Judiciary Exams Exam > Judiciary Exams Tests > Uttarakhand Judicial Services Prelims Mock Test - 2 - Judiciary Exams MCQ
Uttarakhand Judicial Services Prelims Mock Test - 2 - Judiciary Exams MCQ
Test Description
30 Questions MCQ Test - Uttarakhand Judicial Services Prelims Mock Test - 2
Uttarakhand Judicial Services Prelims Mock Test - 2 for Judiciary Exams 2024 is part of Judiciary Exams preparation. The Uttarakhand Judicial Services Prelims Mock Test - 2 questions and answers have been prepared
according to the Judiciary Exams exam syllabus.The Uttarakhand Judicial Services Prelims Mock Test - 2 MCQs are made for Judiciary Exams 2024 Exam.
Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests for Uttarakhand Judicial Services Prelims Mock Test - 2 below.
Solutions of Uttarakhand Judicial Services Prelims Mock Test - 2 questions in English are available as part of our course for Judiciary Exams & Uttarakhand Judicial Services Prelims Mock Test - 2 solutions in
Hindi for Judiciary Exams course.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Judiciary Exams Exam by signing up for free. Attempt Uttarakhand Judicial Services Prelims Mock Test - 2 | 200 questions in 180 minutes | Mock test for Judiciary Exams preparation | Free important questions MCQ to study for Judiciary Exams Exam | Download free PDF with solutions
Uttarakhand Judicial Services Prelims Mock Test - 2 - Question 1
Special provision is mentioned regarding evidence relating to electronic record in which of the following sections of the Indian Evidence Act, 1872?
Detailed Solution for Uttarakhand Judicial Services Prelims Mock Test - 2 - Question 1
Uttarakhand Judicial Services Prelims Mock Test - 2 - Question 2
Under Muslim Law, a man is forbidden to have two wives at the same time, if related with each other by
Detailed Solution for Uttarakhand Judicial Services Prelims Mock Test - 2 - Question 2
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
Uttarakhand Judicial Services Prelims Mock Test - 2 - Question 3
Under the Muslim Law, a married woman shall be entitled to obtain a decree for the dissolution of marriage on the ground that 'whereabouts of husband have not been known for a period of four years'. This is provided under the Dissolution of Muslim Marriage Act, 1939, in
Detailed Solution for Uttarakhand Judicial Services Prelims Mock Test - 2 - Question 3
Uttarakhand Judicial Services Prelims Mock Test - 2 - Question 4
Under the Hindu Minority and Guardianship Act, 1956, the custody of a minor who has not completed the age of _____ years shall be with the mother ordinarily.
Detailed Solution for Uttarakhand Judicial Services Prelims Mock Test - 2 - Question 4
Uttarakhand Judicial Services Prelims Mock Test - 2 - Question 5
Which of the following is NOT a duty of the investigating officer under Section 173 of the Criminal Procedure Code?
Detailed Solution for Uttarakhand Judicial Services Prelims Mock Test - 2 - Question 5
Uttarakhand Judicial Services Prelims Mock Test - 2 - Question 6
Can a court exercise the power of re-summoning any witness, if once that power under Section 311 of CrPC has been exercised?
Detailed Solution for Uttarakhand Judicial Services Prelims Mock Test - 2 - Question 6
Uttarakhand Judicial Services Prelims Mock Test - 2 - Question 7
'A' allows an illegal marriage to be solemnized by 'B', a priest in his house. Which of the following statements holds true in this case?
Detailed Solution for Uttarakhand Judicial Services Prelims Mock Test - 2 - Question 7
Uttarakhand Judicial Services Prelims Mock Test - 2 - Question 8
The members of the UPSC are appointed by:
Detailed Solution for Uttarakhand Judicial Services Prelims Mock Test - 2 - Question 8
Uttarakhand Judicial Services Prelims Mock Test - 2 - Question 9
Which of the following cases is related to the constitutionality of 'right to die'?
Detailed Solution for Uttarakhand Judicial Services Prelims Mock Test - 2 - Question 9
Uttarakhand Judicial Services Prelims Mock Test - 2 - Question 10
Which of the following is not an essential requirement for a gift made by a Mohammedan?
Detailed Solution for Uttarakhand Judicial Services Prelims Mock Test - 2 - Question 10
Uttarakhand Judicial Services Prelims Mock Test - 2 - Question 11
Rules relating to sapinda relationship are based on the principle of
Detailed Solution for Uttarakhand Judicial Services Prelims Mock Test - 2 - Question 11
Uttarakhand Judicial Services Prelims Mock Test - 2 - Question 12
Match List I with List II and select the correct answer by using the codes given below it.
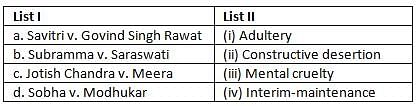
Detailed Solution for Uttarakhand Judicial Services Prelims Mock Test - 2 - Question 12
Uttarakhand Judicial Services Prelims Mock Test - 2 - Question 13
Under Muslim Law, the term "Faskh" is used to denote
Detailed Solution for Uttarakhand Judicial Services Prelims Mock Test - 2 - Question 13
Detailed Solution for Uttarakhand Judicial Services Prelims Mock Test - 2 - Question 14
Detailed Solution for Uttarakhand Judicial Services Prelims Mock Test - 2 - Question 15
Uttarakhand Judicial Services Prelims Mock Test - 2 - Question 16
Which Section of the CrPC provides that a person once convicted or acquitted cannot be tried again for the same offence?
Detailed Solution for Uttarakhand Judicial Services Prelims Mock Test - 2 - Question 16
Uttarakhand Judicial Services Prelims Mock Test - 2 - Question 17
Transgender has been recognised as the third gender with all rights and a right to reservation by the Supreme Court in the case of:
Detailed Solution for Uttarakhand Judicial Services Prelims Mock Test - 2 - Question 17
Uttarakhand Judicial Services Prelims Mock Test - 2 - Question 18
Whoever voluntarily obstructs any person so as to prevent that person from proceeding in any direction in which that person has a right to proceed is said to commit the offence of:
Detailed Solution for Uttarakhand Judicial Services Prelims Mock Test - 2 - Question 18
Uttarakhand Judicial Services Prelims Mock Test - 2 - Question 19
Which country was ranked as the most criminal country in the world in 2023?
Detailed Solution for Uttarakhand Judicial Services Prelims Mock Test - 2 - Question 19
Uttarakhand Judicial Services Prelims Mock Test - 2 - Question 20
The country's strictest Anti-Copying Law came into force in _______, in February 2023.
Detailed Solution for Uttarakhand Judicial Services Prelims Mock Test - 2 - Question 20
Uttarakhand Judicial Services Prelims Mock Test - 2 - Question 21
Ten persons were charged for offence under Section 302/149 of IPC, out of which six persons were acquitted. The remaining four
Detailed Solution for Uttarakhand Judicial Services Prelims Mock Test - 2 - Question 21
Uttarakhand Judicial Services Prelims Mock Test - 2 - Question 22
Under Section 100A of the CPC, where any appeal from an original or appellate decree or order is heard and decided by a single Judge of a High Court,
Detailed Solution for Uttarakhand Judicial Services Prelims Mock Test - 2 - Question 22
Uttarakhand Judicial Services Prelims Mock Test - 2 - Question 23
While executing a decree for maintenance, the salary of the judgement-debtor to the extent of
Detailed Solution for Uttarakhand Judicial Services Prelims Mock Test - 2 - Question 23
Uttarakhand Judicial Services Prelims Mock Test - 2 - Question 24
Which one of the following is 1st leading case decided by Supreme Court on delegated legislation after the Constitution came into force?
Detailed Solution for Uttarakhand Judicial Services Prelims Mock Test - 2 - Question 24
Uttarakhand Judicial Services Prelims Mock Test - 2 - Question 25
Who was the first Law Minister of India?
Detailed Solution for Uttarakhand Judicial Services Prelims Mock Test - 2 - Question 25
Uttarakhand Judicial Services Prelims Mock Test - 2 - Question 26
Under Section 3 of the Transfer of Property Act, 1882, 'Immovable Property' does not include:
Detailed Solution for Uttarakhand Judicial Services Prelims Mock Test - 2 - Question 26
Uttarakhand Judicial Services Prelims Mock Test - 2 - Question 27
Who is disentitled to dispose of property of a Hindu minor under Sec. 11 of the Hindu Minority and Guardianship Act, 1956?
Detailed Solution for Uttarakhand Judicial Services Prelims Mock Test - 2 - Question 27
Uttarakhand Judicial Services Prelims Mock Test - 2 - Question 28
The Indian Evidence Act applies to:
Detailed Solution for Uttarakhand Judicial Services Prelims Mock Test - 2 - Question 28
Uttarakhand Judicial Services Prelims Mock Test - 2 - Question 29
According to Section 357A of the CrPC, where the offender is not traced or identified, the victim or his dependent applied for the award of compensation; within what period are the state or district legal services authorities required to complete enquiry in this regard?
Detailed Solution for Uttarakhand Judicial Services Prelims Mock Test - 2 - Question 29
Uttarakhand Judicial Services Prelims Mock Test - 2 - Question 30
The proceedings under the Maintenance and Welfare of Parents and Senior Citizen Act, 2007 are maintainable at:
Detailed Solution for Uttarakhand Judicial Services Prelims Mock Test - 2 - Question 30
View more questions
Information about Uttarakhand Judicial Services Prelims Mock Test - 2 Page
In this test you can find the Exam questions for Uttarakhand Judicial Services Prelims Mock Test - 2 solved & explained in the simplest way possible.
Besides giving Questions and answers for Uttarakhand Judicial Services Prelims Mock Test - 2, EduRev gives you an ample number of Online tests for practice
Download as PDF

















