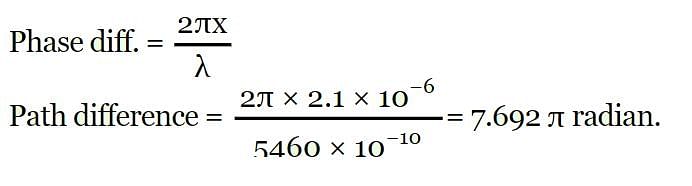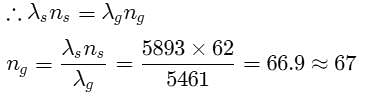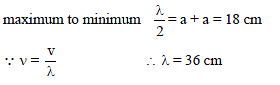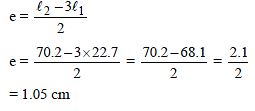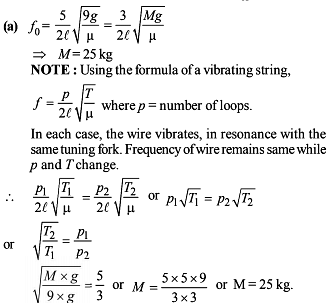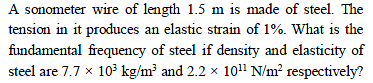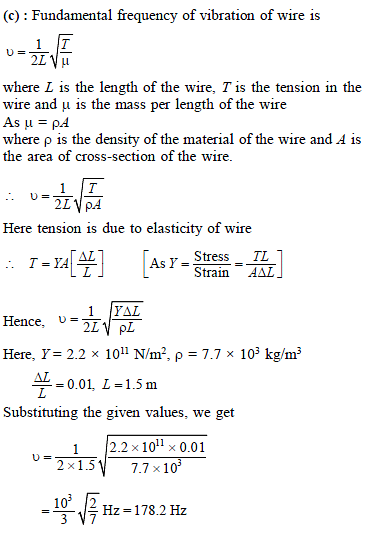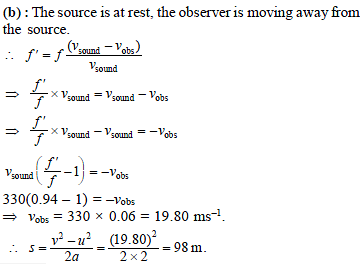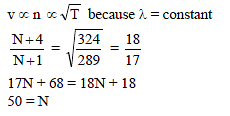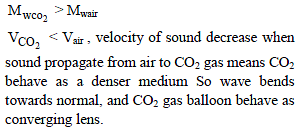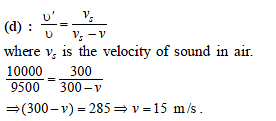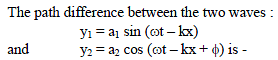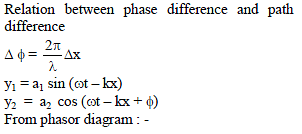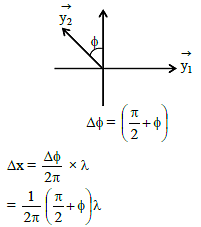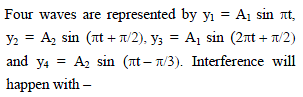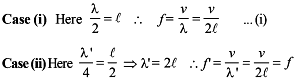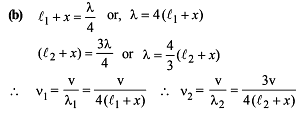Chapter Test: Waves - JEE MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - Chapter Test: Waves
The path difference between two wavefronts emitted by coherent sources of wavelength 5460 Å is 2.1 micron . The phase difference between the wavefronts at that point is _
The path difference between two waves
y1= A1 sin wt and y2= A2 cos (wt + f) will be
y1= A1 sin wt and y2= A2 cos (wt + f) will be
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
The equation for two waves obtained by two light sources are as given below :
y1= A1 sin 3wt, y2 = A2 cos (3wt + p/6). What will be the value of phase difference at the time t _
Figure, shows wave fronts in still water, moving in the direction of the arrow towards the interface PQ between a shallow region and a deep (denser) region. Which of the lines shown may represent one of the wave fronts in the deep region ?
In Young's double slit experiment 62 fringes are visible in the field of view with sodium light (l = 5893Å). If green light (l = 5461Å) is used then the number of visible fringes will be _
In young's double slit experiment, interference pattern is observed on the screen L distance apart from slits, average distance between adjacent fringes is x and slits separation is d, then the wavelength of light will be _
A tuning fork of frequency n is sounded at the open end of a long cylindrical tube having a side opening and fitted with a movable reflecting piston. On moving the piston through 9 cm, the intensity of sound heard by the listener changes from maximum to minimum. If speed of sound is 360 m/s, value of n is
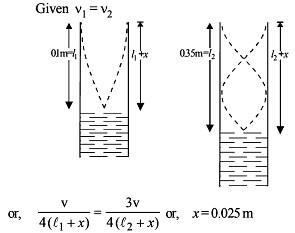
In a resonance pipe the first and second resonance are obtained at lengths 22.7 cm and 70.2 cm respectively. What will be the end correction -
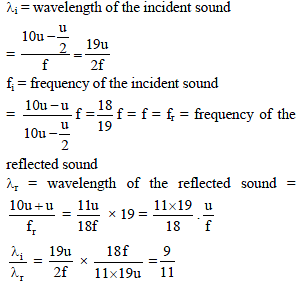
A wall is moving with velocity u and a source of sound moves with velocity u/2 in the same direction as shown in the figure. Assuming that the sound travels with velocity 10u. The ratio of incident sound wavelength on the wall to the reflected sound wavelength by the wall, is equal to -
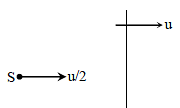
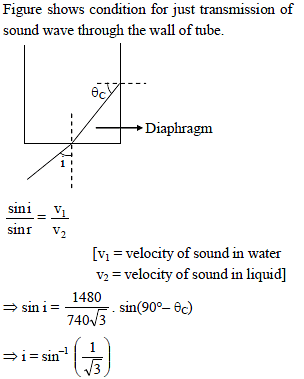
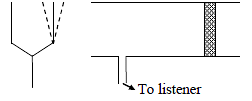
One end of a thin metal tube is closed by thin diaphragm of latex and the tube is lower in water with closed end downward. The tube is filled with a liquid 'x'. A plane progressive wave inside water hits the diaphragm making an angle 'θ' with its normal. Assuming Snell's law to hold true for sound. Maximum angle 'θ' for which sound is not transmitted through the walls of tube is (velocity of sound in liquid x = 740√3 m/s and in water = 1480 m/s)
A tuning fork and an air column in resonance tube whose temperature is 51°C produces 4 beats in 1 second when sounded together. When the temperature of the air column decreases, the number of beats per second decreases. When the temperature remains 16°C, only 1 beat per second is produced. Then the
frequency of the tuning fork is -
A boat at anchor is rocked by waves whose crests are 100 m apart and velocity is 25 m/s. The boat bounces up once in every -
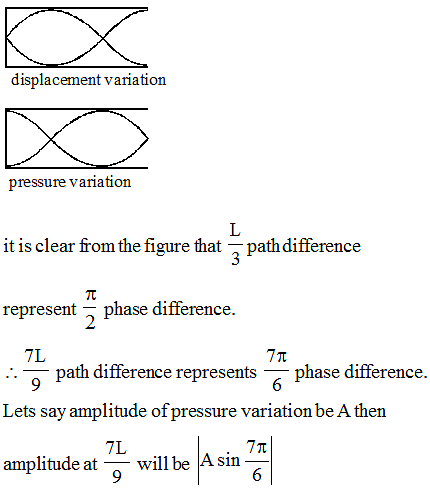
A closed organ pipe of length L is vibrating in its first overtone. There is a point Q inside the pipe at a distance 7 L/9 from the open end. The ratio of pressure amplitude at Q to the maximum pressure amplitude in the pipe is
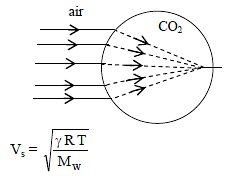
A balloon filled with CO2, then for sound wave this will behave as a -
The speed of sound in air at N.T.P is 300 m/s. If pressure of air is increased to four times keeping the temperature constant, the speed of sound will becomes –
The first overtone of an open organ pipe and the fundamental tone of a closed organ pipe give 5 beats per second when sounded together. If the length of the closed pipe is 25 cm, what are the possible lengths of the open organ pipe (Speed of sound in air = 340 m/sec) -