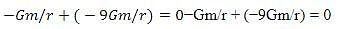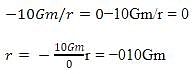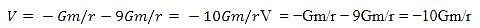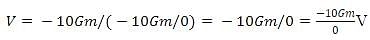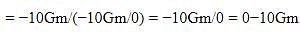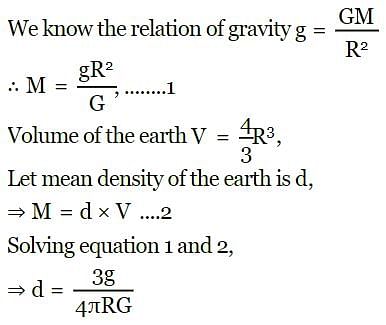Test: The gravitational constant & Acceleration due to gravity (5 August) - JEE MCQ
Test Description
10 Questions MCQ Test - Test: The gravitational constant & Acceleration due to gravity (5 August)
Test: The gravitational constant & Acceleration due to gravity (5 August) for JEE 2024 is part of JEE preparation. The Test: The gravitational constant & Acceleration due to gravity (5 August) questions and answers have been prepared
according to the JEE exam syllabus.The Test: The gravitational constant & Acceleration due to gravity (5 August) MCQs are made for JEE 2024 Exam.
Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests for Test: The gravitational constant & Acceleration due to gravity (5 August) below.
Solutions of Test: The gravitational constant & Acceleration due to gravity (5 August) questions in English are available as part of our course for JEE & Test: The gravitational constant & Acceleration due to gravity (5 August) solutions in
Hindi for JEE course.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for JEE Exam by signing up for free. Attempt Test: The gravitational constant & Acceleration due to gravity (5 August) | 10 questions in 20 minutes | Mock test for JEE preparation | Free important questions MCQ to study for JEE Exam | Download free PDF with solutions
Test: The gravitational constant & Acceleration due to gravity (5 August) - Question 1
What is the mass of a girl who weighs 450 N?
Detailed Solution for Test: The gravitational constant & Acceleration due to gravity (5 August) - Question 1
Test: The gravitational constant & Acceleration due to gravity (5 August) - Question 2
Acceleration due to gravity at the equator _______________
Detailed Solution for Test: The gravitational constant & Acceleration due to gravity (5 August) - Question 2
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
Test: The gravitational constant & Acceleration due to gravity (5 August) - Question 3
Mass of an object on earth is 12. What is its weight on the moon?
Detailed Solution for Test: The gravitational constant & Acceleration due to gravity (5 August) - Question 3
Test: The gravitational constant & Acceleration due to gravity (5 August) - Question 4
Two bodies of mass m and 9m are placed at a distance R. The gravitational potential on the line joining the bodies where the gravitational field equals zero, will be: ( G= gravitational constant)
Detailed Solution for Test: The gravitational constant & Acceleration due to gravity (5 August) - Question 4
Test: The gravitational constant & Acceleration due to gravity (5 August) - Question 5
The weights of the body of mass 50 kg in a free falling artificial satellite is zero
Detailed Solution for Test: The gravitational constant & Acceleration due to gravity (5 August) - Question 5
Test: The gravitational constant & Acceleration due to gravity (5 August) - Question 6
Which of the following freely falling objects will have the maximum acceleration in a vacuum?
Detailed Solution for Test: The gravitational constant & Acceleration due to gravity (5 August) - Question 6
Test: The gravitational constant & Acceleration due to gravity (5 August) - Question 7
The escape velocity of a body on the earth's surface is 11.2 km/s. If the same body is projected upward with a velocity 22.4 km/s, the velocity of this body at infinite distance from the center of the earth will be:
Detailed Solution for Test: The gravitational constant & Acceleration due to gravity (5 August) - Question 7
Test: The gravitational constant & Acceleration due to gravity (5 August) - Question 8
If R is the radius of the earth and g is the acceleration due to gravity on the earth surface. Then the mean density of the earth will be:
Detailed Solution for Test: The gravitational constant & Acceleration due to gravity (5 August) - Question 8
Test: The gravitational constant & Acceleration due to gravity (5 August) - Question 9
A body of mass 60 g experiences a gravitational force of 3.0 N when placed at a particular point. The magnitude of the gravitational field intensity at that point is:
Test: The gravitational constant & Acceleration due to gravity (5 August) - Question 10
A satellite is orbiting just above the surface of the earth with period T. If d is the density of the earth and G is the universal constant of gravitation, the quantity 3?Gd represents:
Information about Test: The gravitational constant & Acceleration due to gravity (5 August) Page
In this test you can find the Exam questions for Test: The gravitational constant & Acceleration due to gravity (5 August) solved & explained in the simplest way possible.
Besides giving Questions and answers for Test: The gravitational constant & Acceleration due to gravity (5 August), EduRev gives you an ample number of Online tests for practice
Download as PDF


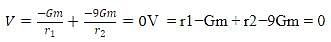
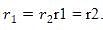 . Let's denote this common distance as
. Let's denote this common distance as