CSIR NET Earth Science Mock Test - 1 - CSIR NET Earth Science MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - CSIR NET Earth Science Mock Test - 1
Which one of the following methods is not used for dating ice cores?
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
Which of the following is a type of calcareous ooze?
Which of the following sequences is the correct order of appearance in the geological history of the Earth?
The condensation trails that are produced by jet aircrafts which often spread out to form broad bands of cirrus clouds are known as
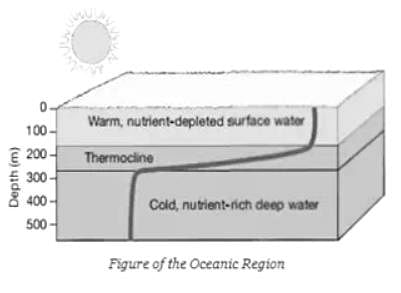
Identify the oceanic region where the depicted biological productivity in the following figure is typical?
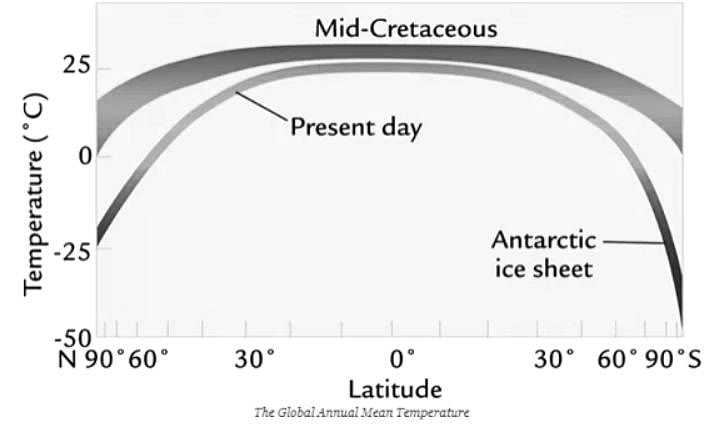
The Global annual mean temperature in the Cretaceous was
Which of the following mineral is an example of having resinous lustre?
Internal density discontinuity or free surface is necessary for the existence of
The most important factor that results in the seasonal temperature changes in the climate is
A large part of the oceanic biological production comes from
Which one of the functions performed by marine benthic polychaetes is ecologically advantageous?
Which two of the following processes most commonly occur when a surface gravity wave propagates into a shallow water region from deep water?
- Refraction
- Reflection
- Diffraction
- Shoaling
Which of the following is not a type of groynes?
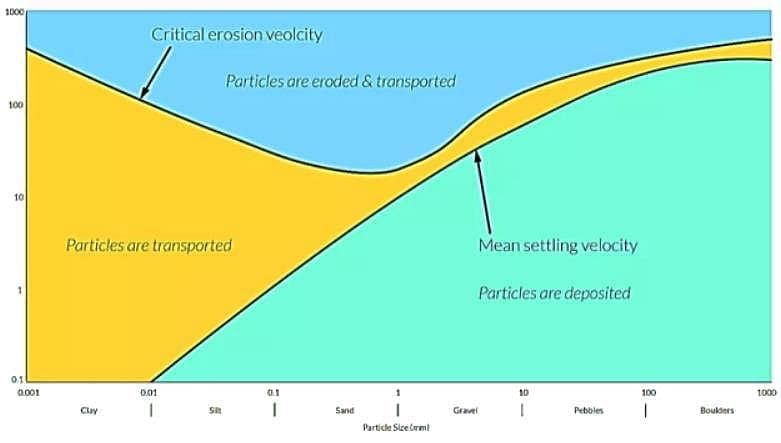
Which one of the following sediment types commonly occurs in ocean in trenches?
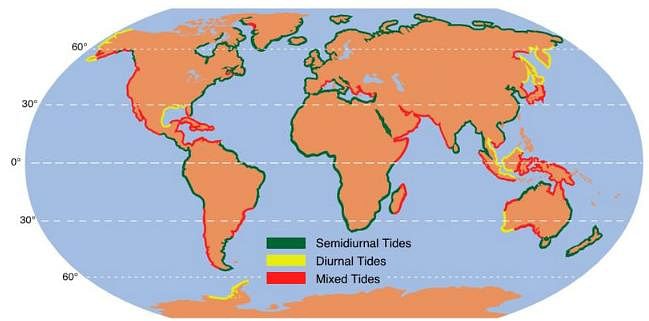
Which one of the following tidal patterns characterizes the West coast of India?
Thermal plumes formed in the mantle ascend upward due to
Find out the incorrect statement regarding the Trade Winds.
During spheroidal weathering, a block of rock converts to a spheroid due to
- The Eastern Indian Ocean is warmer than the Western Indian Ocean
- The Eastern Indian Ocean is colder than the Western Indian Ocean
- Excess anomalous rainfall in the East Africa
- The westerly wind anomaly is in the Eastern Indian Ocean
Which of the above conditions co-occur with the positive Indian Ocean Dipole?