FSSAI TO / AD (Technical) Mock Test - 4 - Agriculture Exams MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - FSSAI TO / AD (Technical) Mock Test - 4
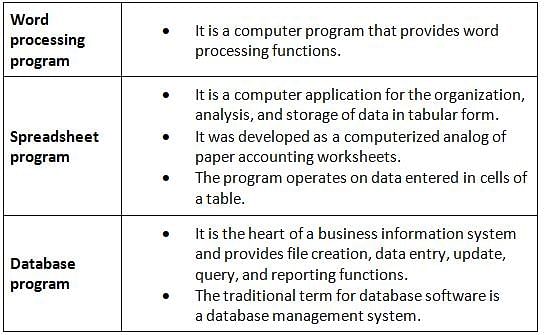
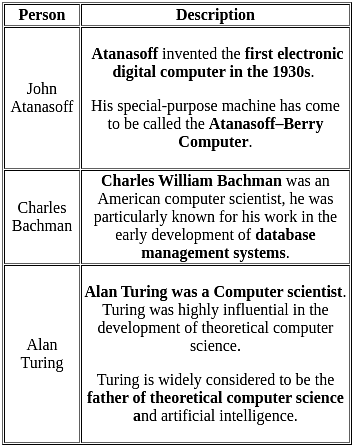
Who is considered the father of computers?
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
Amit is twice as good as Ramit. Working together they can complete the work in 28 days. In how many days can Ramit alone can do the same whole work?
The load instruction is mostly used to designate a transfer from memory to a processor register known as?
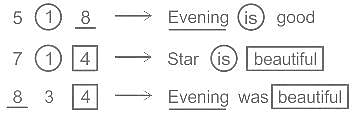
In a certain code language, 518 means 'Evening is good', 714 means 'Star is beautiful', 834 means 'Evening was beautiful'. Find the code for 'was'.
Which of the following setup options can not be set in the page setup dialog box?
What is the term used when you press and hold the left mouse key and move the mouse around the slide?
Select the number which can be placed at the sign of the question mark (?) from the given alternatives.

Which of the following statements is correct related +F endorsements?
Which of the following statement(s) is/are NOT true regarding NMR Spectroscopy?
A psychrophillic halophile would be a microbe that prefers
A portal that allows a consumer to share their concerns, know their rights, authenticate the license/registration certificate of food business operators, etc., is called?
As per the provisions of FSS (Food Products Standards and Food Additives) Regulations, 2011 Dehydrated Green Leafy Vegetables should not contain sulphur dioxide more than _______
Which of the following programs aims for provision of subsidized food grains to eligible households?
Agreement on Technical Barriers to Trade applies to: