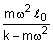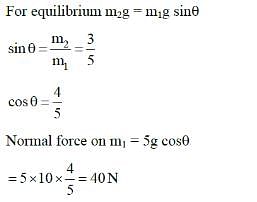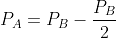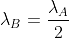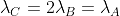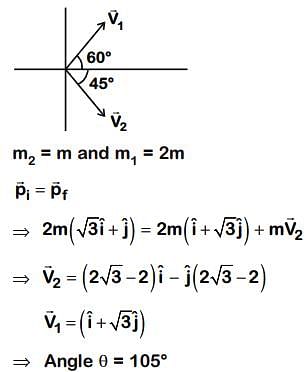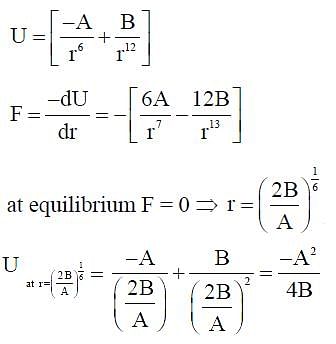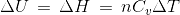PCM - Mock Test (June 30) - JEE MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - PCM - Mock Test (June 30)
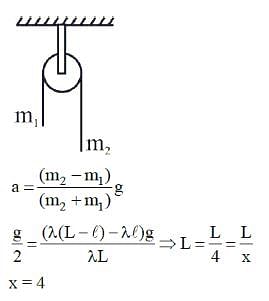
A uniform metal chain of mass m and length 'L' passes over a massless and frictionless pulley. It is released from rest with a part of its length 'l' hanging on one side and rest of its length 'L - l' hanging on the other side of the pulley. At a certain point of time, when  , the acceleration of the chain is g/2. The value of x is .......
, the acceleration of the chain is g/2. The value of x is .......

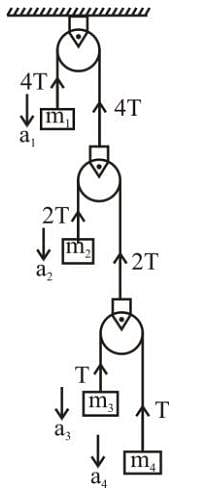
In the arrangement shown in figure a1, a2, a3 and a4 are the accelerations of masses m1, m2, m3 and m4 respectively. Which of the following relation is true for this arrangement?

| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
A uniform sphere of mass 500 g rolls without slipping on a plane horizontal surface with its centre moving at a speed of 5.00 cm/s. Its kinetic energy is
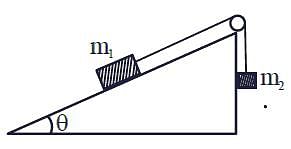
A block of mass M slides down on a rough inclined plane with constant velocity. The angle made by the inclined plane with horizontal is θ. The magnitude of the contact force will be:
An elevator in a building can carry a maximum of 10 persons, with the average mass of each person being 68 kg. The mass of the elevator itself is 920 kg and it moves with a constant speed of 3 m/s. The frictional force opposing the motion is 6000 N. If the elevator is moving up with its full capacity, the power delivered by the motor to the elevator (g = 10 m/s2) must be at least:
A balloon has mass of 10 g in air. The air escapes from the balloon at a uniform rate with velocity 4.5 cm/s. If the balloon shrinks in 5 s completely. Then, the average force acting on that balloon will be (in dyne)
A ball of mass 0.15 kg hits the wall with its initial speed of 12 ms-1 and bounces back without changing its initial speed. If the force applied by the wall on the ball during the contact is 100 N, calculate the time duration of the contact of ball with the wall.
A block of mass 1.9 kg is at rest at the edge of a table of height 1m. A bullet of mass 0.1 kg collides with the block and sticks to it. If the velocity of the bullet is 20 m/s in the horizontal direction just before the collision then the kinetic energy just before the combined system strikes the floor is
[Take g = 10 m/s2. Assume there is no rotational motion and loss of energy after the collision is negligable.]
One end of a massless spring of spring constant k and natural length is fixed while the other end is connected to a small object of mass m lying on a frictionless table. The spring remains horizontal on the table. If the object is made to rotate at an angular velocity
about an axis passing through fixed end, then the elongation of the spring will be:
Two bodies of masses m1 = 5 kg and m2 = 3 kg are connected by a light string going over a smooth light pulley on a smooth inclined plane as shown in the figure. The system is at rest. The force exerted by the inclined plane on the body of mass m1 will be: [Take g = 10 ms-2]
A boy ties a stone of mass 100 g to the end of a 2 m long string and whirls it around in a horizontal plane. The string can withstand the maximum tension of 80 N. If the maximum speed with which the stone can revolve is K/π rev./min. The value of K is
(Assume the string is massless and unstretchable)
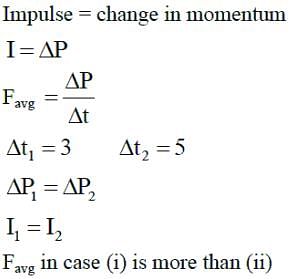
In two different experiments, an object of mass 5 kg moving with a speed of 25 ms-1 hits two different walls and comes to rest within (i) 3 seconds, (ii) 5 seconds, respectively. Choose the correct option out of the following:
A person pushes a box on a rough horizontal platform surface. He applies a force of 200 N over a distance of 15 m. Thereafter, he gets progressively tired and his applied force reduces linearly with distance to 100 N. The total distance through which the box has been moved is 30 m. What is the work done by the person during the total movement of the box?
A body of mass m1, moving with an unknown velocity of , undergoes a collinear collision with a body of mass m2 moving with a velocity
. After collision, m1 and m2 move with velocities of
, respectively.
If m2 = 0.5 m1 and v3 = 0.5 v1, then v1 is:
A nucleus A, with a finite de-Broglie wavelength , undergoes spontaneous fission into two nuclei B and C of equal mass. B flies in the same direction as that of A, while C flies in the opposite direction with a velocity equal to half of that of B. The de-Broglie wavelengths
of B and C are respectively:
A body of mass 2 kg makes an elastic collision with a second body at rest and continues to move in the original direction but with one fourth of its original speed. What is the mass of the second body?
Particle A of mass m1 moving with velocity () ms-1 collides with another particle B of mass m2 which is at rest initially. Let
and
be the velocities of particles A and B after collision, respectively. If m1 = 2m2 and after collision,
= (
) ms-1, the angle between
and
is
A solid sphere and solid cylinder of identical radii approach an incline with the same linear velocity (see figure). Both roll without slipping all throughout. The two climb maximum heights hsph and hcyl on the incline. The ratio is given by:
A uniform cable of mass 'M' and length 'L' is placed on a horizontal surface such that its (1/n)th part is hanging below the edge of the surface. To lift the hanging part of the cable up to the surface, the work done should be:
The potential energy between two molecules is given by U = . At equilibrium, separation between molecules and the potential energy are
At constant volume, 4 mole of an ideal gas when heated from 300 K to 500 K changes its internal energy by 5000 J. The molar heat capacity at constant volume is ________. (Answer up to 2 decimal places)
For the reaction:
A(l) 2B(g),
ΔU = 2.1 kcal, ΔS = 20 cal K-1 at 300 K.
Hence, ΔG in kcal is _________.(Answer up to one decimal place)
For a dimerization reaction,
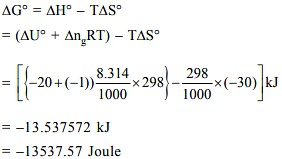
2A(g) → A2(g), at 298 K, ΔU° = -20 kJ mol-1, ΔS° = -30 JK-1 mol-1, then the ΔG° will be _______ J. (Nearest integer)
The internal energy change (in J) when 90 g of water undergoes complete evaporation at 100°C is ______.
(Given: ΔHvap for water at 373 K = 41 kJ/mol, R = 8.314 JK-1 mol-1)
(Nearest integer)
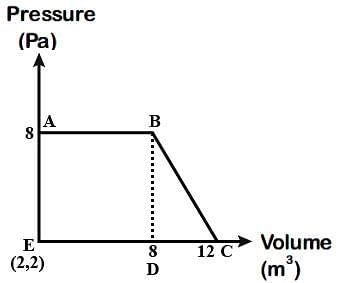
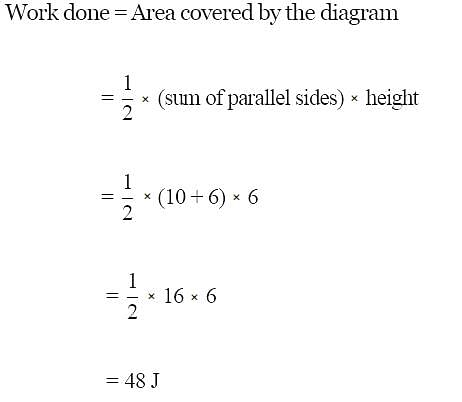
The magnitude of work done by a gas that undergoes reversible expansion along the path ABC shown in the figure is ______. (Nearest integer)
A uniform metal chain of mass m and length 'L' passes over a massless and frictionless pulley. It is released from rest with a part of its length 'l' hanging on one side and rest of its length 'L - l' hanging on the other side of the pulley. At a certain point of time, when , the acceleration of the chain is g/2. The value of x is .......
In the arrangement shown in figure a1, a2, a3 and a4 are the accelerations of masses m1, m2, m3 and m4 respectively. Which of the following relation is true for this arrangement?
A uniform sphere of mass 500 g rolls without slipping on a plane horizontal surface with its centre moving at a speed of 5.00 cm/s. Its kinetic energy is
A block of mass M slides down on a rough inclined plane with constant velocity. The angle made by the inclined plane with horizontal is θ. The magnitude of the contact force will be:
An elevator in a building can carry a maximum of 10 persons, with the average mass of each person being 68 kg. The mass of the elevator itself is 920 kg and it moves with a constant speed of 3 m/s. The frictional force opposing the motion is 6000 N. If the elevator is moving up with its full capacity, the power delivered by the motor to the elevator (g = 10 m/s2) must be at least:


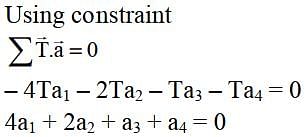
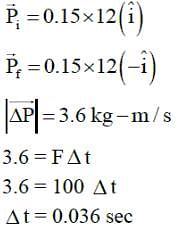
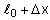 )ω2
)ω2