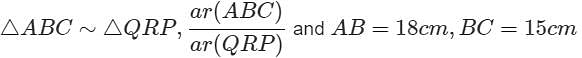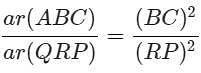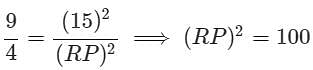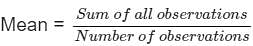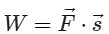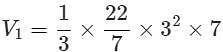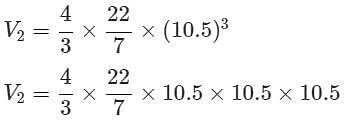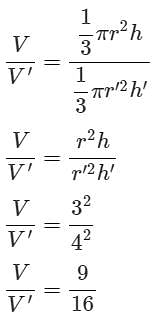MPTET Varg 2 Math Mock Test - 9 - MPTET MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - MPTET Varg 2 Math Mock Test - 9
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
उपर्युक्त गद्यांश के अनुसार, यूरेनियम के केन्द्र के विखण्डन का अध्ययन क्या हो सकता है?
A Sum becomes ₹ 8,800 in 4 years at simple interest at the yearly interest rate of 25% p.a. What is the sum (in rupees)?
The number of lines of symmetry and order of rotational symmetry.
Determine the value of k for which the equations 2x + ky + 4 = 0 and 3x + 15y + 7 = 0 will be inconsistent.
Four figures are plotted on a graph sheet as mentioned in the following table.
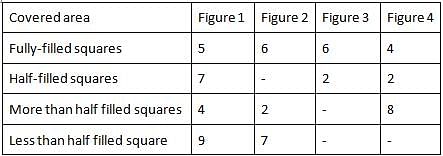
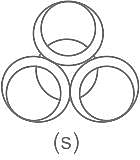
Find which figure with larger area.
Find the mean of median and mode of the given data:
330, 360, 320, 340, 320, 390, 340, 330, 320
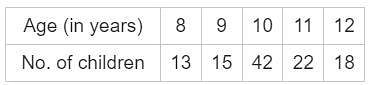
The following table gives the age of the children in a class of a school. Find the number of children in the class whose age is below 11 years but above 8 years.
The weight of Ram and Shyam is 55 kg. Ram takes 5 minutes to climb the stairs while Shyam takes 3 minutes to climb the same steps. Who does more work?
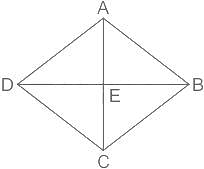
The length of one diagonal of a rhombus is 10 cm. If the side of the rhombus is 13 cm. Then what will be the length of the diagonal?
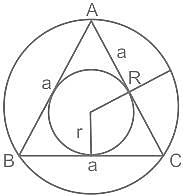
The area of an equilateral triangle is 25√3 cm2,then the ratio of inradius and circumradius is -
A solid cone has radius and height as 3 cm and 7 cm respectively. A solid sphere has radius 10.5 cm. The edge of a cube is 6 cm. What is the ratio of the volumes of cone, sphere and cube?
The base radii of two circular cones of the same height are in the ratio 3 : 4. The ratio of their volumes are
The curved surface area of a cylinder is 594 cm2 and its vol is 1336.5 cm3. What is the height (in cm) of the cylinder?


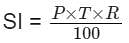
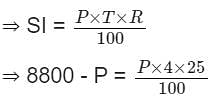
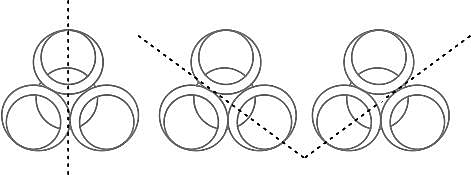
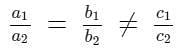
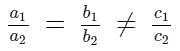
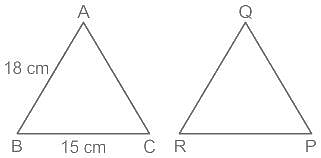
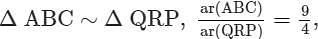 AB = 18 cm and BC = 15 cm, then PR is equal to
AB = 18 cm and BC = 15 cm, then PR is equal to