Test: Laws of chemical combination - JEE MCQ
15 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Laws of chemical combination
The percentage of Se in peroxidase anhydrous enzyme is 0.5% by weight (atomic weight =78.4). Then minimum molecular weight of peroxidase anhydrous enzyme is
The number of water molecules present in a drop of water (volume 0.0018 mL) density = 1g mL−1 at room temperature is
A mixture of 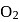 and gas "Y" mol. mass 80 in the mole ratio a
and gas "Y" mol. mass 80 in the mole ratio a 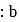 has a mean molecular mass 40. What would be mean molecular mass, if the gases are mixed in the ratio
has a mean molecular mass 40. What would be mean molecular mass, if the gases are mixed in the ratio 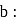 a under, identical conditions? (Assume that gases are non-reacting):
a under, identical conditions? (Assume that gases are non-reacting):
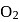 and gas "Y" mol. mass 80 in the mole ratio a
and gas "Y" mol. mass 80 in the mole ratio a 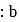 has a mean molecular mass 40. What would be mean molecular mass, if the gases are mixed in the ratio
has a mean molecular mass 40. What would be mean molecular mass, if the gases are mixed in the ratio 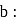 a under, identical conditions? (Assume that gases are non-reacting):
a under, identical conditions? (Assume that gases are non-reacting):If 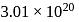 molecules are removed from
molecules are removed from 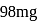 of
of 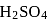 , then the number of moles of
, then the number of moles of 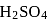 left are
left are
Arrange the following in the order of increasing mass (atomic mass: O = 16, Cu = 63, N = 14)
I. one atom of oxygen
II. one atom of nitrogen
III. 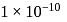 mole of oxygen
mole of oxygen
IV. 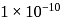 mole of copper
mole of copper
Complete combustion of 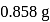 of compound
of compound 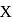 gives
gives 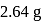 of
of 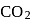 and
and 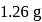 of
of 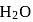 . The lowest molecular mass
. The lowest molecular mass 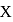 can have:
can have:
When burnt in air, 14.0 g mixture of carbon and sulphur gives a mixture of CO2 and SO2 in the volume ratio of 2:1, volume being measured at the same conditions of temperature and pressure moles of carbon in the mixture is
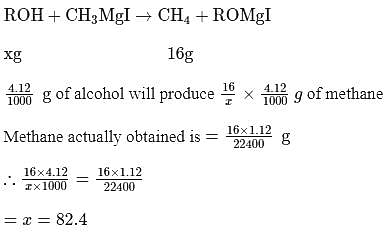
1.12 mL of a gas is produced at S.T.P. by the action of 4.12mg of alcohol ROH with methyl magnesium Iodide. The molecular mass of alcohol is
1 mole of mixture of CO and CO2 requires exactly 28 gKOH in solution for complete conversion of all the CO2 into K2CO3. How much amount more of KOH will be required for conversion into K2CO3 if one mole of mixture is completely oxidized to CO2.
1 mL of water has 25 drops. Let N0 be the Avogadro number. What is the number of molecules present in 1 drop of water ? (Density of water = 1 g/mL)
A 25.0 mm×40.0 mm piece of gold foil is 0.25 mm thick. The density of gold is 19.32 g/cm3. How many gold atoms are in the sheet? (Atomic weight : Au = 197.0)
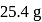 of
of 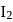 and
and 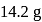 of
of 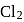 are made to react completely to yield a mixture of
are made to react completely to yield a mixture of 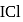 and
and 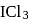 Calculate moles of ICl and
Calculate moles of ICl and 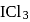 formed
formed
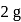 of oxygen contains number of atoms equal to that in
of oxygen contains number of atoms equal to that in
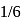 , in place of
, in place of 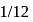 , mass of carbon atom is taken to be the relative atomic mass unit, the mass of one mole of the substance will
, mass of carbon atom is taken to be the relative atomic mass unit, the mass of one mole of the substance will


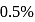 by weight means if Mol. wt. is 100 then mass of Se is
by weight means if Mol. wt. is 100 then mass of Se is 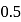 . If at least one atom of Se is present in the molecule then
. If at least one atom of Se is present in the molecule then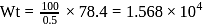
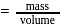
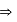 mass
mass 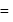 density
density 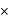 volume
volume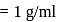
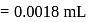 (Given)
(Given) Mass of
Mass of 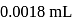 water
water 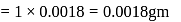
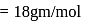
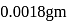 of water
of water 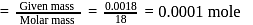
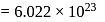 molecules
molecules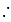 Number of molecules of water in
Number of molecules of water in 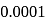 mole
mole 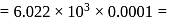
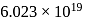
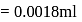 ) at room temperature are
) at room temperature are 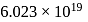 .
.
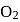 is
is 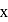
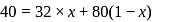
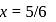
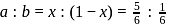
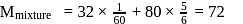
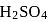 in
in 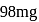 of
of 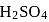
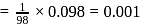
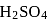 removes
removes 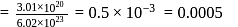
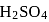 left
left 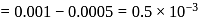
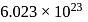 atoms of oxygen
atoms of oxygen  Mass of one atom of oxygen
Mass of one atom of oxygen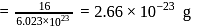
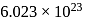 atoms of nitrogen
atoms of nitrogen 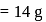
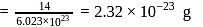
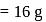 Mass of
Mass of 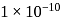 mole of oxygen
mole of oxygen 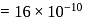 Mass of 1 mole of copper
Mass of 1 mole of copper 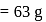 Mass of
Mass of 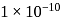 mole of copper
mole of copper 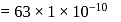
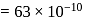
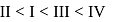
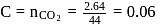
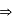 mass of
mass of 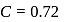
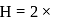 Moles of
Moles of 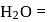
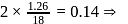 mass of
mass of 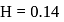
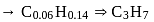
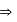 Lowest M.M.
Lowest M.M. 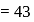
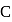 be
be 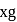 , then
, then 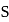 will be
will be 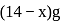
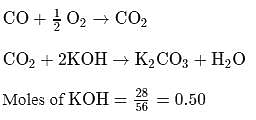
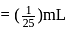
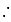 Mass of
Mass of 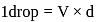
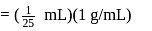
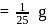

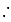 Number of
Number of 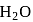 Molecule
Molecule 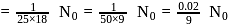
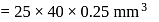
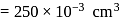
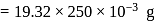
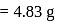
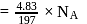
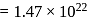
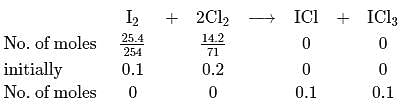
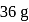 of water
of water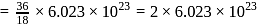
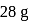 of
of 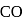
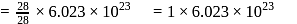
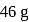 of
of 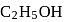
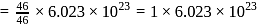
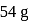 of
of 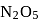
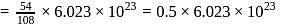
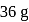 of water has largest number of molecules.
of water has largest number of molecules.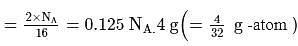 of sulphur also contains atom = 0.125 NA
of sulphur also contains atom = 0.125 NA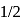 times the old amu - hence,
times the old amu - hence, 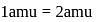 ', but hold on, the mass of 1 mole of carbon will be the mass of carbon in amu'* mass of amu'* avagadro number
', but hold on, the mass of 1 mole of carbon will be the mass of carbon in amu'* mass of amu'* avagadro number 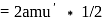 (mass of amu in
(mass of amu in 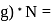 the old mass itself!
the old mass itself!














