayati Raj ?
Which statement is/are correct?
1. Bureaucracy is a pyramid of officials who rationally conduct the work of large organisation.
2. Ideology is a system of ideas which sanctions a set of norms.
3. Caste is a social status, which include occupation assigned by heredity.
Select the correct answer using the codes given below
Which of the following is/are the Aims and Objectives of Labor Welfare?
1. Provide social comfort to employees.
2. Support overall improvement of employees.
3. Provide financial support indirectly to the employees.
4. Contribute in developing sense of responsibility and belongingness among employees.
Find the right code from the given below.
Choose the appropriate answer with regard to Neoliberalism .
1: Neoliberalism challenges the assumption that international anarchy leads to conflict and chaos.
2: Neoliberalism argues for the importance of building a web of international institutions to manage and mitigate global issues.
3: Neoliberalism asserts that states can achieve mutual gains through cooperation and interdependence.
Direction: In the questions below are two statements labelled Assertion (A) and Reason (R). In the context of the two statements which one of the following is correct?
Assertion (A): Labour welfare improves the moral and mental conditions of the workers.
Reason (R): Insurance facility and good working conditions create atmosphere of security and feeling in insecurity is removed.
The Shuddhi movement was launched by which samaj?
Which one of the following is not a type of experimental method?
A survey design meant for collection of data needed from the same selected population at different points of time is known as
Mark out the correct sequence of perspectives on gender and development in India.
Which society destroys private ownership of means of production and in its place creates public ownership of means of production?
I. Socialist
II. Capitalist
Match List-I with List-II and select the correct answer from the codes given below the lists:
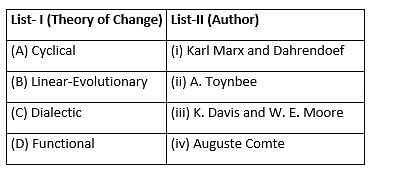
A, B, C, and D are respectively.
Match List-I with List-II.
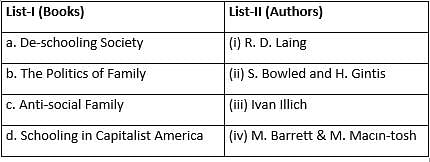
Codes: a, b, c, d
Which one among the following statement is true in the context of the testing of hypotheses?
The 'decentralized city' can be identified by-