Judiciary Exams Exam > Judiciary Exams Tests > Uttarakhand Judicial Services Prelims Mock Test - 4 - Judiciary Exams MCQ
Uttarakhand Judicial Services Prelims Mock Test - 4 - Judiciary Exams MCQ
Test Description
30 Questions MCQ Test - Uttarakhand Judicial Services Prelims Mock Test - 4
Uttarakhand Judicial Services Prelims Mock Test - 4 for Judiciary Exams 2024 is part of Judiciary Exams preparation. The Uttarakhand Judicial Services Prelims Mock Test - 4 questions and answers have been prepared
according to the Judiciary Exams exam syllabus.The Uttarakhand Judicial Services Prelims Mock Test - 4 MCQs are made for Judiciary Exams 2024 Exam.
Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests for Uttarakhand Judicial Services Prelims Mock Test - 4 below.
Solutions of Uttarakhand Judicial Services Prelims Mock Test - 4 questions in English are available as part of our course for Judiciary Exams & Uttarakhand Judicial Services Prelims Mock Test - 4 solutions in
Hindi for Judiciary Exams course.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Judiciary Exams Exam by signing up for free. Attempt Uttarakhand Judicial Services Prelims Mock Test - 4 | 200 questions in 180 minutes | Mock test for Judiciary Exams preparation | Free important questions MCQ to study for Judiciary Exams Exam | Download free PDF with solutions
Detailed Solution for Uttarakhand Judicial Services Prelims Mock Test - 4 - Question 1
Uttarakhand Judicial Services Prelims Mock Test - 4 - Question 2
Nemo dat quod non habet (no man can confer a better title than that which he himself has) is an established principle of
Detailed Solution for Uttarakhand Judicial Services Prelims Mock Test - 4 - Question 2
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
Uttarakhand Judicial Services Prelims Mock Test - 4 - Question 3
Presumption as to dowry death is contained in
Detailed Solution for Uttarakhand Judicial Services Prelims Mock Test - 4 - Question 3
Uttarakhand Judicial Services Prelims Mock Test - 4 - Question 4
Dumb witness may give his evidence by writing or signs in an open court. Such evidence shall be deemed to be
Detailed Solution for Uttarakhand Judicial Services Prelims Mock Test - 4 - Question 4
Uttarakhand Judicial Services Prelims Mock Test - 4 - Question 5
The compensation to the victim under Section 357 of the Code of Criminal Procedure can be passed by which of the following courts?
Detailed Solution for Uttarakhand Judicial Services Prelims Mock Test - 4 - Question 5
Uttarakhand Judicial Services Prelims Mock Test - 4 - Question 6
A' pretends to be 'B', a person who has been deceased. 'A' is liable to be punished under
Detailed Solution for Uttarakhand Judicial Services Prelims Mock Test - 4 - Question 6
Uttarakhand Judicial Services Prelims Mock Test - 4 - Question 7
A woman ran to a well stating that she would jump into the well but she was caught before she could reach it. She is guilty of
Detailed Solution for Uttarakhand Judicial Services Prelims Mock Test - 4 - Question 7
Uttarakhand Judicial Services Prelims Mock Test - 4 - Question 8
Match List I with List II and select the correct answer by using the codes given below the lists.
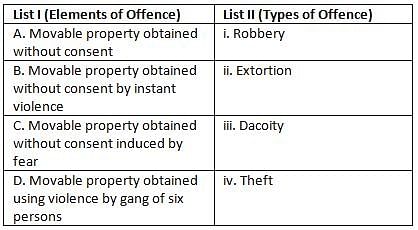
Detailed Solution for Uttarakhand Judicial Services Prelims Mock Test - 4 - Question 8
Uttarakhand Judicial Services Prelims Mock Test - 4 - Question 9
"Philosophy of Law" is a book written by
Detailed Solution for Uttarakhand Judicial Services Prelims Mock Test - 4 - Question 9
Uttarakhand Judicial Services Prelims Mock Test - 4 - Question 10
The International Court of Justice was set up on
Detailed Solution for Uttarakhand Judicial Services Prelims Mock Test - 4 - Question 10
Uttarakhand Judicial Services Prelims Mock Test - 4 - Question 11
In which section of the Protection of Women from Domestic Violence Act, 2005 has the word 'Domestic Violence' been defined?
Detailed Solution for Uttarakhand Judicial Services Prelims Mock Test - 4 - Question 11
Uttarakhand Judicial Services Prelims Mock Test - 4 - Question 12
Which of the following is/are the essential requisites of a valid will under Muslim Law?
Detailed Solution for Uttarakhand Judicial Services Prelims Mock Test - 4 - Question 12
Uttarakhand Judicial Services Prelims Mock Test - 4 - Question 13
Which of the following is not a ground for dissolution of a Muslim marriage under the Dissolution of Muslim Marriage Act, 1939?
Detailed Solution for Uttarakhand Judicial Services Prelims Mock Test - 4 - Question 13
Uttarakhand Judicial Services Prelims Mock Test - 4 - Question 14
Which among the following is/are an immovable property as per the provisions of Transfer of Property Act, 1882?
Detailed Solution for Uttarakhand Judicial Services Prelims Mock Test - 4 - Question 14
Uttarakhand Judicial Services Prelims Mock Test - 4 - Question 15
Primary evidence of a document means
Detailed Solution for Uttarakhand Judicial Services Prelims Mock Test - 4 - Question 15
Uttarakhand Judicial Services Prelims Mock Test - 4 - Question 16
A Magistrate who released on bail an accused in a Sessions case directed him to bind himself to appear before the Magistrate Court as well as the Sessions Court. The direction is
Detailed Solution for Uttarakhand Judicial Services Prelims Mock Test - 4 - Question 16
Uttarakhand Judicial Services Prelims Mock Test - 4 - Question 17
The confession of an accused recorded by a Magistrate under Section 164 Cr.P.C.
Detailed Solution for Uttarakhand Judicial Services Prelims Mock Test - 4 - Question 17
Detailed Solution for Uttarakhand Judicial Services Prelims Mock Test - 4 - Question 18
Uttarakhand Judicial Services Prelims Mock Test - 4 - Question 19
Under Civil Procedure Code, the Court may issue a Commission:
Detailed Solution for Uttarakhand Judicial Services Prelims Mock Test - 4 - Question 19
Uttarakhand Judicial Services Prelims Mock Test - 4 - Question 20
As per Hindu law, who among the following is not entitled for maintenance?
Detailed Solution for Uttarakhand Judicial Services Prelims Mock Test - 4 - Question 20
Uttarakhand Judicial Services Prelims Mock Test - 4 - Question 21
Under Muslim Law, when wife and husband seek divorce on mutual consent, it is called:
Detailed Solution for Uttarakhand Judicial Services Prelims Mock Test - 4 - Question 21
Uttarakhand Judicial Services Prelims Mock Test - 4 - Question 22
Appointment of retired High Court Judges at the sitting of High Courts is provided in Constitution of India, under:
Detailed Solution for Uttarakhand Judicial Services Prelims Mock Test - 4 - Question 22
Uttarakhand Judicial Services Prelims Mock Test - 4 - Question 23
'A' denied food to his wife 'B' for several days by keeping her confined in a room with intention to accelerate her death. 'B' anyhow managed to escape. What offence has 'A' committed?
Detailed Solution for Uttarakhand Judicial Services Prelims Mock Test - 4 - Question 23
Uttarakhand Judicial Services Prelims Mock Test - 4 - Question 24
India's first Artificial Intelligence based digital Lok Adalat was launched in July 2022 in which State?
Detailed Solution for Uttarakhand Judicial Services Prelims Mock Test - 4 - Question 24
Uttarakhand Judicial Services Prelims Mock Test - 4 - Question 25
Under the Muslim Women (Protection of Rights on Marriage) Act, 2019, the punishment for pronouncing Talaq is
Detailed Solution for Uttarakhand Judicial Services Prelims Mock Test - 4 - Question 25
Uttarakhand Judicial Services Prelims Mock Test - 4 - Question 26
Mohan borrowed a bicycle from Ram promising to return it in three days but disposed of the same and appropriated the proceeds for his own use. Mohan is guilty of offence of:
Detailed Solution for Uttarakhand Judicial Services Prelims Mock Test - 4 - Question 26
Uttarakhand Judicial Services Prelims Mock Test - 4 - Question 27
A transfers property to B in trust for C and directs B to give possession of the property to C when he attains the age of 25 years. C's interest in the property is:
Detailed Solution for Uttarakhand Judicial Services Prelims Mock Test - 4 - Question 27
Uttarakhand Judicial Services Prelims Mock Test - 4 - Question 28
Rule against perpetuity applies to:
Detailed Solution for Uttarakhand Judicial Services Prelims Mock Test - 4 - Question 28
Uttarakhand Judicial Services Prelims Mock Test - 4 - Question 29
Which of the following provisions of Indian Penal Code, 1860, is based on the principle of 'Volenti non fit injuria'?
Detailed Solution for Uttarakhand Judicial Services Prelims Mock Test - 4 - Question 29
Uttarakhand Judicial Services Prelims Mock Test - 4 - Question 30
Offences affecting the human body are provided under which of the following chapters under Indian Penal Code, 1860?
Detailed Solution for Uttarakhand Judicial Services Prelims Mock Test - 4 - Question 30
View more questions
Information about Uttarakhand Judicial Services Prelims Mock Test - 4 Page
In this test you can find the Exam questions for Uttarakhand Judicial Services Prelims Mock Test - 4 solved & explained in the simplest way possible.
Besides giving Questions and answers for Uttarakhand Judicial Services Prelims Mock Test - 4, EduRev gives you an ample number of Online tests for practice
Download as PDF

















