Test: Covalent and Co-ordinate Bonding - JEE MCQ
15 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Covalent and Co-ordinate Bonding
Among the following ions, the pπ−dπ overlap could be present in
The bond dissociation energy of B−F in BF3 is 646 kJ mol−1 whereas that of C−F in CF4 is 515 kJ mol−1. The correct reason for higher B−F bond dissociation energy as compared to that of C−F is
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
In  ion the formal charge on the oxygen atom of P−O bond is ___
ion the formal charge on the oxygen atom of P−O bond is ___
 ion the formal charge on the oxygen atom of P−O bond is ___
ion the formal charge on the oxygen atom of P−O bond is ___Which of the following contains both covalent and ionic bond?
Which of the following species is a radical?
The correct order in which the O − O bond length increases in the following is-
 is incorrect?
is incorrect?
The molecules  and
and  are both covalent compounds, but
are both covalent compounds, but  is non polar whereas
is non polar whereas 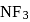 is polar. The reason for this is
is polar. The reason for this is
The number and type of bonds in ion in  are:
are:
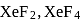 and
and  , the number of lone pairs on Xe are respectively
, the number of lone pairs on Xe are respectively
 molecules participating in hydrogen bonding in
molecules participating in hydrogen bonding in  is/are
is/are
Which of the following has least covalent P − H bond?
Which one of the following has longest covalent bond distance?



 ion, formal charge on each
ion, formal charge on each  -atom of
-atom of 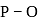


 Odd electrons (seven valency electrons of nitrogen and eight valency electrons of oxygen), so this species work as radical.
Odd electrons (seven valency electrons of nitrogen and eight valency electrons of oxygen), so this species work as radical.  , the total electrons are
, the total electrons are 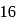 (even), in case of nitro ion, total valency electrons are
(even), in case of nitro ion, total valency electrons are  (even), In case of cyanide ion, total valency electrons are
(even), In case of cyanide ion, total valency electrons are  (even).
(even).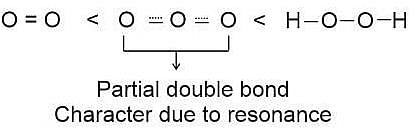
 can be represented as
can be represented as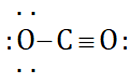
 (Incorrect structure)
(Incorrect structure)

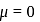 hence it is non polar.
hence it is non polar. is pyramidal
is pyramidal
 hence it is polar.
hence it is polar.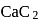 is
is 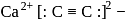
 and two
and two  bonds
bonds Total number of valence electrons of
Total number of valence electrons of  , two electrons shared with
, two electrons shared with  atoms, 6 electrons left hence 3 lone pairs, in
atoms, 6 electrons left hence 3 lone pairs, in  shared with
shared with 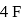 atoms 4 left hence 2 lone pairs; in
atoms 4 left hence 2 lone pairs; in 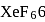 shared with
shared with 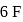 atoms 2 left hence 1 lone pair.
atoms 2 left hence 1 lone pair. is the represenation of given compound.
is the represenation of given compound. molecule, two H-bonds are formed with
molecule, two H-bonds are formed with  atom and two are formed with
atom and two are formed with 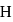 atoms of the
atoms of the  molecule.
molecule. and
and  is zero because these are symmetrical molecules. Dipole moment of
is zero because these are symmetrical molecules. Dipole moment of  is greater than
is greater than  .
.
 bond will have ionic character due to electron attracting tendency of P-carrying positive charge and least covalent.
bond will have ionic character due to electron attracting tendency of P-carrying positive charge and least covalent.














