Test: Group 13 Elements: Boron Group - JEE MCQ
20 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Group 13 Elements: Boron Group
Boron has an exceptionally high melting point in the group 13th elements, because–
The elements having the maximum and minimum melting points among the members of group 13 are respectively -
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
B has a smaller first ionization enthalpy than Be. Consider the following statements
(i) it is easier to remove 2p electron than 2s electron
(ii) 2p electron of B is more shielded from the nucleus by the inner core of electrons than the 2s electrons of Be
(iii) 2s electron has more penetration power than 2p electron
(iv) atomic radius of B is more than Be
(atomic number B = 5, Be = 4)
The correct statements are
(i) it is easier to remove 2p electron than 2s electron
(ii) 2p electron of B is more shielded from the nucleus by the inner core of electrons than the 2s electrons of Be
(iii) 2s electron has more penetration power than 2p electron
(iv) atomic radius of B is more than Be
(atomic number B = 5, Be = 4)
The correct statements are
The correct order of atomic radii in group 13 elements is
Which of the following sequence is not correct for the property mentioned against it?
Which of the following statements is not true for both B and Al?
Consider the following dioxide of group 14
1. CO2
2. SiO2
3. GeO2
4. SnO2
5. PbO2
The basicity of the dioxide alters in the order
What is the chief constituent of pyrex glass?
When an inorganic compound X having 3c−2e− as well as 2c−2e− bonds react with NH 3 gas at a certain temperature, gives a compound Y, isostructural with benzene. Compound X with ammonia at a high temperature produces a substance Z, then
In borax, the number of - OH group attached to boron atoms is
Which of the following is the correct formula of borax?
Which of the following statements is not correct?
Which of the following statements is correct?
Which of the following equations is not correctly formulated?
Which of the following statements is not correct?



 and
and 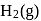 .
.








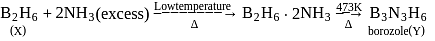

 units which are held together by hydrogen bonds.
units which are held together by hydrogen bonds.


















