Judiciary Exams Exam > Judiciary Exams Tests > Uttarakhand Judicial Services Prelims Mock Test - 5 - Judiciary Exams MCQ
Uttarakhand Judicial Services Prelims Mock Test - 5 - Judiciary Exams MCQ
Test Description
30 Questions MCQ Test - Uttarakhand Judicial Services Prelims Mock Test - 5
Uttarakhand Judicial Services Prelims Mock Test - 5 for Judiciary Exams 2024 is part of Judiciary Exams preparation. The Uttarakhand Judicial Services Prelims Mock Test - 5 questions and answers have been prepared
according to the Judiciary Exams exam syllabus.The Uttarakhand Judicial Services Prelims Mock Test - 5 MCQs are made for Judiciary Exams 2024 Exam.
Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests for Uttarakhand Judicial Services Prelims Mock Test - 5 below.
Solutions of Uttarakhand Judicial Services Prelims Mock Test - 5 questions in English are available as part of our course for Judiciary Exams & Uttarakhand Judicial Services Prelims Mock Test - 5 solutions in
Hindi for Judiciary Exams course.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Judiciary Exams Exam by signing up for free. Attempt Uttarakhand Judicial Services Prelims Mock Test - 5 | 200 questions in 180 minutes | Mock test for Judiciary Exams preparation | Free important questions MCQ to study for Judiciary Exams Exam | Download free PDF with solutions
Uttarakhand Judicial Services Prelims Mock Test - 5 - Question 1
Which of the following punishments cannot be awarded under the Indian Penal Code?
Detailed Solution for Uttarakhand Judicial Services Prelims Mock Test - 5 - Question 1
Uttarakhand Judicial Services Prelims Mock Test - 5 - Question 2
In which year was the Uttaranchal (Alteration of Name) Act passed?
Detailed Solution for Uttarakhand Judicial Services Prelims Mock Test - 5 - Question 2
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
Uttarakhand Judicial Services Prelims Mock Test - 5 - Question 3
Which of the following confessions can be proved as against a person accused of any offence?
Detailed Solution for Uttarakhand Judicial Services Prelims Mock Test - 5 - Question 3
Uttarakhand Judicial Services Prelims Mock Test - 5 - Question 4
Under the provisions of Section 45 of the Evidence Act, the opinion of an expert can be for
Detailed Solution for Uttarakhand Judicial Services Prelims Mock Test - 5 - Question 4
Uttarakhand Judicial Services Prelims Mock Test - 5 - Question 5
Which of the following offences of the Indian Penal Code is not correctly matched?
Detailed Solution for Uttarakhand Judicial Services Prelims Mock Test - 5 - Question 5
Uttarakhand Judicial Services Prelims Mock Test - 5 - Question 6
A, being a public servant directed by law to take property in execution, in order to satisfy a decree pronounced in B's favour by a court of law, knowingly disobeys that discretion of law, with the knowledge that he is likely thereby to cause injury to B. A has committed the offence defined in Section
Detailed Solution for Uttarakhand Judicial Services Prelims Mock Test - 5 - Question 6
Uttarakhand Judicial Services Prelims Mock Test - 5 - Question 7
Under which Article of the Indian Constitution has the Supreme Court developed the concept of 'curative petition'?
Detailed Solution for Uttarakhand Judicial Services Prelims Mock Test - 5 - Question 7
Uttarakhand Judicial Services Prelims Mock Test - 5 - Question 8
The name of the first woman judge of the International Court of Justice is
Detailed Solution for Uttarakhand Judicial Services Prelims Mock Test - 5 - Question 8
Uttarakhand Judicial Services Prelims Mock Test - 5 - Question 9
Which of the following is transferable property?
Detailed Solution for Uttarakhand Judicial Services Prelims Mock Test - 5 - Question 9
Uttarakhand Judicial Services Prelims Mock Test - 5 - Question 10
The main principle(s) of succession under Muslim law is/are:
Detailed Solution for Uttarakhand Judicial Services Prelims Mock Test - 5 - Question 10
Uttarakhand Judicial Services Prelims Mock Test - 5 - Question 11
A dying declaration to be admissible
Detailed Solution for Uttarakhand Judicial Services Prelims Mock Test - 5 - Question 11
Uttarakhand Judicial Services Prelims Mock Test - 5 - Question 12
Section 129 of the Evidence Act, 1872 states that no one shall be compelled to disclose to the Court any confidential communication which has taken place between
Detailed Solution for Uttarakhand Judicial Services Prelims Mock Test - 5 - Question 12
Uttarakhand Judicial Services Prelims Mock Test - 5 - Question 13
Section 306 (Tender of pardon to accomplice) applies to
Detailed Solution for Uttarakhand Judicial Services Prelims Mock Test - 5 - Question 13
Uttarakhand Judicial Services Prelims Mock Test - 5 - Question 14
A person who does any act which causes any common injury, danger or annoyance to the people in general who dwell or occupy property in the vicinity commits the offence of
Detailed Solution for Uttarakhand Judicial Services Prelims Mock Test - 5 - Question 14
Uttarakhand Judicial Services Prelims Mock Test - 5 - Question 15
On being informed that six persons armed with deadly weapons are coming to loot their house, the inmates of the house fled away in fear of being killed. The accused entered the house and took away the property without use of any violence. The offence committed was
Detailed Solution for Uttarakhand Judicial Services Prelims Mock Test - 5 - Question 15
Uttarakhand Judicial Services Prelims Mock Test - 5 - Question 16
The Lokpal and Lokayukta Act came into force in the year:
Detailed Solution for Uttarakhand Judicial Services Prelims Mock Test - 5 - Question 16
Uttarakhand Judicial Services Prelims Mock Test - 5 - Question 17
The eleventh schedule of the Constitution of India provides for:
Detailed Solution for Uttarakhand Judicial Services Prelims Mock Test - 5 - Question 17
Uttarakhand Judicial Services Prelims Mock Test - 5 - Question 18
Representative suit is dealt with in CPC under:
Detailed Solution for Uttarakhand Judicial Services Prelims Mock Test - 5 - Question 18
Uttarakhand Judicial Services Prelims Mock Test - 5 - Question 19
Which one of the following is not the valid object of waqf under Muslim Law?
Detailed Solution for Uttarakhand Judicial Services Prelims Mock Test - 5 - Question 19
Uttarakhand Judicial Services Prelims Mock Test - 5 - Question 20
Which one of the following Sections of the Indian Evidence Act provides about the production of documents or electronic records which another person, having possession, could refuse to produce?
Detailed Solution for Uttarakhand Judicial Services Prelims Mock Test - 5 - Question 20
Uttarakhand Judicial Services Prelims Mock Test - 5 - Question 21
Which one of the following Sections of CrPC deals with the summary dismissal of Appeal?
Detailed Solution for Uttarakhand Judicial Services Prelims Mock Test - 5 - Question 21
Uttarakhand Judicial Services Prelims Mock Test - 5 - Question 22
Which of the following countries is not a permanent member of the United Nations Security Council?
Detailed Solution for Uttarakhand Judicial Services Prelims Mock Test - 5 - Question 22
Uttarakhand Judicial Services Prelims Mock Test - 5 - Question 23
Which of the following is not correctly matched?
Detailed Solution for Uttarakhand Judicial Services Prelims Mock Test - 5 - Question 23
Uttarakhand Judicial Services Prelims Mock Test - 5 - Question 24
Who was the Constitutional advisor of the Constituent Assembly of India?
Detailed Solution for Uttarakhand Judicial Services Prelims Mock Test - 5 - Question 24
Detailed Solution for Uttarakhand Judicial Services Prelims Mock Test - 5 - Question 25
Uttarakhand Judicial Services Prelims Mock Test - 5 - Question 26
Which one of the following is correctly matched?
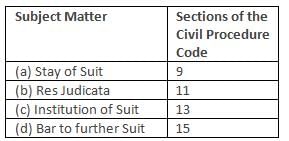
Detailed Solution for Uttarakhand Judicial Services Prelims Mock Test - 5 - Question 26
Uttarakhand Judicial Services Prelims Mock Test - 5 - Question 27
Under Muslim Law, 'Specified dower' can be fixed
Detailed Solution for Uttarakhand Judicial Services Prelims Mock Test - 5 - Question 27
Uttarakhand Judicial Services Prelims Mock Test - 5 - Question 28
Grave and sudden provocation is
Detailed Solution for Uttarakhand Judicial Services Prelims Mock Test - 5 - Question 28
Uttarakhand Judicial Services Prelims Mock Test - 5 - Question 29
Muhammad Afzal Vs. Ghulam Kasim (1903) is a leading case on:
Detailed Solution for Uttarakhand Judicial Services Prelims Mock Test - 5 - Question 29
Uttarakhand Judicial Services Prelims Mock Test - 5 - Question 30
Which section of Transfer of Property Act, 1882 talks about 'Onerous Gift'?
Detailed Solution for Uttarakhand Judicial Services Prelims Mock Test - 5 - Question 30
View more questions
Information about Uttarakhand Judicial Services Prelims Mock Test - 5 Page
In this test you can find the Exam questions for Uttarakhand Judicial Services Prelims Mock Test - 5 solved & explained in the simplest way possible.
Besides giving Questions and answers for Uttarakhand Judicial Services Prelims Mock Test - 5, EduRev gives you an ample number of Online tests for practice
Download as PDF

















